Comprehensive Guide to Diabetes Screening and Monitoring: Essential Tests and Their Significance
This comprehensive guide covers essential tests for detecting and monitoring diabetes. It explains various diagnostic methods like the Random Blood Glucose Test, Hemoglobin A1C, Fasting Blood Sugar, and Oral Glucose Tolerance Test. Early detection and continuous monitoring are key to effective management and preventing complications. Learn how these tests work, their importance, and tips for maintaining optimal blood sugar control with professional medical advice. Stay proactive and protect your health with routine screenings tailored to your individual risk factors and lifestyle.
Diabetes has become one of the most prevalent chronic health conditions worldwide, affecting millions of people across different age groups. Early detection and continuous monitoring are critical in preventing the serious complications associated with diabetes, such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney failure, and vision loss. Regular screening not only helps in early diagnosis but also plays a crucial role in managing the condition effectively, improving quality of life, and reducing long-term health costs.
Whether you have a family history of diabetes, are exhibiting symptoms, or are at risk due to lifestyle factors, understanding the various diagnostic tests available can empower you to take proactive steps toward your health. It’s vital to work with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate screening schedule and methods suitable for your individual health profile.
Why Regular Diabetes Testing Is Essential
Consistent monitoring of blood glucose levels can aid in detecting diabetes early, often before symptoms appear. Early diagnosis enables timely intervention, which can delay disease progression and lower the risk of complications. Furthermore, ongoing assessment helps in tailoring treatment plans, adjusting medication doses, and providing lifestyle recommendations.
Regular testing is particularly recommended for individuals with high risk factors, including:
Family history of diabetes
Obesity or overweight status
Sedentary lifestyle
High blood pressure
History of gestational diabetes
Age over 45 years
Key Diabetes Diagnostic Tests
There are several widely used diagnostic tests to assess blood glucose levels. Each of these tests offers unique advantages and is suitable for specific scenarios. Understanding these options can help you and your healthcare provider choose the most effective strategy for prevention, early detection, and ongoing management.
Random Blood Glucose Test
The random blood glucose test involves drawing a blood sample at any time of the day, regardless of when you last ate. This test is quick and convenient, providing immediate insights into your current blood sugar levels. It is frequently used in emergency situations or initial screenings, especially when symptoms such as excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, or unexplained weight loss are present. However, because it reflects blood sugar at a single point in time, it may not always give a comprehensive view of your glycemic control.
Hemoglobin A1C Test
The Hemoglobin A1C test measures the percentage of glucose attached to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Since red blood cells have a lifespan of about three months, this test provides an average of your blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. The A1C test is widely recommended for both diagnosing diabetes and monitoring disease management. It does not require fasting, making it convenient for routine screening. Nevertheless, certain conditions like anemia, hemoglobinopathies, or recent blood transfusions can affect the accuracy of results, so healthcare providers will consider these factors.
Fasting Blood Sugar Test
This standard test requires fasting for at least 8 hours prior to blood sample collection, making it usually scheduled in the morning. During fasting, only water is permitted. The fasting blood sugar test measures your blood glucose after a period of rest from food intake, providing a baseline value critical for diagnosing diabetes and prediabetes. Elevated fasting sugar levels indicate impaired glucose metabolism, serving as an early marker for potential future diabetes development. Proper preparation and timing are essential for reliable results.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
The OGTT is often considered the most comprehensive test for diagnosing diabetes and gestational diabetes. It involves fasting overnight, then consuming a sugary solution containing a specified amount of glucose. Blood samples are taken at intervals—usually at baseline, and then after 30 minutes, 1 hour, 2 hours, and sometimes at 3 hours—to track how efficiently your body processes glucose. This test provides insight into how your body manages sugar and can detect subtle abnormalities in glucose metabolism that other tests might miss. It’s especially useful during pregnancy to identify gestational diabetes, which can pose health risks for both mother and baby if left untreated.
The Importance of Regular Monitoring
Diabetes management is a lifelong process that requires diligent monitoring of blood glucose levels. Regular testing allows patients and healthcare providers to understand how lifestyle, medication, stress, illness, or other factors influence blood sugar control. Maintaining target blood glucose ranges is key to preventing complications and promoting overall well-being.
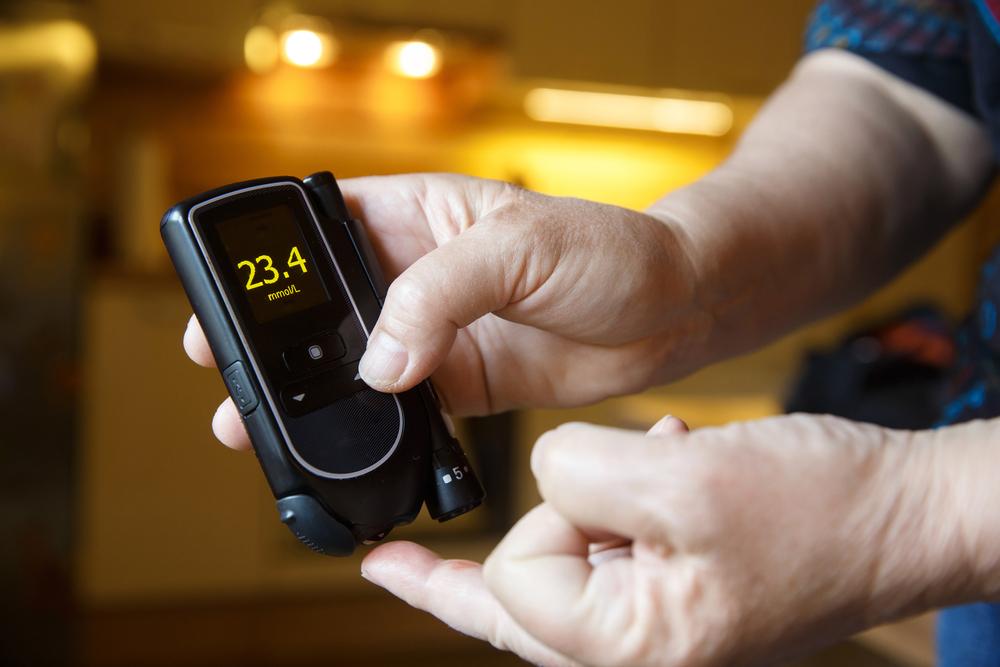
Aside from laboratory testing, individuals are often encouraged to use personal blood glucose meters for daily monitoring. This immediate feedback enables timely adjustments in diet, activity, or medication, fostering better control over the disease.
Conclusion: Take Charge of Your Health
If you fall into the high-risk category or are experiencing symptoms of abnormal blood sugar levels, consult your healthcare provider promptly. They can recommend appropriate tests based on your health history and lifestyle. Early detection through comprehensive screening tests is your first step toward effective management and long-term health preservation. Remember, proactive health habits, combined with regular testing, can significantly improve your quality of life and reduce the burden of diabetes and its complications.