Comprehensive Guide to Causes of Posterior Knee Discomfort and How to Address Them
This comprehensive guide explores the various causes of posterior knee discomfort, from common issues like cysts and injuries to serious conditions such as blood clots. It highlights symptoms, home remedies, and when to seek medical help. Learning about these potential causes helps individuals better understand their symptoms and take timely action to prevent aggravation or complications, ensuring swift recovery and improved knee health.

In-depth Exploration of Posterior Knee Pain and Its Causes
Discomfort located at the back of the knee, commonly referred to as posterior knee pain, can result from a wide array of underlying issues. Recognizing the root cause is vital for effective treatment and management. This detailed guide aims to clarify the most prevalent reasons behind posterior knee pain, from common conditions like arthritis and injuries to less frequent but serious health concerns, providing you with a thorough understanding of this condition.
Posterior knee discomfort can present in various intensities—from mild soreness after prolonged physical activity to debilitating pain that hampers daily movements. Many individuals experience accompanying symptoms such as joint stiffness, swollen muscles, or tenderness that intensifies upon touch. Identifying these signs early can prevent further complications and ensure timely intervention.
It is important to differentiate between minor discomforts and signs of serious health conditions. While most cases are due to musculoskeletal issues like strains or degenerative changes, conditions such as joint inflammation, tumors, or blood clots require prompt medical attention. Additionally, nerve compression syndromes can lead to inflamed muscles around the knee, intensifying pain and discomfort.
Baker's Cyst (Popliteal Cyst)
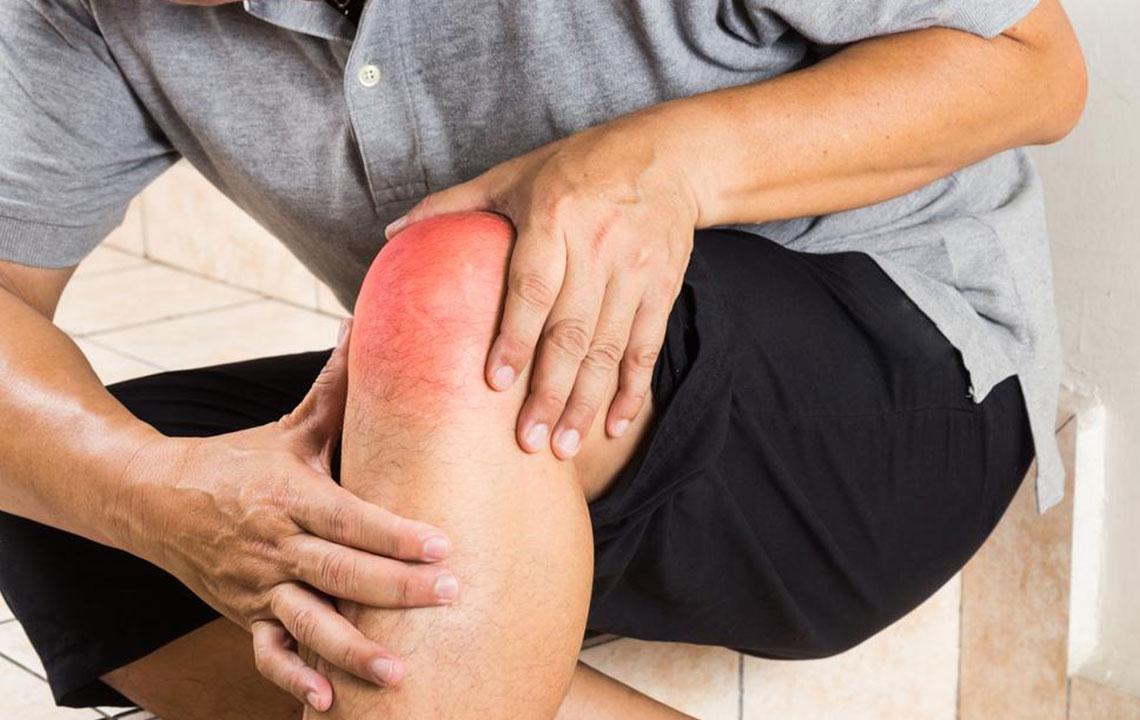
One of the most common causes of posterior knee swelling is the Baker's cyst, which is a fluid-filled sac that develops at the back of the knee joint. This cyst often becomes noticeable in individuals suffering from arthritis or joint inflammation, as excess joint fluid leaks out and accumulates in the cyst. The swelling resembles a small balloon just behind the knee, making it uncomfortable to bend, stretch, or flex the knee joint. Accompanying symptoms may include tenderness, mild to severe pain, and stiffness, especially during physical activity or prolonged standing.
Home remedies can provide relief for mild cases. Applying ice packs to reduce swelling, elevating the leg, and resting the knee are effective initial measures. In some cases, physical therapy or medical interventions such as aspiration (removal of fluid) may be necessary for persistent or symptomatic cysts. Recognizing when to seek medical help is essential, especially if the swelling worsens or is accompanied by increasing pain.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
A more serious concern linked to posterior knee pain is Deep Vein Thrombosis, which involves the formation of blood clots in the deep veins behind the knee. This condition can pose significant health risks, including the potential for a clot to dislodge and travel to the lungs, resulting in a life-threatening pulmonary embolism. Symptoms of DVT include swelling, redness, warmth, and tenderness behind the knee.
Immediate medical attention is crucial if DVT is suspected. Proper diagnosis typically involves ultrasound imaging, and treatment may include blood-thinning medications and lifestyle modifications to prevent clot propagation and recurrence.
Trauma from accidents or sports injuries can also lead to posterior knee pain. Muscle or tendon tears resulting from sudden impacts or overexertion may take weeks or months to heal, depending on severity. Some common injury-related causes are outlined below:
Gastrocnemius Tendinopathy
This condition involves overuse or degeneration of the calf muscle tendons, particularly common among athletes such as runners, cyclists, and sprinters. Symptoms include pain directly behind the knee, swelling, and restricted movement. Treatment typically involves rest, physical therapy, stretching exercises, and sometimes anti-inflammatory medications.
Biceps Femoris Tendinopathy
Excessive strain or repetitive use during sports activities can cause small tears in the biceps femoris tendon, which is part of the hamstring group. This often results in pain on the outer side of the knee and requires physiotherapy, strengthening exercises, and adequate rest for recovery.
Hamstring Tendonitis
Repetitive movements, poor stretching routines, or improper sports techniques can inflame the hamstring tendons, leading to mild pain that improves with activity modification and physical therapy. Addressing biomechanics and muscle flexibility plays a crucial role in recovery.
Tennis Leg
A sudden, sharp pain behind the knee can occur due to a strain or tear in the calf muscles or the plantaris muscle during vigorous activity, such as sprinting or jumping. Immediate rest and gentle stretching are recommended, with medical evaluation if symptoms persist or worsen.
Posterolateral Corner Injury
This rare but serious injury results from traumatic impacts or falls, leading to pain on the back and outer side of the knee. Proper diagnosis often involves imaging, and treatment may require surgical intervention in severe cases.
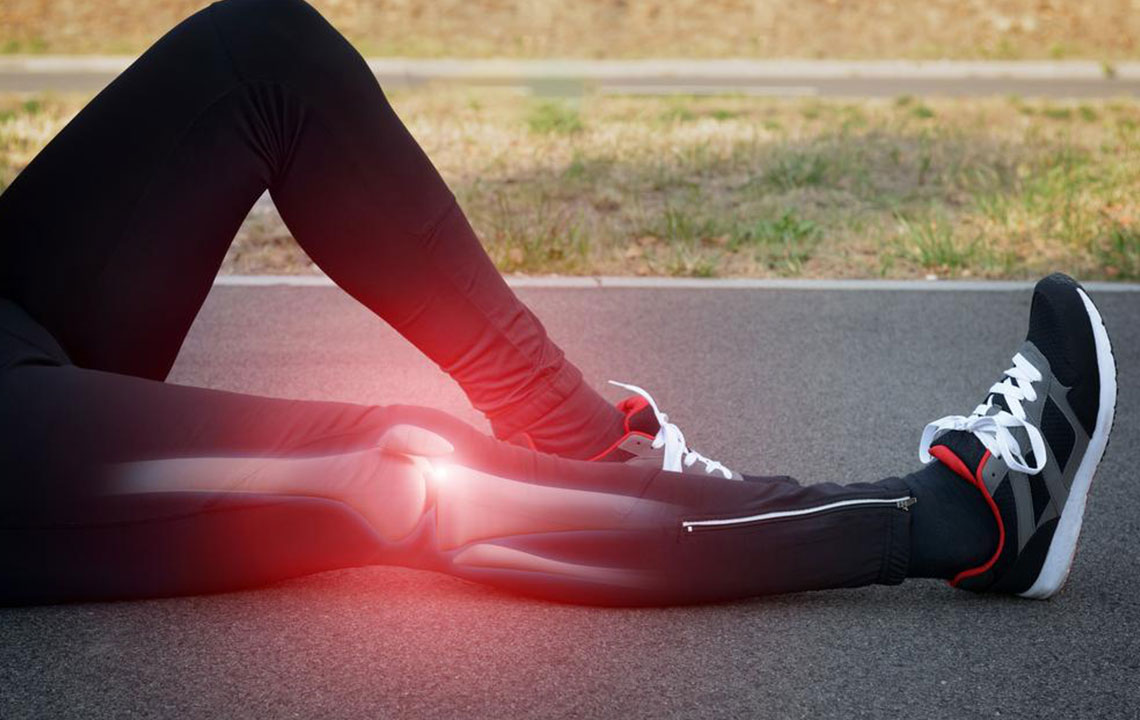
Torn Meniscus
The meniscus acts as a shock absorber within the knee joint. Tears in this cartilage are a common injury, often caused by twisting motions or direct impact. Symptoms include severe pain, swelling, stiffness, and difficulty bearing weight. Immediate medical attention and sometimes surgical repair are necessary depending on the tear's severity.
Understanding the multiple causes of posterior knee pain is critical in determining appropriate treatment strategies. Whether the pain results from minor injuries or more complex health issues, timely diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve outcomes and restore mobility. If you experience persistent or worsening symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive assessment and tailored treatment plan.