Comprehensive Guide to Effective Psoriasis Management Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for managing psoriasis, including topical therapies, phototherapy options, and lifestyle tips. Understanding these treatments helps patients control symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and improve skin health. Personalized treatment plans developed with healthcare providers are essential for optimal results. With ongoing advances, managing psoriasis more effectively is within reach, enhancing quality of life for millions affected by this chronic condition.

Comprehensive Guide to Effective Psoriasis Management Strategies
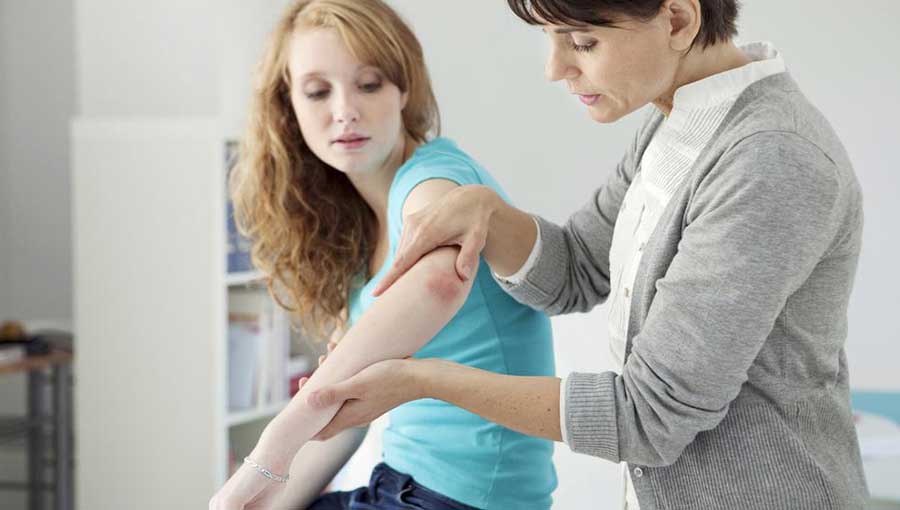
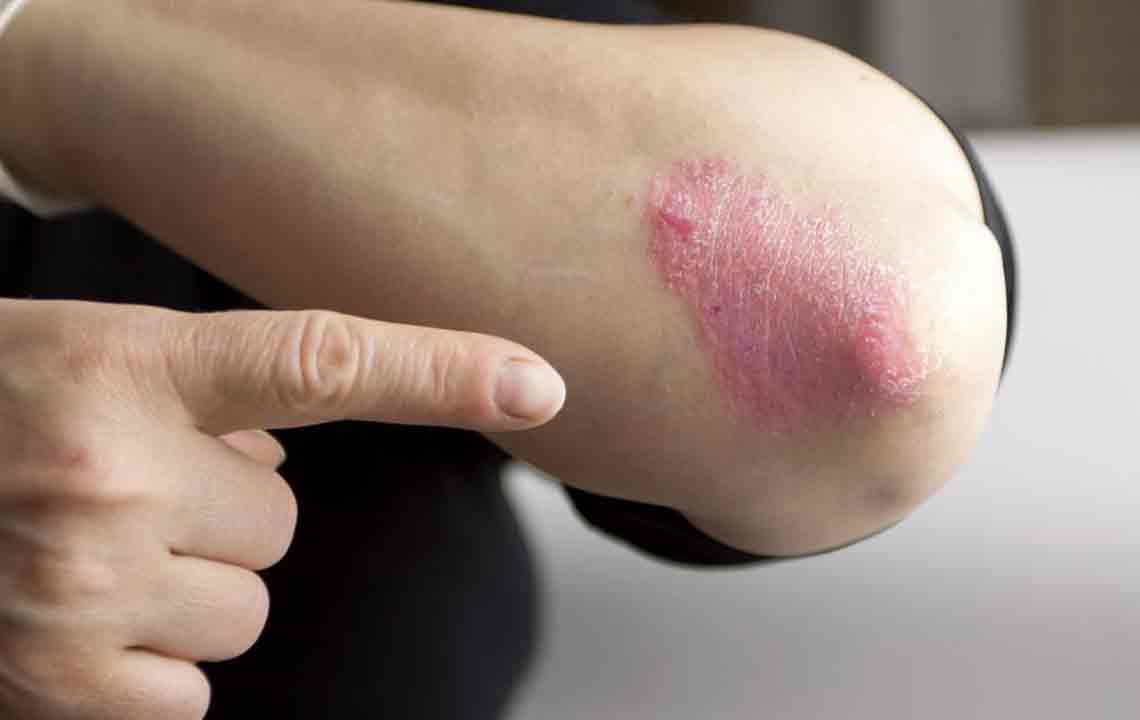
Psoriasis is a prevalent chronic skin condition that affects millions worldwide. Characterized by red, inflamed patches covered with silvery scales, this autoimmune disorder can significantly impact a person's quality of life. While currently there is no cure for psoriasis, numerous treatment options are available that aim to alleviate symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and improve skin appearance. These treatments vary depending on the severity of the condition, the specific area affected, and the individual patient’s response to therapies. Understanding the various management strategies is essential for patients and healthcare providers alike to develop tailored treatment plans that maximize efficacy and minimize side effects.
This article provides an in-depth overview of the most effective approaches to managing psoriasis, including topical therapies, phototherapy options, and lifestyle modifications. Whether you are newly diagnosed or seeking ways to better control your symptoms, this comprehensive guide will offer valuable insights into current treatments and emerging therapies.
Understanding Topical Therapies for Psoriasis
One of the primary treatment modalities for psoriasis involves topical applications directly targeted at affected skin areas. These medications are often the first line of defense for mild to moderate psoriasis and can be used in conjunction with other treatments for more severe cases. Topical therapies are generally considered safe, especially when used appropriately, and they aim to reduce inflammation, slow down excessive skin cell production, and alleviate discomfort such as itching and scaling.
Since psoriasis manifests differently across individuals, there is no one-size-fits-all topical medication. The choice depends on factors like lesion size, location, severity, and patient tolerance. Sometimes, medications need to be combined or adjusted to optimize benefits and limit side effects. Patients should always consult healthcare providers for personalized recommendations.
Some of the most common topical treatments for psoriasis include:
Topical corticosteroids: These are the most frequently prescribed relief agents for mild to moderate psoriasis. Corticosteroids work by reducing skin inflammation and suppressing immune responses that contribute to lesion formation. They are effective at decreasing redness, swelling, and itching, providing quick symptomatic relief. However, prolonged use can cause skin thinning and other side effects, so they should be used under medical supervision.
Vitamin D analogs: Calcipotriene (calcipotriol) and similar compounds belong to this category. They help normalize skin cell growth, slowing down the rapid turnover that characterizes psoriasis. Usually formulated as creams or ointments, vitamin D analogs can be used alone or combined with corticosteroids for enhanced results.
Anthralin: This medicated ointment aids in smoothing skin by removing scales and limiting excessive cell proliferation. Although effective, it can sometimes cause skin irritation and staining, so application protocols need to be carefully followed.
Retinoids: Derived from vitamin A, topical retinoids such as tazarotene help diminish inflammation and normalize skin cell differentiation. They are often used in combination with other therapies for resistant cases.
Salicylic acid: Widely available over-the-counter or by prescription, salicylic acid promotes the shedding of dead skin cells and reduces scaling. When used in conjunction with moisturizers or other medications, it can improve overall treatment effectiveness.
Coal tar: An older but still effective option, coal tar reduces scaling, itching, and inflammation. It’s available in various formulations, including shampoos, creams, and solutions.
Moisturizers: Essential for preventing dryness, alleviating scaling, and soothing irritated skin, moisturizers are a cornerstone of psoriasis self-care. Using emollients regularly can significantly improve skin comfort and reduce flare-ups.
Phototherapy: Harnessing Natural and Artificial UV Light
Phototherapy, also known as light therapy, is an effective treatment for psoriasis, especially when topical therapies alone are insufficient. This method involves exposing the skin to specific wavelengths of ultraviolet (UV) light, which can modulate immune responses and slow down abnormal skin cell growth. Both natural sunlight and controlled artificial UV light are used in clinical settings to manage psoriasis.
Sunlight phototherapy encourages the regulation of skin cell activity, reducing scaling and inflammation. However, natural sunlight exposure must be carefully monitored to prevent overexposure, which can increase the risk of skin aging and skin cancer. Controlled indoor phototherapy devices deliver precise doses of UVB light, providing a safer and more effective alternative.
How UVB Phototherapy Works in Psoriasis Treatment
Controlled doses of UVB light, either from natural sources or artificial lamps, are used to manage mild to moderate psoriasis symptoms. The therapy involves exposing affected skin to UVB wavelengths within a safe and prescribed range, typically administered multiple times weekly.
This approach is particularly beneficial for widespread psoriasis or stubborn patches resistant to topical treatments.
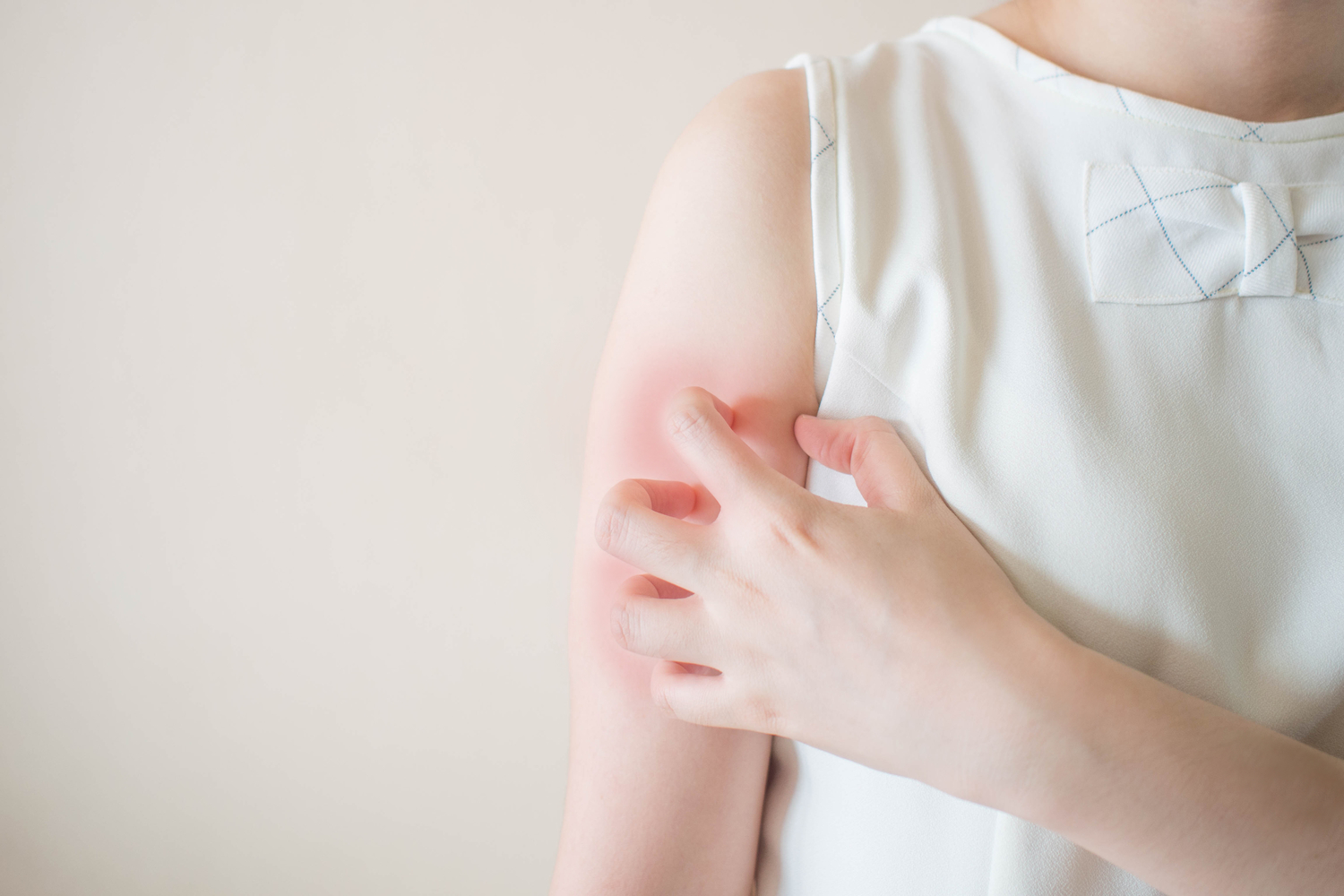
Potential side effects include redness, dryness, and irritation. These can usually be mitigated with diligent use of moisturizers and careful treatment planning.
More potent narrowband UV-B therapy delivers targeted wavelengths for increased effectiveness while reducing exposure time and side effects.
Typically, a series of sessions is necessary, with treatments often continuing until significant symptom improvement is achieved. The frequency can vary from two to three times a week, depending on individual response.
Some clinicians combine UVB therapy with topical coal tar (known as the Goeckerman method) to enhance efficacy. Coal tar increases the skin’s absorption of UV light, boosting the treatment’s benefits.
Managing Side Effects and Ensuring Safety
While topical therapies and phototherapy are generally safe when overseen by healthcare professionals, they can have adverse effects. Skin irritation, dermatitis, or thinning are common concerns, especially with prolonged or improper use of corticosteroids or retinoids. Headaches and, rarely, viral infections can also occur. To minimize risks, patients should follow their provider’s instructions diligently and report any adverse reactions promptly.
In conclusion, managing psoriasis requires a combination of therapies tailored to individual needs. Topical treatments, phototherapy, and lifestyle modifications such as moisturization and sun protection are key components. Advances in treatment options continue to evolve, promising better control and improved quality of life for those affected by this chronic skin condition. Regular consultation with dermatology specialists ensures optimal management and minimizes potential side effects.