Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Viral Infection Symptoms and Prevention
This article provides an in-depth overview of managing viral infection symptoms effectively, emphasizing diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention techniques such as vaccination. It highlights how understanding transmission modes and early intervention can prevent severe health outcomes related to viral diseases, offering valuable insights for healthcare providers and the general public alike.
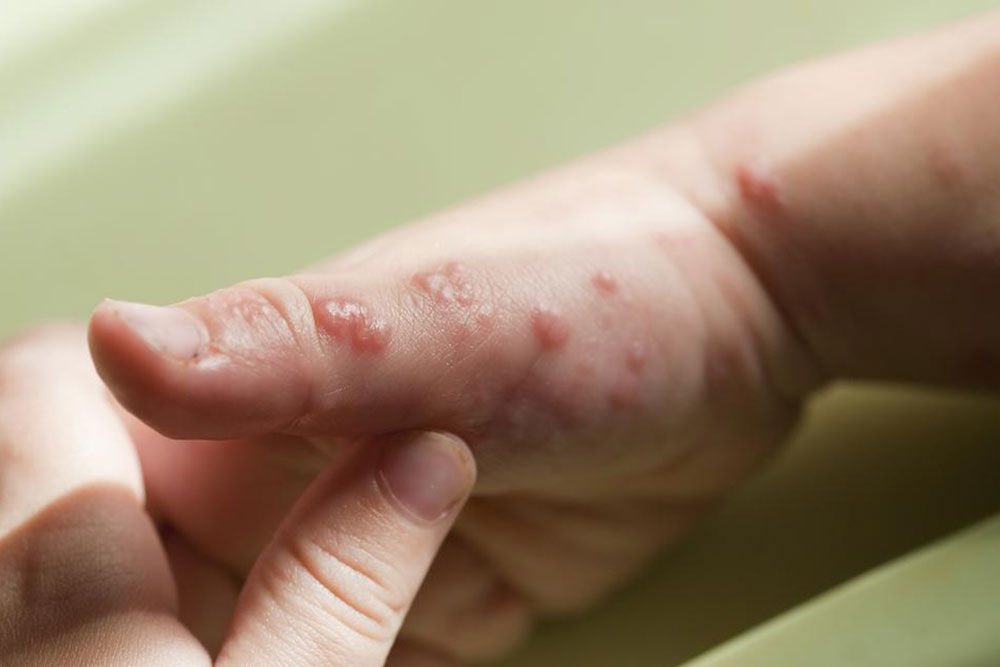
Effective Approaches to Alleviate Viral Disease Symptoms and Prevent Outbreaks
Viral infections are caused by a diverse range of viruses that exist in our environment, each capable of spreading via different pathways depending on the specific virus. Understanding these modes of transmission is crucial for effective prevention and management. Respiratory viruses, such as influenza and common cold viruses, primarily spread through airborne droplets expelled when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Conversely, foodborne viruses like norovirus can transmit through contaminated food and beverages, often resulting from lapses in food hygiene or handling practices.
Some viruses can also transmit through close personal contact, such as kissing, sexual activity, or sharing utensils, entering the body via saliva or mucous membranes. This highlights the importance of practicing good hygiene and safe interactions to limit exposure.
The symptoms caused by viral infections can vary widely, with initial signs frequently including fever, fatigue, muscle aches, and skin rashes. Respiratory symptoms such as coughing, sneezing, and nasal discharge are common, along with gastrointestinal issues like vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. Other common indicators include chills, headaches, and general malaise. In more severe cases, symptoms can escalate to neurological and systemic complications, including personality changes, neck stiffness, excessive drowsiness, urinary or bowel disturbances, dehydration, seizures, back pain, confusion, and even limb paralysis. These serious symptoms require immediate medical attention.
Differentiating between various viral infections based solely on symptoms can be complicated due to their overlap. Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment and better patient outcomes. It is particularly important to seek medical advice promptly when symptoms are severe or persistent, especially in vulnerable groups such as children, older adults, and immunocompromised individuals. Early diagnosis enables targeted intervention and minimizes complications.
Diagnostic procedures encompass a variety of tests:
A comprehensive blood test can identify the presence of specific viruses by detecting viral antigens, antibodies, or genetic material. These tests help confirm the infection type and stage.
Laboratory procedures, including blood cultures, urine or stool analysis, and viral cultures, assist in isolating the virus and determining its strain, which is critical for appropriate management.
For infections impacting the skin or neurological system, sampling affected tissues, cerebrospinal fluid, or other bodily fluids is necessary for precise diagnosis. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing is a powerful technique that amplifies viral DNA or RNA, enabling exact identification of the viral species, which guides effective treatment planning.
When it comes to managing and preventing viral infections, several strategies are highly effective:
Prophylactic vaccination stands out as the most reliable method to prevent specific viral infections. Immunizations prime the immune system to recognize and combat viruses efficiently, reducing the incidence and severity of diseases. Keeping up-to-date with recommended vaccination schedules is vital for individual and community health security.
Antiviral medications are prescribed to mitigate symptoms and control virus replication within the body. While they are important for treatment, they are generally less effective than vaccines for prevention. Antivirals are particularly useful in managing outbreaks and reducing disease severity when administered early.
In addition to medical interventions, supportive care measures such as hydration, rest, and symptom management play a crucial role in recovery. Use of over-the-counter medications like analgesics and antipyretics can alleviate discomfort and reduce fever.
Public health initiatives, including hygiene practices like regular handwashing, using masks in crowded places, and sanitizing surfaces, help limit the spread of viruses. Educating the public about transmission routes and prevention strategies enhances community resilience against outbreaks.
In conclusion, comprehending the nature of viral infections, recognizing symptoms early, obtaining appropriate diagnostic testing, and implementing preventive measures like vaccination are essential components of effective viral infection management. Staying informed and proactive can significantly reduce the health burden posed by these contagious organisms.