Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing Early Signs and Indicators of Colorectal Cancer
This comprehensive guide explores the early signs and key indicators of colorectal cancer, emphasizing the importance of recognizing symptoms for early detection and successful treatment. Learn about symptoms, risk factors, and screening recommendations to protect your health.
Understanding the Early Signs and Key Indicators of Colorectal Cancer
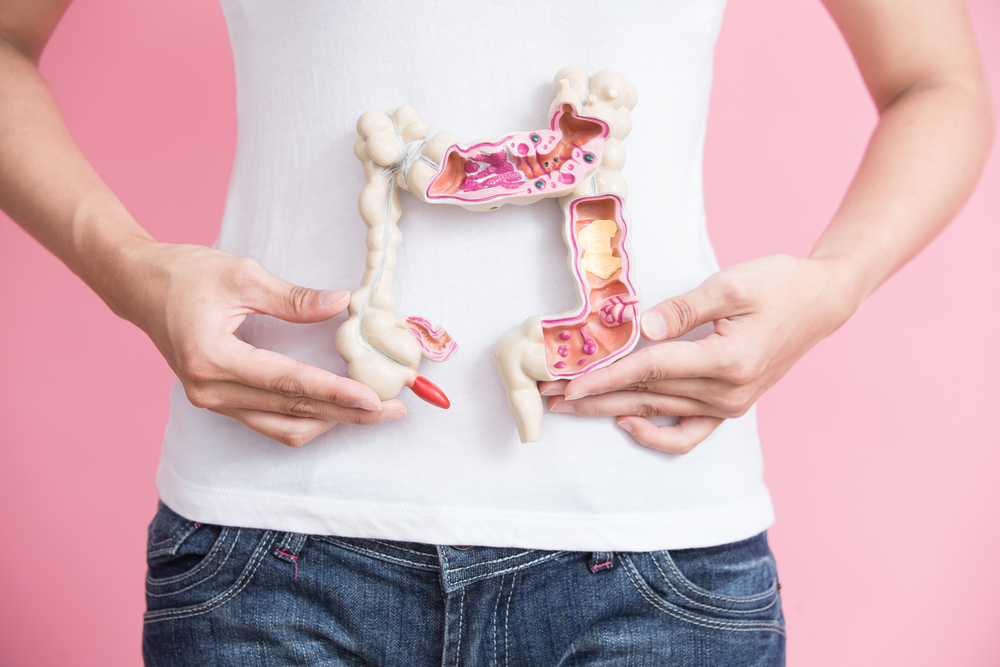
Colorectal cancer, a type of malignancy that develops in the colon or rectum, is one of the most common cancers worldwide. The colon, a vital part of the digestive system, processes waste material from food and absorbs water and nutrients. When cancer develops within this organ, early detection becomes critical for successful treatment and improved survival rates. The progression of colorectal cancer often begins with benign growths called polyps, which can gradually transform into malignant tumors if not diagnosed and managed early.
Awareness of the early warning signs and key indicators is essential for individuals and healthcare providers alike. Many early symptoms are subtle or even absent, which underscores the importance of routine screening and vigilance for any changes in bowel habits or health status. If identified early, the prognosis improves significantly, with a high chance of successful treatment and long-term remission.
Important symptoms and signs to monitor include:
Sudden or persistent changes in bowel habits, such as frequent diarrhea or constipation that lasts for weeks
The appearance of blood in stool, which may manifest as bright red blood or darker, tarry stools indicative of bleeding higher in the digestive tract
Noticing that stools are narrower or thinner than usual, sometimes described as elongated or pencil-thin
Rectal bleeding, which can be painless or associated with discomfort
Feeling of incomplete evacuation after bowel movements or a frequent urgency to defecate
Persistent abdominal pain, cramps, or discomfort that lasts for days or weeks
As colorectal tumors grow and penetrate deeper into the tissues, symptoms tend to become more severe and specific, including:
Intense pelvic pain often associated with advanced disease
Unexplained bloating, abdominal swelling, or a sense of fullness
Rapid weight loss, fatigue, and decreased appetite, which are signs of systemic illness or advanced-stage cancer
Persistent or worsening symptoms should prompt immediate consultation with healthcare professionals. Since early-stage colorectal cancer may not produce noticeable symptoms, routine screening measures are vital for early detection. The American Cancer Society recommends that individuals begin screening at age 45, or earlier if they have a family history or other risk factors. Common screening options include colonoscopy, fecal occult blood tests, and sigmoidoscopy. Early detection via screening greatly enhances treatment success rates; data shows that approximately 90% of cases detected early are curable with appropriate medical intervention.
Prevention strategies also involve maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet rich in fiber, regular exercise, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption. Being vigilant about symptoms and adhering to screening guidelines can save lives by catching colorectal cancer at an earliest stage when treatment options are most effective.