Comprehensive Guide to Preventing and Managing Hemophilia Effectively
This comprehensive guide provides essential strategies for preventing and managing hemophilia effectively. It covers safety precautions, medication guidelines, and lifestyle adjustments crucial for minimizing bleeding risks and improving quality of life for those affected. Learn how proactive care and education can help manage this hereditary condition successfully.
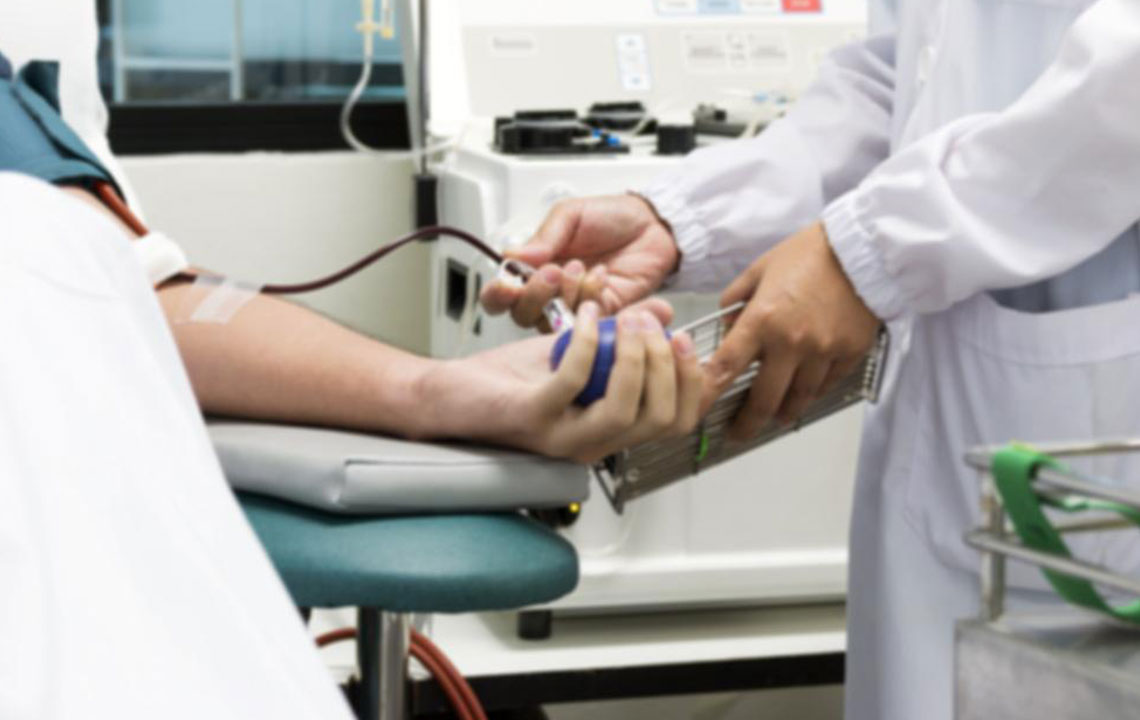
Proven Strategies for Hemophilia Prevention and Safe Management
Hemophilia is a hereditary bleeding disorder that affects the body's ability to form blood clots, leading to prolonged bleeding episodes after injuries, surgeries, or even minor cuts. This complex condition results from low levels or malfunctioning of specific clotting factors, primarily factors VIII and IX, which are essential for normal blood coagulation. Hemophilia manifests predominantly in two forms: Hemophilia A, caused by deficiency of factor VIII, and Hemophilia B, caused by deficiency of factor IX. Although there is currently no cure for hemophilia, advances in medical management have made it possible for many affected individuals to lead vibrant, active lives with proper care and prevention strategies.
Preventing and managing hemophilia effectively requires a comprehensive understanding of the condition and adherence to specific safety measures. These precautions are vital to minimize the risk of spontaneous bleeding, internal hemorrhages, and joint damages, which can significantly impair quality of life. While there is no universal cure, modern therapies, regular monitoring, and lifestyle adjustments enable individuals with hemophilia to maintain good health and avoid life-threatening complications. Proper education about the condition, proactive health management, and safety awareness are essential components of a successful treatment approach.
Effective management of hemophilia involves adopting multiple safety and preventive measures, including:
Medication Avoidance: Patients should strictly avoid non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and aspirin, as these medications inhibit platelet function and increase bleeding risk. Alternatives like acetaminophen are typically safer for managing pain.
Vaccination Programs: Ensuring vaccination against hepatitis B virus (HBV) is crucial for individuals with hemophilia due to their higher risk of blood-borne infections from transfusions or improper medical procedures. Regular immunizations can prevent serious liver diseases and other complications.
Clotting Factor Replacement Therapy: Regular infusions of clotting factors such as Factor VIII or IX are often used prophylactically to prevent bleeding episodes or to treat acute hemorrhages effectively. Personalized treatment plans should be developed with healthcare providers for optimal outcomes.
Careful Consideration for Circumcision and Surgical Procedures: Male infants with hemophilia should avoid circumcision or any surgical intervention unless absolutely necessary and performed with appropriate clotting factor support. Carriers may transmit the disorder to male offspring even if they are asymptomatic, requiring careful evaluation before such procedures.
Injury Prevention and Safety Measures: Individuals under treatment must vigilantly avoid cuts, bruises, or any injuries. Using protective gear like helmets during sports, padding during physical activities, and safe environments can significantly reduce injury risk.
Beyond medication, additional preventive steps are critical for minimizing bleeding risks. Maintaining excellent dental health is essential since dental procedures and routine oral activities can trigger bleeding episodes. Regular dental checkups, consistent brushing, flossing, and fluoride treatments contribute to oral health and reduce complication risks. For infants and young children, avoiding bed-time bottles after teething helps prevent oral injuries that could lead to bleeding. In daily life, safety gear like helmets during cycling, skating, or contact sports significantly decreases the chances of head injuries and bleeding. Educating patients, their families, and caregivers about these precautions ensures better health outcomes and enhances their ability to manage the disorder effectively.
In conclusion, while hemophilia remains a challenging hereditary condition, advancements in medical therapies and proactive preventive strategies have dramatically improved the quality of life for many affected individuals. Staying informed about potential risks, adhering to treatment protocols, and practicing comprehensive safety measures are fundamental in reducing complications. Ongoing medical monitoring, patient education, and community support also play vital roles in helping individuals with hemophilia lead safe and healthy lives. Healthcare providers, patients, and families must work together to implement these strategies confidently to prevent bleeding episodes and manage the disease proactively.