Exploring the Hidden Dangers of Osteoporosis Medications and How to Protect Your Bone Health
This comprehensive article explores the hidden dangers of osteoporosis medications, shedding light on their side effects and long-term risks. It emphasizes the importance of holistic approaches—including lifestyle changes, diet, and natural remedies—to maintain healthy bones. By understanding both the benefits and potential harms of pharmaceutical treatments, patients and healthcare providers can work together to develop safer, more effective osteoporosis management plans that prioritize long-term health and bone integrity.
Exploring the Hidden Dangers of Osteoporosis Medications and How to Protect Your Bone Health
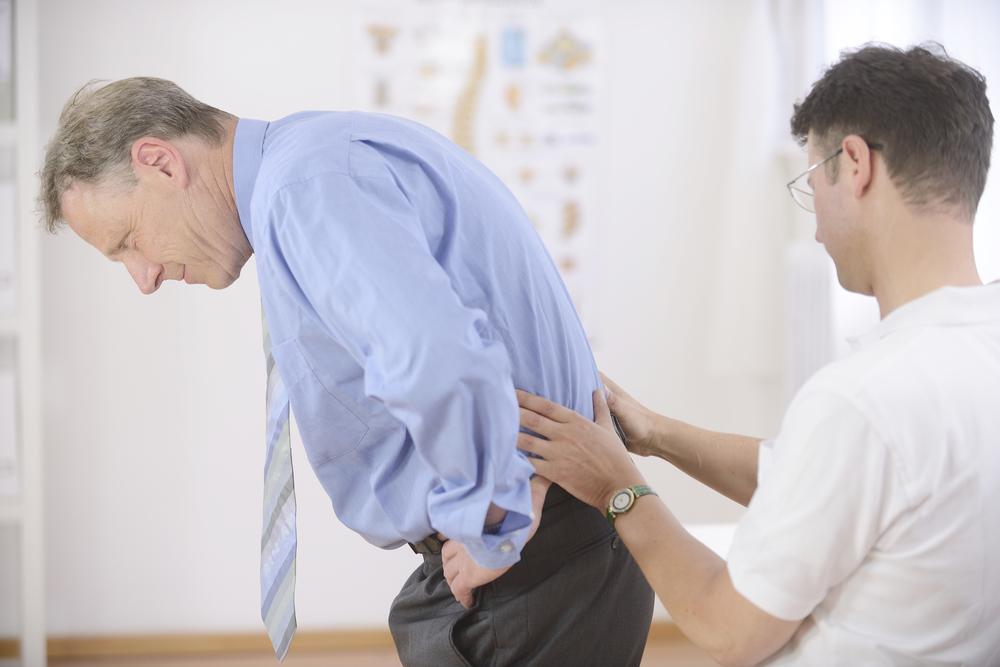
Osteoporosis affects millions of individuals worldwide, especially postmenopausal women and older adults, leading to fragile bones and increased fracture risk. To combat this, many patients rely on prescribed medications aimed at strengthening bones. However, it is vital to uncover the less obvious, potentially dangerous side effects of these drugs. While they may seem effective initially, many of these treatments come with hidden health risks that could outweigh their benefits if not carefully managed.
Many patients tend to follow their healthcare provider’s prescriptions blindly, assuming these medications are entirely safe. Unfortunately, the reality is that osteoporosis drugs, mostly synthetic chemicals, are designed to modify bone metabolism but can sometimes cause adverse effects that compromise overall health. These medications are often marketed as quick solutions that mask the symptoms of osteoporosis without addressing the root causes, such as poor diet, lack of physical activity, or hormonal imbalance.
Understanding how these medications work is essential. Osteoporosis drugs often interfere with natural bone remodeling—a process involving the breakdown of old bone tissue and the formation of new, healthy bone. Many pharmaceuticals inhibit the activity of osteoclasts, the cells responsible for breaking down bone. While this can lead to increased bone density temporarily, it also hampers natural renewal and repair mechanisms. Over time, this disruption may result in bones becoming denser yet more brittle, ironically increasing the risk of fractures, especially in critical weight-bearing bones like the femur.
Despite their intended benefits, no medication is without side effects. Common adverse reactions among osteoporosis patients include gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, abdominal cramps, and bloating, as well as joint pain, vision disturbances, and fatigue. Some users report increased joint discomfort, which can diminish quality of life and physical function. Moreover, long-term use of certain drugs, such as bisphosphonates, has been linked to rare but severe conditions like atypical femoral fractures and osteonecrosis of the jaw, highlighting the importance of cautious, monitored therapy.
One of the ironic dangers lies in the fact that drugs designed to strengthen bones can actually weaken them in the long run. For example, certain bisphosphonates, while making the bones appear denser on scans, may increase bone brittleness, particularly in the femur—a resilient bone typically less prone to fracture. This paradox underscores the necessity for a holistic approach to osteoporosis management, integrating lifestyle, dietary modifications, and natural supplements alongside or instead of pharmaceutical treatments.
Beyond fractures prevention, bone fragility remains a persistent concern even when fractures are avoided. Anxiety about potential injuries often affects patients’ confidence and mobility, reducing their overall quality of life. Additionally, some medications can cause systemic side effects that impact other parts of the body, including vision problems, cardiovascular issues, and gastrointestinal discomfort. This underscores the importance of personalized treatment plans that consider each individual's unique health profile and risks.
While medications have their place, they should be viewed as part of a comprehensive strategy for maintaining bone health. Lifestyle interventions such as a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, weight-bearing and resistance exercises, smoking cessation, and moderation of alcohol intake are fundamental. Natural supplements and alternative therapies might also offer benefits without the adverse effects associated with synthetic drugs.
Healthcare professionals emphasize the importance of regular monitoring and reassessment of osteoporosis treatment plans. Patients should be fully informed about potential side effects, signs to watch for, and the benefits versus risks of long-term medication use. Exploring integrated approaches involving nutrition, physical activity, and possibly natural remedies can help facilitate a more sustainable and safer pathway to stronger bones.
In conclusion, while osteoporosis medications can provide short-term benefits in increasing bone density, their hidden risks warrant careful evaluation and management. Patients must be vigilant and proactive in seeking balanced treatment strategies that prioritize long-term health and bone strength through lifestyle and natural support, alongside medication when necessary. Awareness and early intervention remain the best tools in preventing serious complications and maintaining an active, healthy life well into old age.