Essential Dietary Guidelines: Foods to Avoid for People with Asthma
This comprehensive article explores key foods that individuals with asthma should avoid to prevent symptom exacerbation. It covers common triggers like sulfites, eggs, dairy, and allergies to peanuts, soy, and shellfish. Emphasizing the importance of dietary awareness and professional consultation, it offers practical advice to help manage asthma effectively through proper nutrition and trigger avoidance. Understanding these dietary factors empowers asthma sufferers to reduce attacks, enhance lung health, and improve overall well-being.

Comprehensive Guide on Foods That May Worsen Asthma Symptoms
For individuals living with asthma, understanding the relationship between diet and respiratory health is crucial. While environmental factors such as pollen, dust, and pollution are well-known triggers, dietary choices also play a significant role in either aggravating or alleviating asthma symptoms. Certain foods contain substances that can provoke airway inflammation, cause allergic reactions, or increase mucus production, leading to heightened risks of asthma attacks. By identifying and steering clear of these problematic foods, asthma sufferers can better control their condition, reduce the frequency of attacks, and enhance overall quality of life.
Common Environmental and Dietary Triggers
Besides common environmental irritants like pollen, dust mites, cigarette smoke, and air pollution, your diet can directly influence the severity and frequency of asthma symptoms. This highlights the importance for asthma patients to be vigilant about their eating habits and food choices. Recognizing foods that may trigger breathing difficulties and allergic reactions is vital for effective asthma management and prevention of severe episodes.
Here are some key foods and ingredients that individuals with asthma should consider limiting or avoiding entirely to safeguard their respiratory health:
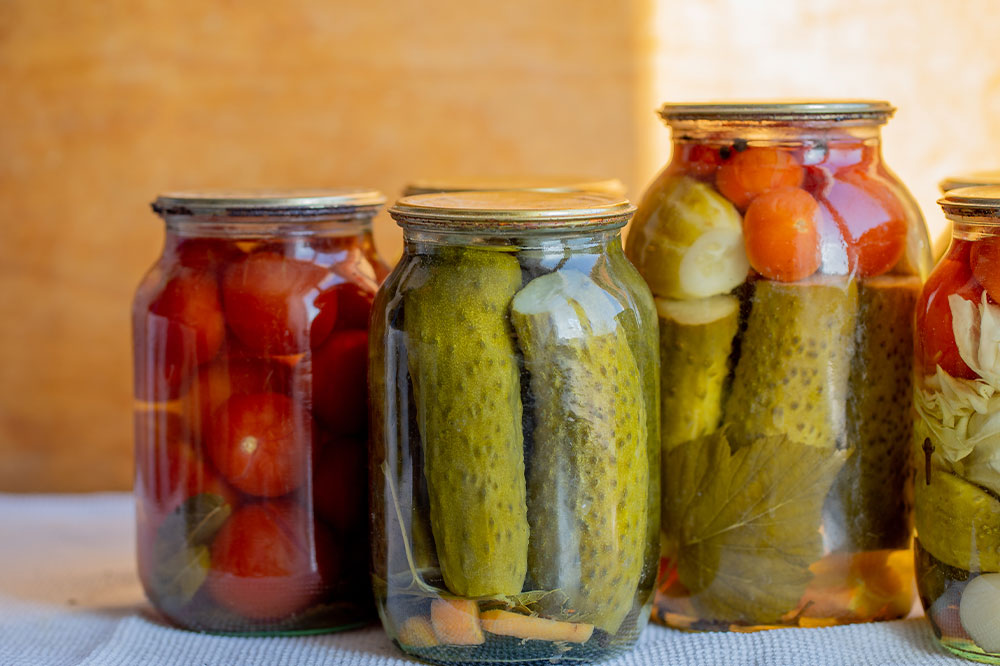
Sulfites:
Sulfites are preservatives commonly used in a variety of foods and beverages, including pickles, dried fruits, wine, beer, shrimp, and bottled lemon juice. For some asthma sufferers, sulfites can cause bronchospasm or airway constriction, leading to severe asthma attacks. It is advisable to read labels carefully and opt for sulfite-free products if necessary.
Eggs:
Egg allergies are prevalent, especially among children, and can trigger symptoms such as skin reactions, nasal congestion, and difficulty breathing. Those with known egg allergies should avoid eggs and foods containing eggs, such as baked goods, mayonnaise, and some processed foods. Many children tend to outgrow this allergy over time, but vigilance remains essential.
Milk and Dairy Products:
While warm milk is sometimes used as a home remedy to soothe coughs and congestion, some people with asthma find that dairy products exacerbate their symptoms. Dairy can increase mucus production, which may worsen airway obstruction. It is wise to monitor individual reactions to dairy and consider reducing intake if breathing difficulties worsen after consumption of milk, cheese, yogurt, butter, or other dairy items.
To minimize respiratory issues, asthma patients should also be cautious with certain foods known to cause gas and bloating, such as beans, lentils, cabbage, broccoli, onions, and carbonated beverages. These foods can lead to discomfort and pressure in the chest, potentially aggravating asthma symptoms. Smaller, more frequent meals are recommended to prevent overeating and reduce gastrointestinal distress.
Potential Allergens and Asthma Triggers
In addition to sulfites, other common allergens that could trigger asthma or allergic symptoms include:
Peanuts:
Peanut allergies are among the most severe food allergies, with a high risk of causing anaphylaxis—a life-threatening allergic response that can result in airway swelling and breathing difficulties. Strict avoidance of peanuts and foods containing peanuts (such as peanut butter, snacks, baked goods, and sauces) is crucial for individuals with known peanut allergies.
Soy:
Soy and soy-derived ingredients can provoke allergic reactions in some people, leading to respiratory symptoms similar to other food allergies. Avoiding soy-based products such as soy milk, tofu, soy protein isolates, and processed foods containing soy is necessary for allergic individuals.
Shellfish:
Shellfish allergies, including reactions to shrimp, lobster, crab, and crayfish, are common triggers for asthma attacks in sensitive individuals. These proteins can provoke immediate allergic responses, leading to airway constriction. Patients allergic to shellfish should eliminate these from their diet completely.
Keeping a detailed food diary can help individuals with asthma identify specific foods or ingredients that provoke reactions. Tracking symptoms in relation to dietary intake provides valuable insights for managing triggers and preventing severe attacks.
Engaging with healthcare providers, allergists, or dietitians is essential to determine personalized dietary restrictions. Proper guidance ensures that individuals avoid harmful foods while maintaining a balanced, nutritious diet that supports overall health and respiratory function.
Effective dietary management combined with environmental control measures can significantly improve asthma control, reduce emergency episodes, and improve the quality of life for those affected by this chronic respiratory condition.