Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Preventing Shoulder Muscle Discomfort
This comprehensive guide explores the causes of shoulder muscle discomfort, including rotator cuff injuries and bursitis, and provides effective management and prevention strategies. From medical treatments to exercise routines, learn how to maintain optimal shoulder health and prevent long-term issues. Ideal for athletes, manual workers, and anyone experiencing shoulder pain, this article offers valuable insights to promote lasting shoulder resilience.

The human shoulder joint is one of the most complex and mobile joints in the entire body, making it highly susceptible to injury and discomfort. Due to its extensive range of motion, the shoulder endures frequent use, and any imbalance, overuse, or trauma can lead to pain and functional limitations. Recognizing the importance of maintaining shoulder health involves understanding common causes of discomfort, effective management strategies, and preventive measures to ensure long-term functionality.
Shoulder pain and muscle discomfort are prevalent issues faced by athletes, manual workers, and individuals with sedentary lifestyles alike. Several factors can contribute to shoulder problems, including injuries to ligaments, tendons, or muscles, especially the rotator cuff. The rotator cuff is a group of four muscles and their tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint, allowing for smooth, controlled movements. Damage or inflammation of these tendons can significantly impact shoulder mobility and cause persistent pain.
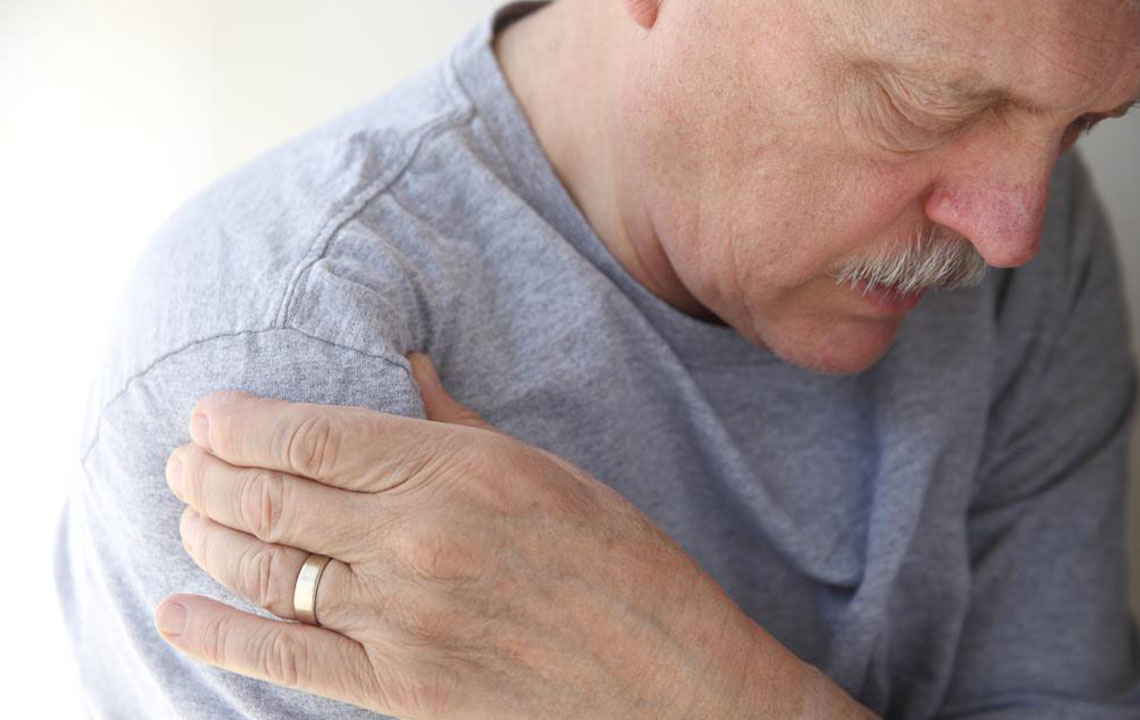
One of the primary causes of shoulder discomfort is rotator cuff tendinitis or tears, often resulting from repetitive overhead activities, sudden trauma, or degeneration due to aging. Tendon inflammation, or tendinitis, causes soreness, swelling, and reduced range of motion. Inflammation of the subacromial bursa, a small fluid-filled sac that cushions the shoulder joint, can also contribute to pain, especially during activities involving lifting or raising the arm.
The anatomy of the shoulder is intricate, with structures such as the acromion process, clavicle, humerus, rotator cuff muscles, and bursae working together to facilitate complex movements. Understanding this anatomy is essential for diagnosing and managing shoulder issues effectively.
The rotator cuff itself comprises four muscles: supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis. The supraspinatus tendon, located at the top of the shoulder, is particularly vulnerable to injury, especially with repetitive overhead motions or excessive lifting. When inflamed or torn, this tendon can lead to pain on the outer shoulder, which often intensifies during activities such as reaching overhead or lifting objects.
Effective treatment strategies for shoulder discomfort involve a combination of rest, ice or heat therapy, pharmacological interventions, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Rest allows inflamed tissues to recover, while applying ice packs can reduce swelling and alleviate pain. Heat therapy may promote blood flow and muscle relaxation. Over-the-counter medications such as NSAIDs can help manage inflammation and pain but should be used under medical supervision.
Recent advances in medical diagnostics include ultrasound imaging, which allows detailed visualization of soft tissue injuries like tendons and bursae. In some cases, corticosteroid injections are administered to reduce inflammation rapidly. For more severe cases, surgical interventions or minimally invasive procedures may be necessary.
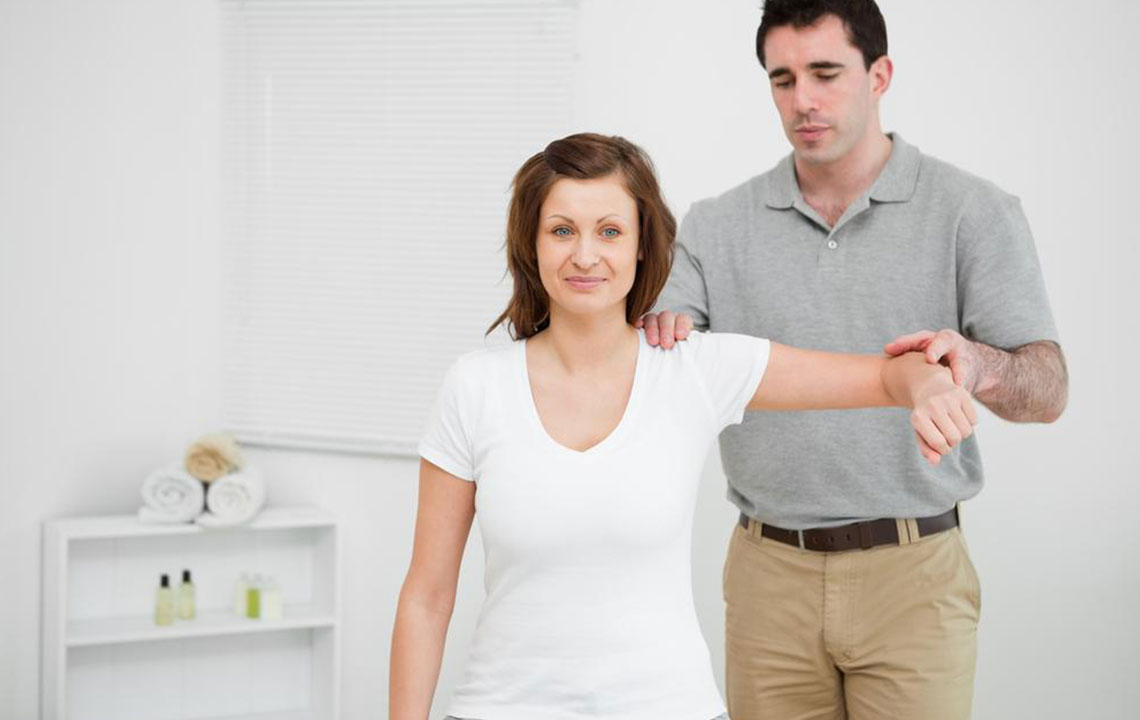
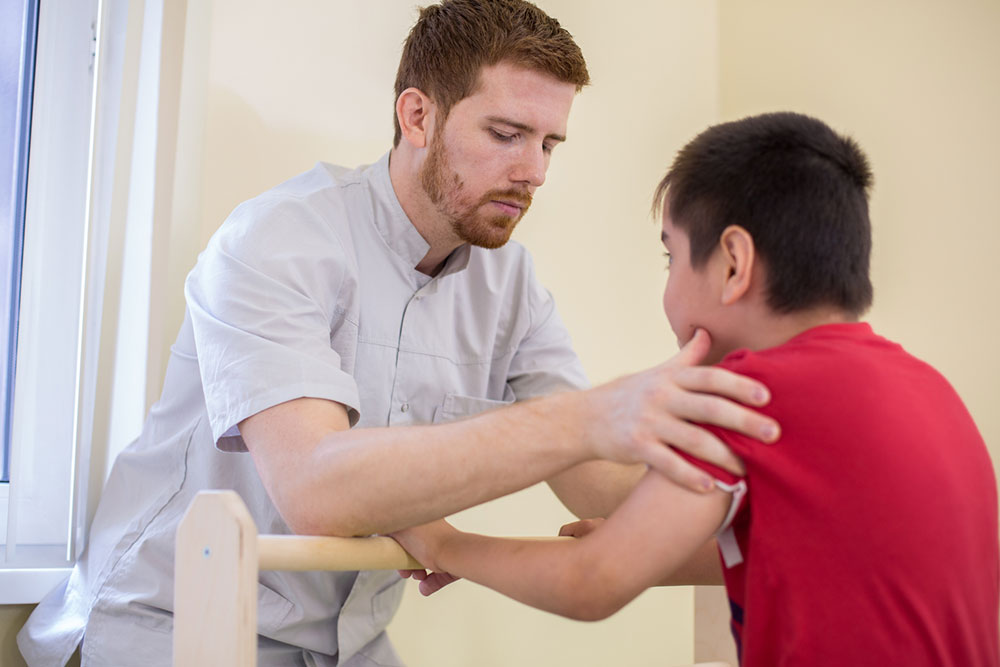
Beyond medical treatments, targeted physical therapy is vital for recovery and prevention. Specific stretching exercises help improve flexibility, while strengthening routines focusing on the rotator cuff muscles restore stability and support joint health. Incorporating gentle upper-body exercises can also promote overall shoulder resilience. However, it is crucial to consult healthcare professionals before initiating any new exercise program, especially after injury.
Preventive measures are key to avoiding shoulder discomfort. Maintaining good posture, practicing proper lifting techniques, and avoiding repetitive overhead activities can reduce strain on shoulder structures. Regular shoulder strengthening exercises, combined with adequate rest, can enhance muscle endurance and prevent overuse injuries.
In conclusion, shoulder muscle discomfort is a common, yet manageable condition. Understanding the underlying anatomy, causes, and treatment options provides a solid foundation for promoting shoulder health. Timely intervention, appropriate therapy, and preventive strategies can help individuals maintain shoulder strength and mobility over the long term, reducing the risk of chronic pain and functional limitations.