Choosing the Ideal Hearing Device: Digital vs. Analog Options
Discover the differences between digital and analog hearing aids to find the perfect solution for your hearing needs. Learn about their features, advantages, and which device best suits your lifestyle. Consult with an audiologist to make an informed decision and improve your quality of life with the right hearing aid technology.
Comparing Digital and Analog Hearing Aids: Making the Right Choice for Your Hearing Needs
Hearing loss affects a significant portion of the population worldwide, with millions experiencing difficulties in daily communication and social interactions. According to the World Health Organization, over 50 million Americans suffer from some form of hearing impairment, and nearly one in five individuals aged 12 and above are impacted. The American Academy of Audiology emphasizes that hearing loss is a widespread health issue, surpassing conditions such as diabetes and Alzheimer's disease in prevalence. Despite these staggering numbers, only a small percentage of those affected actively use hearing aids to improve their quality of life.
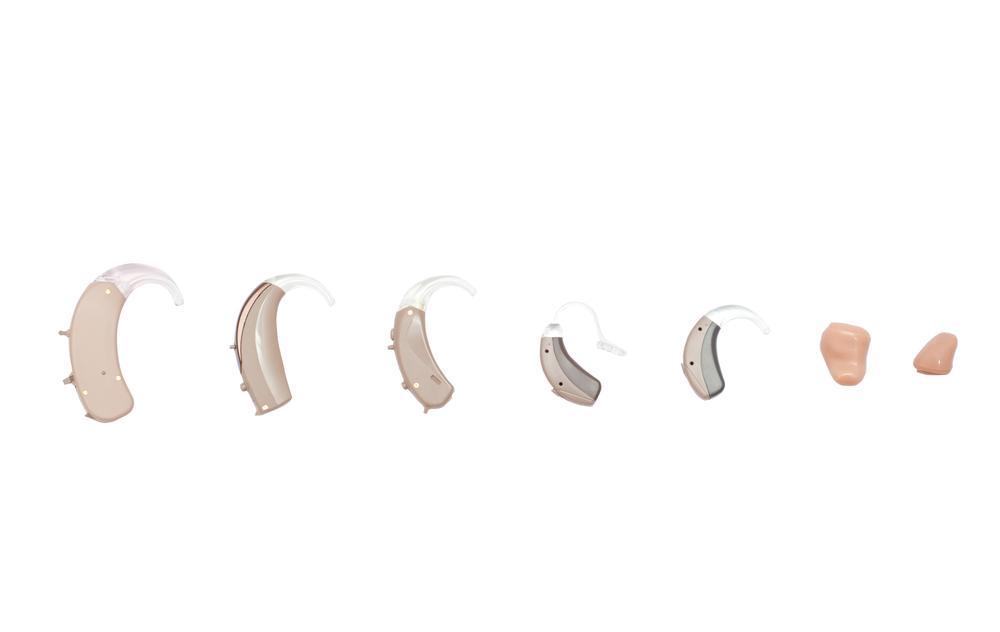
Thanks to technological advancements, modern hearing aid options have expanded, offering users more choices than ever before. These devices are primarily categorized into two types: analog and digital hearing aids. Each type comes with its unique features, benefits, and considerations. To determine which is best suited to your hearing needs and lifestyle, it's essential to consult with a qualified audiologist or hearing specialist. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your specific hearing profile, budget, and daily environment.
Here's an in-depth comparison of analog and digital hearing aids to help you make an informed decision:
Analog Hearing Aids:
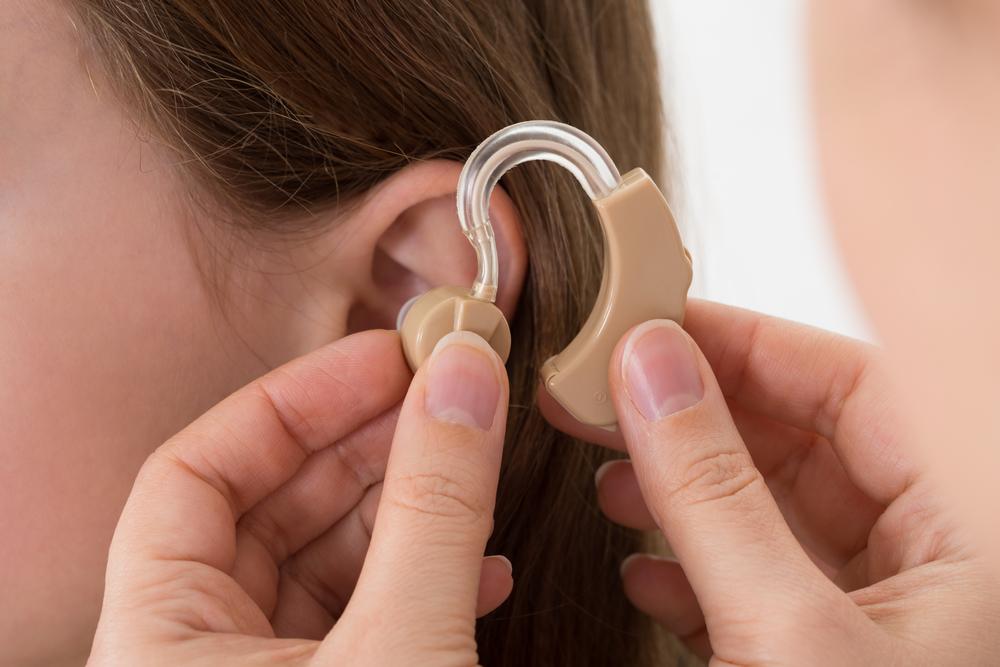
Analog hearing aids have been around for decades and are known for their straightforward design and reliable performance. These devices function by amplifying incoming sound waves directly, much like traditional volume amplifiers. They convert sound into electrical signals, amplify them, and then convert back into sound within the ear canal. One of their key advantages is their simplicity, making them easy to operate and maintain.
Customizable through user-defined programming, allowing adjustments to suit different environments or preferences.
Seamlessly adjust to varying noise levels, providing consistent amplification whether in quiet settings or noisy environments.
Typically more affordable, making them a cost-effective choice for long-term use.
Known for their robustness and durability, they often require fewer repairs or technical tweaks.
Ideal for users seeking a basic amplification solution without advanced noise reduction capabilities.
Digital Hearing Aids:
Digital hearing aids represent the cutting edge of hearing technology. These devices convert sound waves into digital signals that are processed electronically for enhanced clarity and noise reduction. This digital processing allows for more precise adjustments tailored to the individual's specific hearing loss profile. Digital aids usually feature multiple programs, enabling users to switch between settings optimized for different environments such as indoor conversations, outdoor noises, or noisy public places.
Offer superior sound quality thanks to sophisticated digital signal processing algorithms.
Effectively reduce background noise and feedback, resulting in clearer speech perception.
Provide customizable settings that can be fine-tuned by audiologists during fitting sessions.
Adjust dynamically in real time based on the listening environment, ensuring comfort and clarity.
Enhance overall hearing accuracy, especially in complex sound environments.
Both analog and digital hearing aids have their place, depending on individual preferences, needs, and budgets. Analog options are often favored for their simplicity, durability, and affordability, making them suitable for those seeking a reliable basic solution. Digital models, on the other hand, appeal to users who prioritize high sound quality, versatility, and advanced noise management features. An audiologist can assess your hearing profile and recommend the most appropriate technology to suit your lifestyle and hearing challenges.