Comprehensive Approaches to Effectively Treating and Managing Kidney Infections
This article provides an in-depth overview of strategies to effectively diagnose, treat, and manage kidney infections, emphasizing early detection, appropriate antibiotic use, and preventive measures to avoid complications. It aims to educate patients and healthcare providers on best practices for maintaining renal health and preventing recurrent infections.
Effective Strategies for Managing Kidney Infections
Kidney infections, medically known as pyelonephritis, are serious medical conditions that occur when bacteria invade the renal system, impacting either one or both kidneys. These infections can cause significant discomfort, and if left untreated, may lead to severe complications such as kidney damage or systemic infections. Therefore, understanding the best practices for early detection, diagnosis, and management is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike.
Kidney infections typically originate from bacteria that ascend from the lower urinary tract, including the bladder and urethra, into the kidneys. The most common culprits are Escherichia coli bacteria, although other pathogens can also be involved. Several factors can predispose individuals to develop kidney infections, including urinary tract obstructions, kidney stones, diabetes, weakened immune systems, or anatomical abnormalities.
Early recognition of symptoms is essential for prompt intervention. Common signs include persistent lower abdominal or groin pain, which may radiate to the lower back or sides of the body. Patients often experience fever and chills, which can become severe if the infection worsens. Other symptoms may include painful or frequent urination, cloudy or foul-smelling urine, blood in the urine, and general fatigue or malaise.
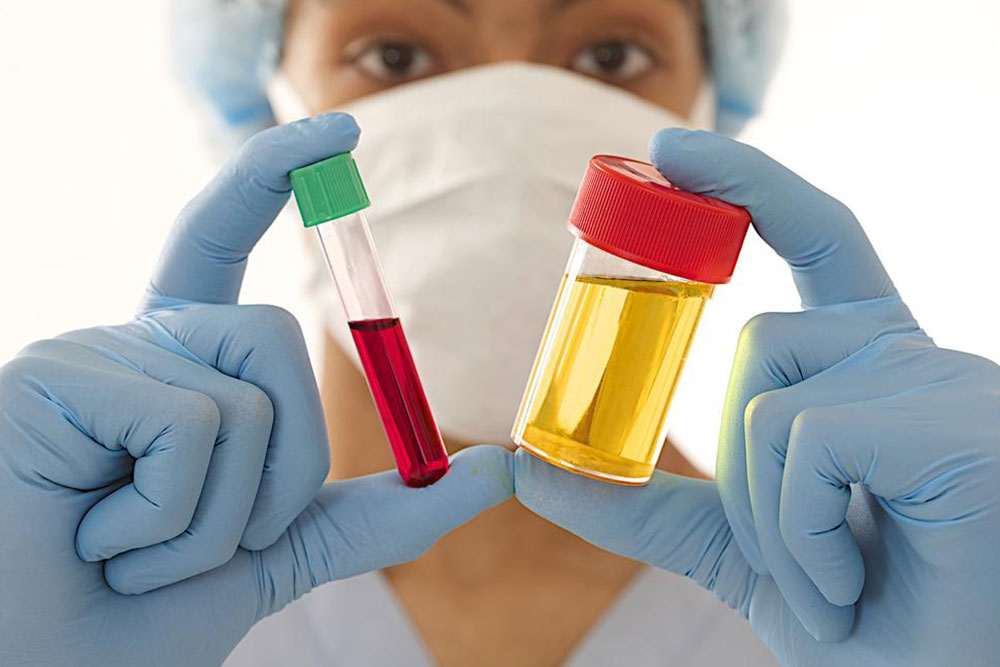
Timely diagnostic evaluation is key to effective management. Healthcare providers typically rely on a combination of laboratory tests, imaging studies, and clinical examination. Urinalysis helps identify signs of infection, such as the presence of bacteria, white blood cells, or blood. Urine cultures are critical for pinpointing the causative organism and determining antibiotic sensitivity, which guides the choice of therapy. Blood tests may reveal signs of systemic infection or kidney impairment.
Imaging techniques like renal ultrasounds, CT scans, or nuclear medicine scans assist in assessing the extent of infection, detecting anatomical abnormalities, kidney stones, or abscesses. These diagnostic tools are essential in complex cases or when initial treatment fails.
Management of kidney infections primarily involves antibiotic therapy. The choice of antibiotic depends on the severity of the infection and the pathogen identified through cultures. Mild cases can often be managed outpatient with oral antibiotics, but severe infections or those with complications necessitate hospitalization for intravenous antibiotics and supportive care. Adequate hydration, pain management, and rest are vital components of recovery.
For recurrent or complicated infections, further investigations may be warranted to identify underlying causes. Preventive strategies include maintaining good hygiene, staying well-hydrated, and managing predisposing conditions such as diabetes or obstructive uropathy.
In some cases, surgical intervention might be necessary to remove obstructions, stones, or treat structural abnormalities contributing to recurrent infections. Follow-up care is essential to ensure complete resolution and to monitor kidney function.
In conclusion, effective management of kidney infections hinges on early diagnosis, targeted antimicrobial therapy, and addressing underlying risk factors. Patients should seek medical attention at the first sign of symptoms and adhere to prescribed treatments to prevent complications. With prompt and comprehensive care, most individuals recover fully and can avoid long-term renal damage.