Recognizing the Key Signs and Symptoms of Advanced Lung Cancer Spread (Metastasis)
This comprehensive article explores the vital signs and symptoms indicating advanced lung cancer metastasis. It emphasizes the importance of early detection for better management, detailing symptoms like persistent cough, blood in sputum, weight loss, bone pain, liver jaundice, and neurological signs due to brain involvement. Recognizing these symptoms promptly can lead to timely medical intervention, potentially improving outcomes and quality of life. The article also discusses how metastasis impacts vital organs such as the bones, liver, and brain, outlining their associated symptoms and emphasizing the importance of a proactive approach in lung cancer management.

Understanding the Signs and Symptoms of Advanced Lung Cancer Spread (Metastasis)
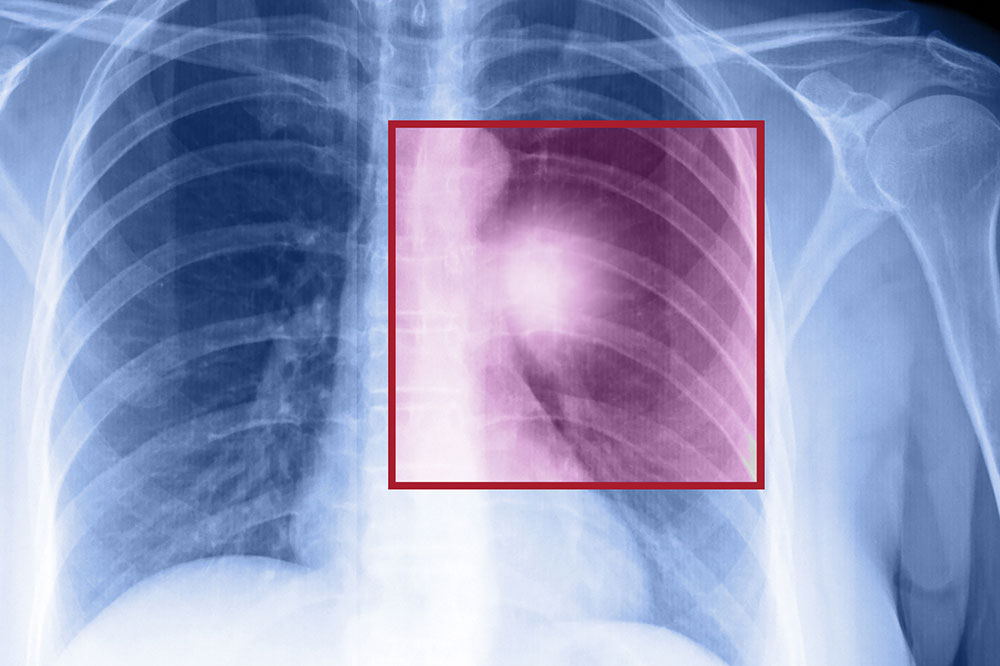
Lung cancer in its advanced stages, particularly when it has metastasized, often presents with subtle or no initial symptoms. Many individuals discover the disease incidentally during routine chest imaging for unrelated medical issues. As the cancer progresses, malignant cells escape the primary tumor and disseminate through the lymphatic system and bloodstream, ultimately spreading to distant organs. This stage, known as stage IV lung cancer, signifies a serious progression where cancerous activity is evident beyond the lungs, often complicating treatment options and prognosis.
Detecting metastasis early is crucial for managing lung cancer effectively. Several symptoms may indicate that the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. Recognizing these warning signs and seeking timely medical assessment can significantly impact treatment success and quality of life. The most common symptoms associated with lung cancer metastasis include persistent or worsening cough, hemoptysis (coughing up blood), and blood-streaked sputum. Other noteworthy symptoms encompass unexplained weight loss, persistent fatigue, recurrent respiratory infections, shortness of breath, and voice changes such as hoarseness.
If a cough becomes more severe or lasts for a prolonged period, it warrants urgent evaluation by a healthcare professional. The presence of hemoptysis is particularly alarming, as it frequently indicates bleeding caused by tumor invasion of blood vessels. Shortness of breath and ongoing chest pain are also important symptoms that should not be ignored, as they may indicate disease progression and involvement of the thoracic structures.
Beyond the lungs, metastasis can involve vital organs like the bones, liver, and brain. Bone metastases might manifest as persistent bone pain, often in the ribs, vertebrae, or long bones such as the thighs. Liver involvement could cause symptoms like jaundice, characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes, although some patients may be asymptomatic for a period. When the cancer spreads to the brain, symptoms can include severe headaches, neurological deficits such as weakness or numbness on one side of the body, seizures, and changes in mental status. The specific symptoms experienced depend on the affected organ and extent of spread, emphasizing the importance of early detection and multidisciplinary management.
Understanding these signs and symptoms enables patients and caregivers to seek prompt medical care. Given that lung cancer metastasis often involves complex symptomatology, a comprehensive approach including advanced imaging and laboratory tests is essential for accurate staging and treatment planning. Treatment options at this stage may include chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and supportive care to improve quality of life and prolong survival. The prognosis varies depending on the metastatic sites and the overall health status of the patient, underscoring the importance of early diagnosis and intervention.