Comprehensive Guide to Effective Methods for Reducing Limb Swelling
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies to reduce limb swelling, including compression therapy, elevation, proper hydration, and medical treatments. It emphasizes lifestyle changes, dietary recommendations, and when to seek medical advice, helping readers manage swelling naturally and effectively while preventing potential complications.

Comprehensive Guide to Effective Methods for Reducing Limb Swelling
Experiencing swelling in the feet, ankles, and legs can be a common issue caused by various factors such as prolonged periods of standing or sitting. While minor swelling often resolves on its own, persistent or severe swelling may indicate underlying health problems that require attention. Understanding the causes of limb swelling and adopting effective strategies can significantly improve comfort, enhance circulation, and prevent potential complications.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore a wide range of proven techniques and lifestyle modifications that can help alleviate limb swelling. Whether you are dealing with temporary discomfort or chronic issues, implementing these methods can promote better fluid management and support overall limb health.
However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional if swelling is sudden, painful, accompanied by skin changes, or persistent despite self-care measures. Recognizing when to seek medical advice ensures appropriate diagnosis and treatment, especially in cases linked to cardiovascular, renal, or lymphatic conditions.
Below are detailed strategies to manage and reduce limb swelling effectively.
Using Compression Therapy
Incorporating Elevation Techniques
Benefiting from Epsom Salt Baths
Medical Interventions and Diuretics
Maintaining Proper Hydration
Regular Physical Activity and Movement
Massage and Lymphatic Drainage
Considering Surgical Options
Optimizing Magnesium Intake through Diet
Compression Stockings and Gear
One of the most effective ways to combat limb swelling is through compression therapy. Compression stockings or sleeves exert gentle pressure on the limbs, helping to improve blood flow and prevent fluid from accumulating in the tissues. These garments are available in various compression levels, typically measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). For general use, compression levels between 12-20 mmHg provide sufficient support for mild to moderate swelling. For more severe cases, higher compression levels may be recommended under medical supervision.
Today, you can find a variety of compression gear online and at local stores, tailored for different activities such as daily wear, sports, or travel. Lightweight and breathable materials ensure all-day comfort, making it easier to incorporate into your routine. Consulting a healthcare provider is advisable to determine the most appropriate compression level and fit for your specific needs.
Leg Elevation and Positioning
Another highly effective method for reducing limb swelling involves elevating the legs above the level of the heart. Elevation encourages gravitational drainage of excess fluid, which alleviates pressure and assists blood and lymph flow back toward the torso. Simple techniques include lying on your back with legs supported by pillows, stacking cushions, or using the wall yoga pose — Legs Up the Wall.
Implementing this practice several times a day, especially after periods of standing or sitting, can dramatically decrease swelling. Make a habit of elevating your legs for 15-30 minutes to enhance circulation and reduce discomfort.
Epsom Salt Baths for Magnesium Absorption
Magnesium deficiency is linked to inflammation and fluid retention. Soaking your feet or legs in warm water infused with Epsom salts provides an effective way to increase magnesium levels through the skin. Magnesium helps relax blood vessels, reduce inflammation, and promote lymphatic drainage, all of which contribute to relieving swelling.
For best results, soak your limbs for 15-20 minutes in a tub or basin filled with warm water and Epsom salts. Repeat this treatment regularly, especially if you notice persistent swelling or discomfort.
Healthcare-Driven Medical Treatments
When home remedies are inadequate, or swelling persists or worsens, medical intervention becomes necessary. Diuretic medications, prescribed by a healthcare professional, serve to increase urine production, helping the body eliminate excess salt and fluid. These are particularly effective in cases of severe edema caused by heart failure, kidney issues, or other systemic conditions.
There are various types of diuretics—potassium-sparing, loop, and thiazide—that may be recommended based on the underlying cause. It is vital to use medications only under medical supervision to avoid dehydration or electrolyte imbalances. If limb swelling is due to injuries such as fractures or infections like cellulitis, appropriate antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, or other treatments may be necessary.
Stay Well Hydrated
Contrary to some beliefs, dehydration can actually worsen swelling. When the body lacks enough fluid, it triggers water retention mechanisms that cause tissues to swell. Drinking sufficient water—generally at least eight glasses a day—helps maintain fluid balance, flush out toxins, and supports healthy circulation. Adequate hydration is a fundamental yet often overlooked factor in managing edema.
Active Movement and Exercise
Prolonged inactivity often results in fluid pooling in the lower limbs. Incorporating regular movement into your daily routine prevents sluggish circulation and reduces swelling. Simple activities like short walks post meals, ankle rolls, or stretching exercises at the office can make a big difference.
Engaging in low-impact aerobic exercises, such as swimming or cycling, also enhances blood flow and lymphatic drainage. Consistency is key; aim to move at least 30 minutes daily to keep lymphatic and vascular systems active.
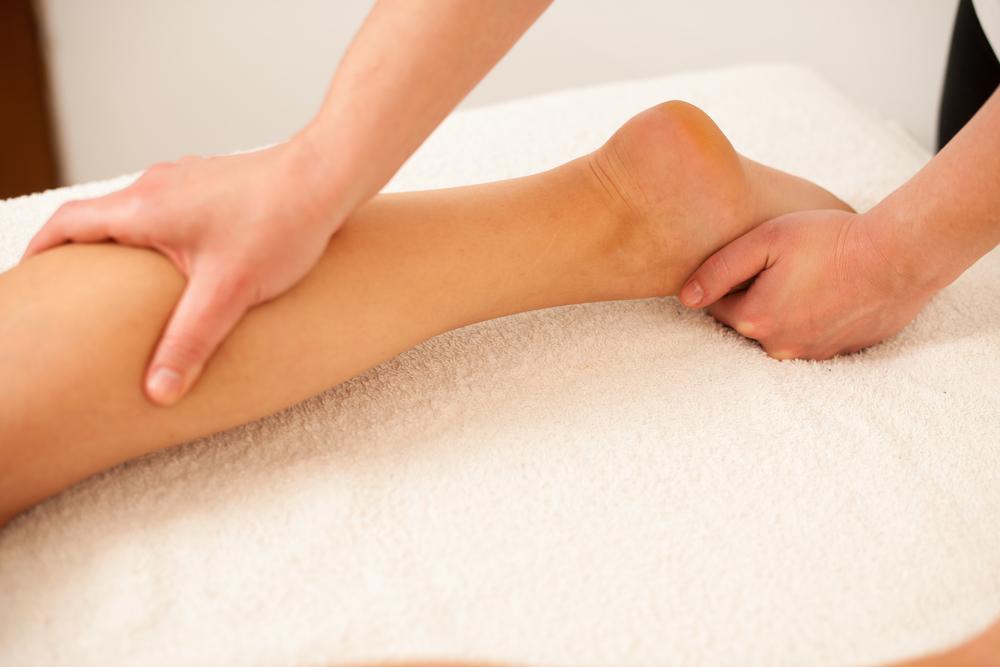
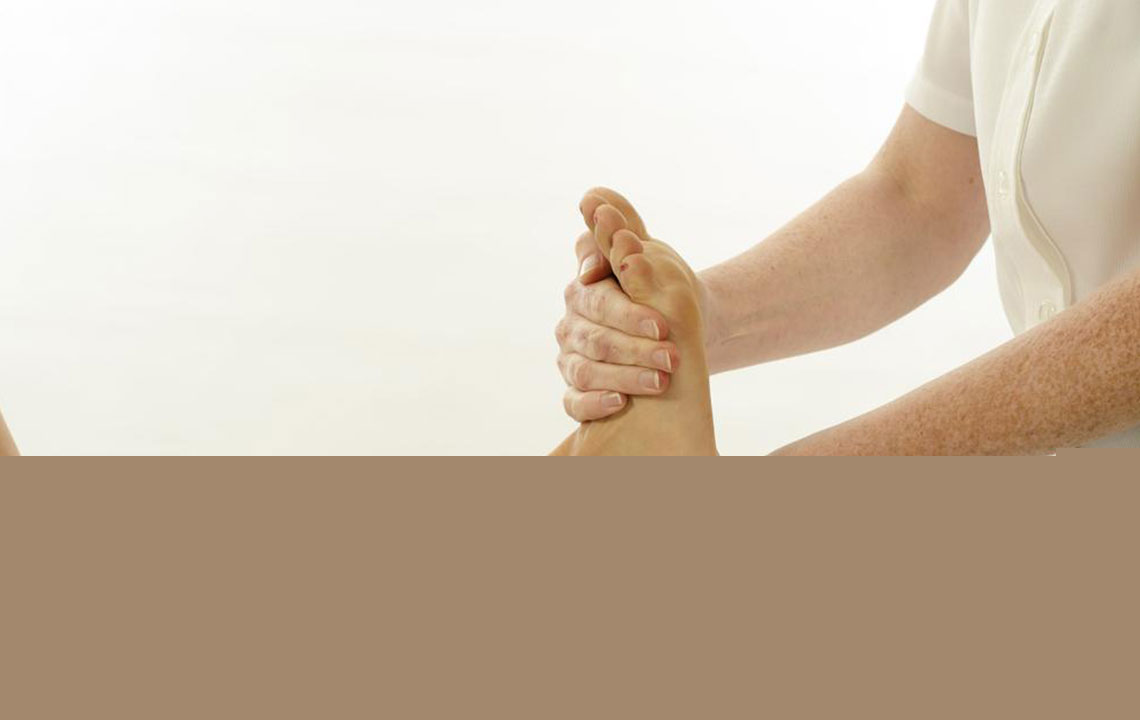
Massage and Lymphatic Drainage Therapy
Gentle massage techniques can stimulate the lymphatic system, aiding in the removal of excess fluids from tissues. Lymphatic drainage massage, performed by trained therapists, involves light rhythmic strokes that encourage lymph flow and reduce swelling. Self-massage using soft, upward strokes on the limbs can also be beneficial, especially after elevation or exercise.
This therapy can be particularly helpful for individuals with lymphatic system issues or post-surgical swelling.
Surgical Interventions
In cases where conservative treatments do not yield results, surgical options may be considered. Procedures aim to remove obstructions, repair damaged vessels, or improve vascular and lymphatic function. Examples include vascular bypass surgeries, lymphaticovenular anastomosis, or removal of cysts or tumors causing blockage.
Such interventions are typically reserved for severe or persistent medical cases and require thorough evaluation by specialists. Postoperative care and lifestyle adjustments are crucial for optimal recovery.
Dietary Strategies for Better Limb Health
Ensuring adequate magnesium intake through diet can prevent deficiencies associated with swelling. Foods rich in magnesium include dark chocolate, leafy greens like spinach or kale, low-fat dairy, whole grains such as oats and brown rice, beans, nuts, and seeds. Regularly incorporating these foods into meals supports vascular health and reduces inflammation.
Additionally, limiting salt intake helps prevent fluid retention. Eating balanced meals and maintaining a healthy weight also play vital roles in overall limb health.
In summary, limb swelling is a common but manageable condition. By understanding its causes and applying these comprehensive strategies, individuals can significantly reduce discomfort, improve circulation, and prevent complications. Early medical consultation is essential if symptoms are severe or persist despite self-care efforts.