Comprehensive Dietary Guidelines for Managing Bladder Cancer: Foods to Avoid and Tips for Better Comfort
This comprehensive guide discusses essential dietary restrictions for bladder cancer patients. It highlights foods to avoid, such as caffeine, alcohol, citrus fruits, spicy foods, tomato products, and chocolates. The article explains how these foods can irritate the bladder and worsen symptoms. It emphasizes the importance of personalized diet management, moderation, and proper hydration to improve comfort and support treatment. Suitable for patients seeking practical dietary advice to manage bladder cancer effectively, this article offers insights into minimizing discomfort and enhancing quality of life.

Comprehensive Dietary Guidelines for Managing Bladder Cancer: Foods to Avoid and Tips for Better Comfort
Living with bladder cancer requires a multifaceted approach that includes not only medical treatments but also significant attention to lifestyle modifications, particularly diet. The right dietary choices can influence symptom control, enhance quality of life, and potentially slow disease progression. For patients diagnosed with bladder cancer, understanding which foods to avoid is essential in minimizing bladder irritation, reducing discomfort, and preventing complications. Coupled with proper hydration and monitoring fluid intake, dietary management becomes a cornerstone of effective disease control and improved well-being.
Various foods have been identified as bladder irritants that can worsen symptoms or contribute to inflammation. Patients should aim to eliminate or severely limit these foods from their diet to manage their condition better. Awareness and prevention are key—by avoiding common irritants, individuals with bladder cancer can experience less discomfort and enhance their treatment outcomes.
Foods that are known to irritate the bladder include:
All sources of caffeine, such as coffee, black tea, green tea, and caffeinated soft drinks
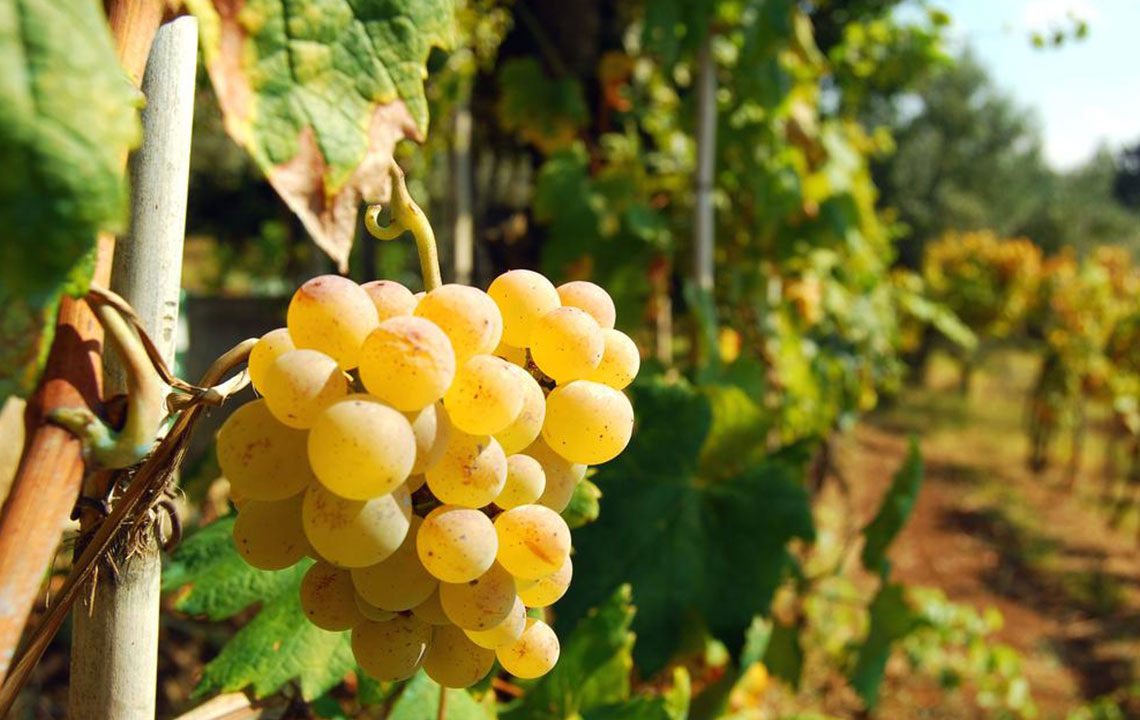
Alcoholic beverages, which can increase bladder irritation and disrupt hydration levels
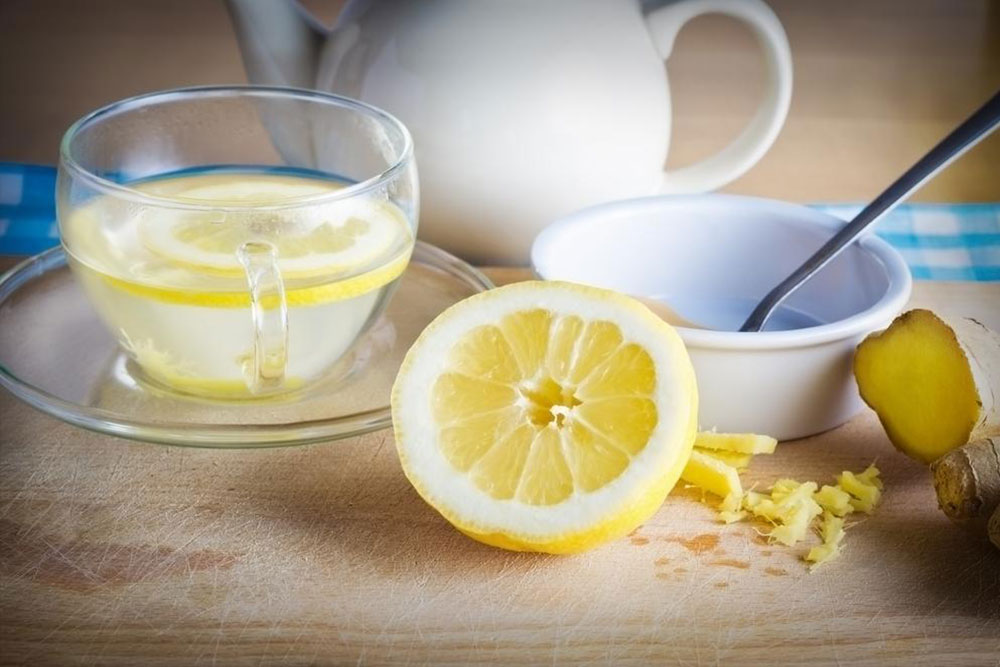
Citrus fruits like oranges, grapefruits, lemons, limes, and their juices, which are highly acidic and can inflame the bladder lining
Spicy foods, including hot peppers, curry, and other spicy seasonings that can cause increasing irritation
Tomato-based products, such as sauces, ketchup, and tomato juice, known to cause or worsen inflammation
Chocolates and cocoa-containing products, as they contain compounds that may trigger discomfort in sensitive individuals
It’s crucial to recognize that individual reactions to certain foods can vary significantly. Some patients may find specific foods highly irritating, while others might tolerate them with minimal issues. Keeping a detailed food diary can help identify personal triggers, allowing patients to tailor their diet for optimal comfort. Moderation is vital; even foods that are generally considered safe should be consumed judiciously, avoiding excessive intake that could aggravate symptoms.
In addition to dietary restrictions, maintaining proper hydration is essential. Adequate fluid intake helps flush irritants from the bladder, dilutes urine, and decreases the risk of infection. However, both overhydration and dehydration can pose risks—overhydration may increase bladder capacity and frequency issues, while dehydration can concentrate toxins and irritants in the bladder. Striking a balance by monitoring fluid consumption according to individual tolerance levels enhances bladder health and minimizes nocturnal bathroom trips and stress on the bladder.
In summary, adopting a bladder-friendly diet is a practical and effective strategy for those battling bladder cancer. By avoiding known irritants, practicing moderation, and maintaining proper hydration, patients can significantly improve their comfort levels, alleviate symptoms, and potentially support their overall treatment plan. Always consult with healthcare providers or a registered dietitian before making substantial dietary changes, especially when managing complex conditions like bladder cancer. Personalized guidance ensures that nutritional needs are met without compromising disease management.