Comprehensive Guide to Melanoma: Understanding Risks and Effective Prevention Strategies
Melanoma, a deadly form of skin cancer, often results from excessive UV exposure. This comprehensive guide discusses risk factors, early detection signs, and essential prevention tips. Protect your skin by avoiding tanning beds, using broad-spectrum sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and conducting regular skin self-exams. Early diagnosis greatly improves treatment outcomes, so awareness and proactive measures are vital. Stay informed and safeguard your skin to reduce melanoma risk and promote overall health.

Comprehensive Guide to Melanoma: Understanding Risks and Effective Prevention Strategies
Skin cancer remains a significant health concern worldwide, with melanoma being one of the most aggressive and deadly types. Despite accounting for only about 1% of skin cancer cases, melanoma is responsible for the majority of skin cancer-related deaths due to its ability to spread rapidly if not detected early. Many individuals underestimate the risks associated with sun exposure, leading to preventable cases of melanoma. A thorough understanding of melanoma's causes, risk factors, early symptoms, and preventive measures is crucial for reducing its incidence and improving early detection rates.
According to data from the Skin Cancer Foundation, in the year 2017 alone, there were approximately 87,110 new cases of melanoma diagnosed across the globe, with nearly 9,730 fatalities. These statistics highlight the importance of awareness and proactive measures. The good news is that when diagnosed early, melanoma can often be effectively treated through minor surgical procedures, significantly increasing the chances of complete recovery. Therefore, awareness, vigilance, and prevention are vital components in combating this serious skin condition.
Melanoma originates in melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that determines skin color. Melanin provides some natural protection against the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. However, individuals with lighter skin tones, blue or green eyes, and blonde or red hair tend to produce less melanin, making them more vulnerable to UV damage and melanoma. While melanin does offer some degree of protection, excessive sun exposure can overwhelm these defenses, increasing the risk of DNA damage within skin cells, which can lead to melanoma development.
Understanding Melanoma
Melanoma is a form of skin cancer that begins in melanocytes. These pigment-producing cells, when damaged by UV radiation, can undergo genetic mutations, resulting in uncontrolled proliferation of abnormal cells. If left untreated, melanoma can invade nearby skin tissues and spread to lymph nodes and other parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system. This invasive nature makes early detection and intervention essential for favorable prognosis.
Although melanoma primarily appears on skin frequently exposed to the sun, it can also develop in areas not commonly exposed, such as the soles of the feet, palms of the hands, or underneath the nails. Recognizing early warning signs is critical for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Sun Exposure and Melanoma Risk Factors
Extended exposure to UV rays from the sun or tanning beds remains the leading cause of melanoma. UV radiation damages the DNA within skin cells, increasing the likelihood of mutations that can lead to cancer. The risk amplifies with patterns of intense, intermittent sun exposure, such as sunbathing or outdoor activities without protection. Additionally, individuals who have a history of sunburns, especially blistering sunburns during childhood or adolescence, face a higher risk of developing melanoma later in life.
Genetic predisposition also plays a vital role. People with a family history of melanoma, multiple atypical moles, or a history of other skin cancers are at increased risk. Fair-skinned individuals with light hair and eyes are more susceptible, but melanoma can affect anyone regardless of skin tone.
Protective Measures and Prevention Tips
Preventing melanoma hinges on effective sun safety practices and regular skin monitoring. Here are some essential tips:
Avoid using tanning beds entirely, as they emit UV radiation that can accelerate skin damage.
When outdoors, wear loose-fitting, long-sleeved clothing, a wide-brimmed hat, and UV-protective sunglasses to shield your skin and eyes.
Seek shade, especially during peak UV hours from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m., when the sun's rays are the strongest.
Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher at least 30 minutes before outdoor exposure. Make sure to cover all exposed skin areas thoroughly.
Reapply sunscreen regularly—every two hours—and more frequently if swimming or sweating.
Use water-resistant sunscreens for beach or pool days to maintain protection during water activities.
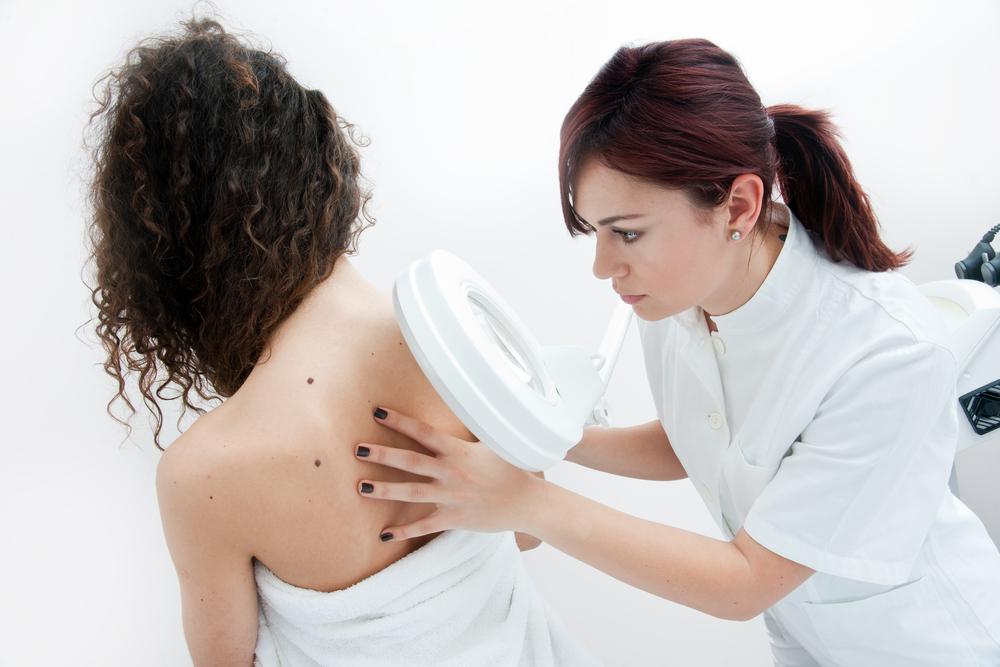
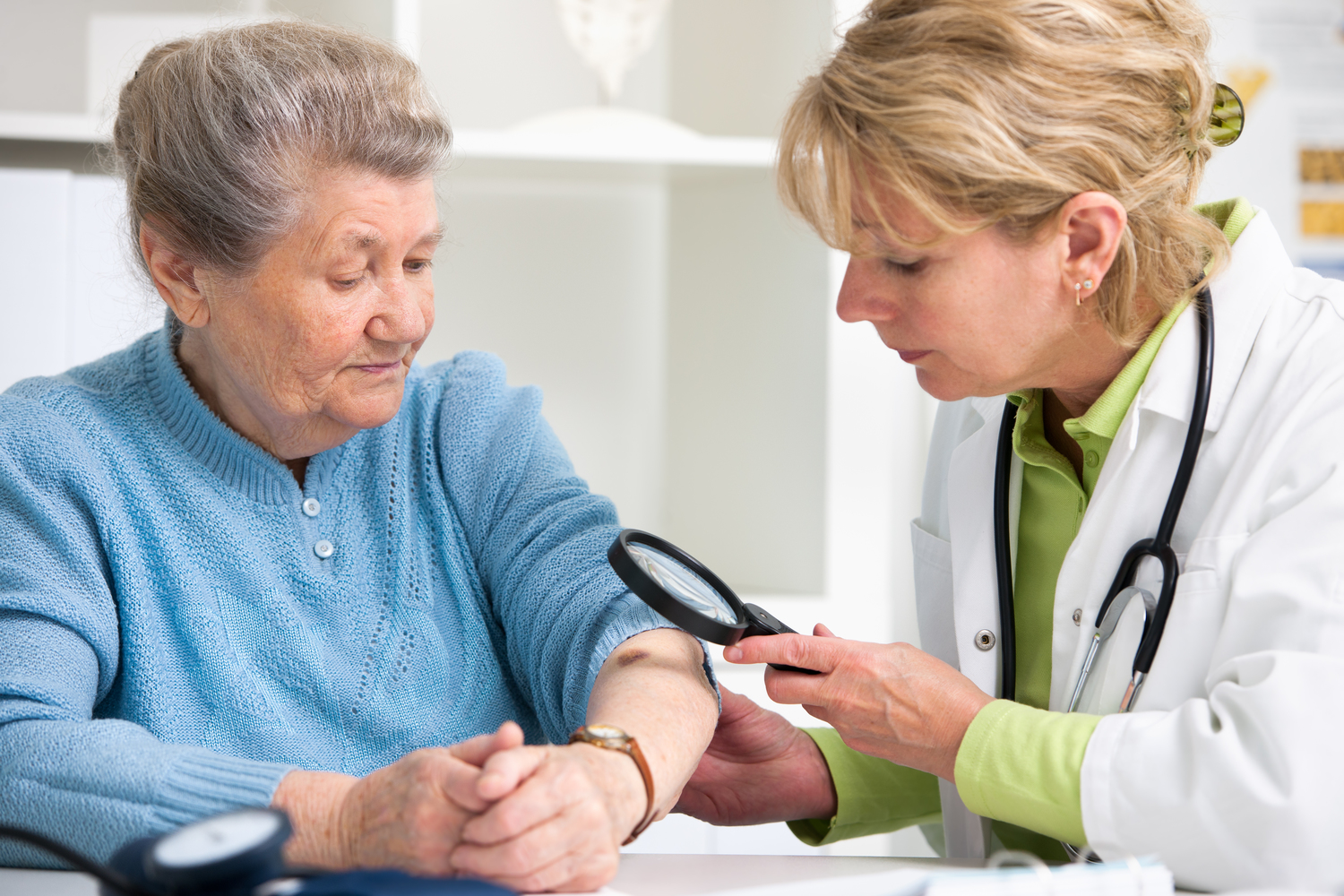
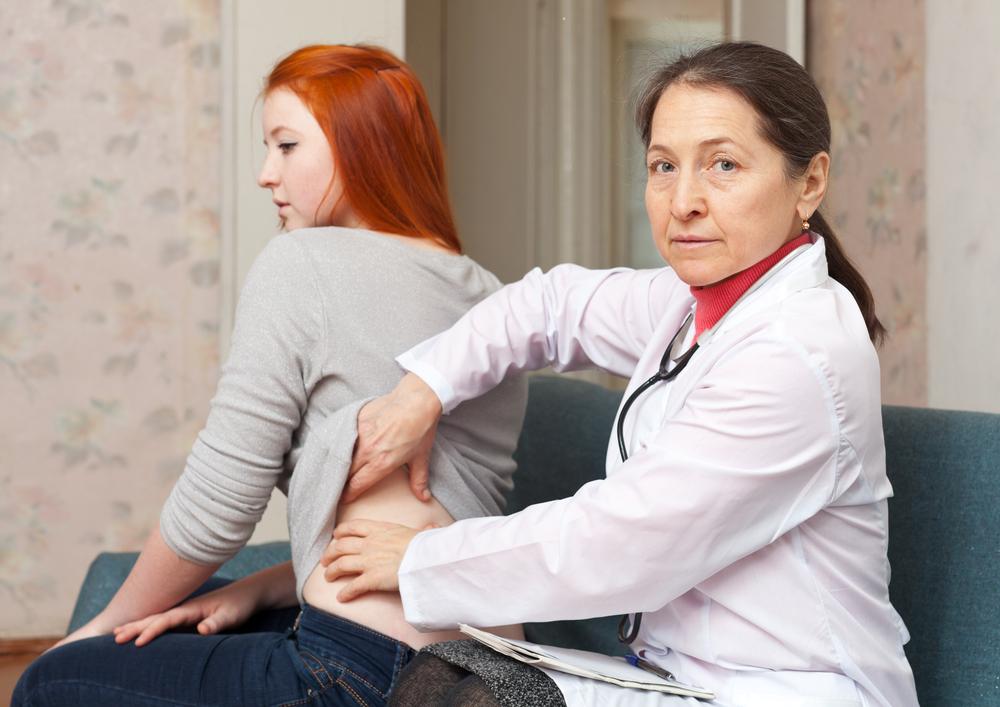
Perform weekly skin self-examinations to look for new or changing moles, freckles, or spots, especially ones that look irregular, asymmetrical, or have uneven borders and multiple colors.
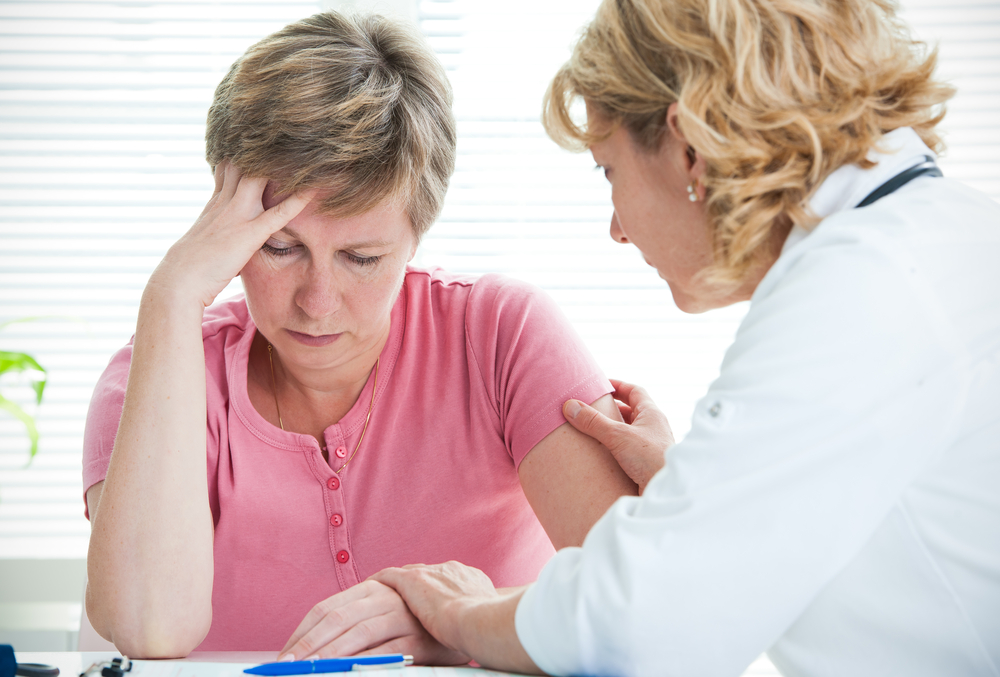
Consult a dermatologist for annual skin checks or if you notice any suspicious skin changes.
Early detection enhances treatment effectiveness and can save lives. Recognizing abnormal moles or skin markings and seeking medical advice promptly are crucial steps in melanoma prevention.
Public health campaigns continue to emphasize skin cancer awareness, encouraging individuals to adopt protective behaviors and undergo regular skin assessments. Advances in dermatology and oncology are improving diagnosis and treatment options, but prevention remains the most effective strategy in reducing melanoma incidence.