Comprehensive Dietary Strategies for Effective Arthritis Management
Explore comprehensive dietary strategies tailored for arthritis management. Discover the best foods that reduce inflammation, support joint health, and improve overall well-being. Learn how incorporating omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and whole grains can help alleviate symptoms and enhance mobility, with tips on foods to avoid for optimal health.

Essential Nutrition Strategies to Alleviate Arthritis Symptoms
Managing arthritis effectively requires a comprehensive approach that includes adopting a nutrient-dense diet tailored specifically for joint health. Proper nutrition not only helps in reducing inflammation and alleviating joint pain but also promotes overall well-being by supporting weight management, cardiovascular health, and immune function. Implementing dietary adjustments focusing on anti-inflammatory foods, rich in essential vitamins and minerals, can significantly improve the quality of life for arthritis sufferers. This article explores scientifically-backed dietary tips to help manage arthritis symptoms more effectively and improve joint comfort over time.
Effective dietary management is a cornerstone of arthritis care. Incorporating nutrient-rich foods that combat inflammation and support joint health while avoiding foods that can worsen symptoms is essential. Focus on consuming omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that bolster immune function and reduce joint inflammation. Tailoring your diet with these key components can help diminish pain, improve mobility, and prevent further joint damage. Understanding the role of specific nutrients and foods will empower you to make smarter dietary choices that promote long-term joint health and overall vitality.
In-depth Nutritional Recommendations for Arthritis Relief
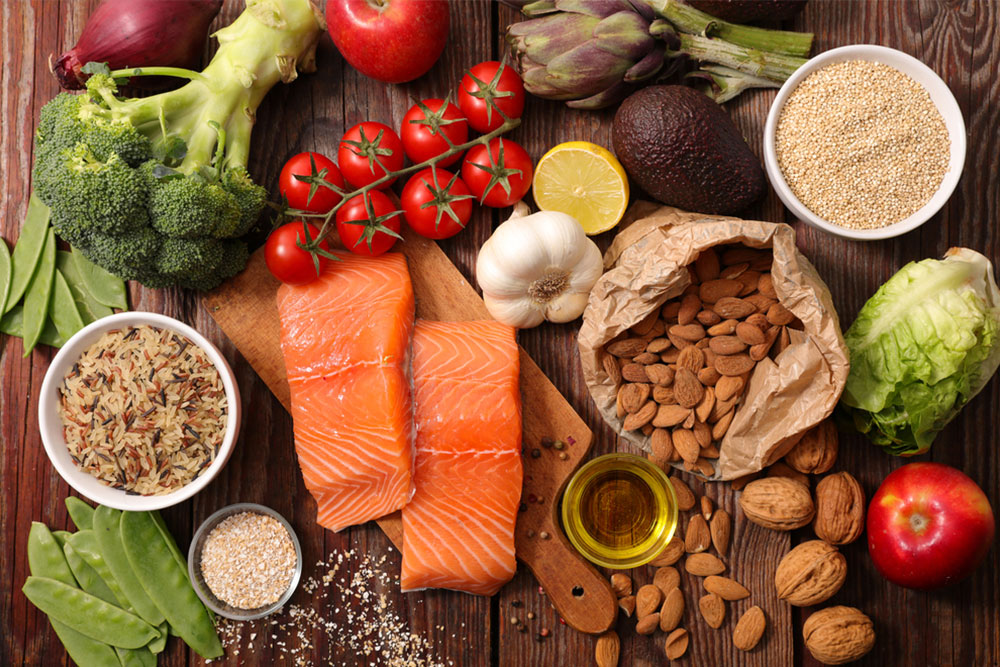
Achieving relief from arthritis symptoms is closely linked to what you eat. A well-structured diet emphasizing anti-inflammatory foods can reduce swelling and joint discomfort. Here are some detailed dietary strategies and specific foods to incorporate into your daily routine:
Fatty Fish and Omega-3 Rich Foods
Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and tuna are some of the most potent natural sources of omega-3 fatty acids, which have been proven to significantly reduce joint inflammation and stiffness. Aim to include 3-6 servings of oily fish per week to maximize benefits. For those concerned about mercury exposure, it’s advisable to choose smaller fish varieties and consider dietary supplements if recommended by a healthcare provider. Omega-3 fatty acids not only lower inflammation but also contribute to overall cardiovascular health, making them a vital part of an arthritis-friendly diet.
Vegetation Powerhouses: Vegetables
Vegetables are fundamental to an anti-inflammatory diet. Leafy greens such as spinach, kale, and collard greens are rich in antioxidants like vitamins C and E, which help neutralize free radicals and reduce tissue damage. Colorful vegetables like bell peppers, carrots, sweet potatoes, and broccoli provide carotenoids and phytochemicals that support immune health. Preparing vegetables through steaming, roasting, or light seasoning helps preserve their nutritional content while making them more palatable. Regular consumption of vegetables is associated with decreased joint swelling and improved physical function for those suffering from arthritis.
Fruits with Antioxidant Properties
Fruits high in antioxidants, particularly berries such as strawberries, blueberries, and blackberries, play a vital role in managing arthritis. Tart cherries are especially effective due to their natural anti-inflammatory compounds. Incorporating a variety of fruits such as grapes, avocados, and watermelons into your daily diet ensures a broad spectrum of antioxidants and phytochemicals that combat oxidative stress and inflammation. These fruits also contain vitamins C and E, which are essential in collagen synthesis and tissue repair, further supporting joint health.
Whole Grains and Their Role in Reducing Inflammation
Replacing refined grains with whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, barley, farro, and buckwheat can help lower systemic inflammation. Whole grains are rich in fiber, which promotes gut health and reduces inflammatory mediators in the bloodstream. Aim for 3-6 ounces of whole grains daily to support joint integrity and overall health. Limiting highly processed carbohydrate foods such as white bread, pastries, and sugary snacks is crucial, as these can trigger inflammatory responses and exacerbate arthritis symptoms.
Green Tea and Its Anti-Inflammatory Benefits
Green tea is loaded with polyphenols, especially epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), which possess potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Drinking two cups of green tea daily can contribute to pain reduction and decreased joint stiffness. For those sensitive to caffeine, decaffeinated variants are equally beneficial. Including green tea as a regular beverage in your diet is an easy and effective dietary intervention to help manage arthritis symptoms naturally.
Nuts, Seeds, and Healthy Fats
Walnuts, almonds, pistachios, flaxseeds, and chia seeds are excellent sources of anti-inflammatory fats, vitamins, and minerals like magnesium and Vitamin E. Regular intake of nuts and seeds can help reduce joint pain and swelling thanks to their omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants. Incorporate them as snacks or add them to salads, oatmeal, and smoothies for a nutrient boost. Using healthy oils such as extra virgin olive oil, avocado oil, and walnut oil for cooking and dressings further enhances anti-inflammatory effects while supporting cardiovascular health.
Foods to Limit or Avoid
While incorporating beneficial foods, it’s equally important to avoid certain dietary triggers that can worsen arthritis symptoms. These include processed sugars, trans fats found in many baked goods and fried foods, refined carbohydrates, gluten (for some individuals with sensitivity), and excessive alcohol consumption. These foods can promote systemic inflammation and contribute to joint pain and stiffness. Maintaining a balanced diet with mindful choices plays a key role in managing arthritis effectively and prolonging joint health.
In conclusion, adopting a strategic, nutrient-rich diet tailored for arthritis can significantly alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. Emphasize anti-inflammatory foods, such as omega-3-rich fish, vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, while limiting inflammatory triggers. Coupled with regular physical activity and proper medical management, dietary adjustments serve as a powerful tool in fighting arthritis and supporting joint well-being in the long term.