Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Lowering Your Cholesterol Levels for Better Heart Health
This comprehensive guide provides essential insights into managing cholesterol levels effectively through diet, lifestyle changes, and medical options. It emphasizes the importance of regular testing and proactive health measures to prevent heart disease, with practical tips for maintaining optimal cholesterol profiles and improving cardiovascular health for a healthier future.

Understanding the Importance of Cholesterol Control
Cholesterol management plays a pivotal role in maintaining cardiovascular health. Understanding how to effectively regulate your cholesterol levels can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease, strokes, and other related health issues. This extensive guide explores the vital aspects of cholesterol, including the causes of high cholesterol, how to monitor levels through testing, dietary and lifestyle strategies to maintain healthy numbers, and medical interventions when necessary. With proper knowledge and proactive steps, you can take charge of your heart health and improve your overall quality of life.
High blood cholesterol is one of the leading contributors to the development of cardiovascular disease. Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance naturally produced by the liver and also obtained through certain foods. While cholesterol is essential for building cell membranes and producing hormones, excess levels can lead to fatty deposits in arteries, known as atherosclerosis. Over time, these deposits can narrow the arteries, restrict blood flow, and increase the likelihood of serious health events such as heart attacks and strokes. Recognizing this, health authorities worldwide emphasize the importance of regular cholesterol screenings and adopting healthy lifestyle habits.
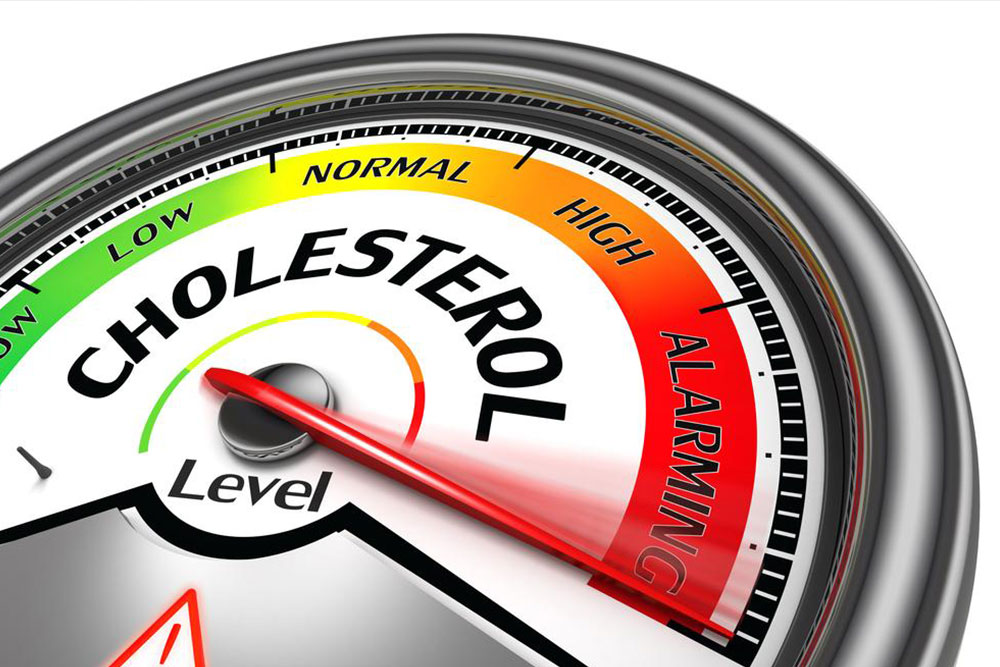
Early detection through routine testing can help identify abnormal cholesterol levels before they cause significant damage. Medical professionals typically measure four key indicators of cholesterol in the blood:
Total Cholesterol – The sum of all cholesterol particles in your blood. Ideal levels are below 200 mg/dl. Levels above this increase the likelihood of cardiovascular disease.
LDL Cholesterol (Low-Density Lipoprotein) – Often called the 'bad' cholesterol because it contributes to plaque buildup in arteries. Optimal levels are under 100 mg/dl; levels exceeding 190 mg/dl are considered very high and pose substantial risks.
HDL Cholesterol (High-Density Lipoprotein) – Known as the 'good' cholesterol because it helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream. Levels above 60 mg/dl are protective, while below 40 mg/dl for men and below 50 mg/dl for women increase the risk of heart disease.
Triglycerides – A type of fat stored in fat cells. Elevated triglycerides (over 150 mg/dl) are associated with increased risk of artery disease, especially when combined with other abnormal lipid levels.
Effective Dietary Practices for Managing Cholesterol
Diet plays a critical role in controlling cholesterol levels. Making informed food choices can significantly influence your lipid profile and overall heart health. Here are some dietary tips endorsed by health professionals:
Incorporate Soluble Fiber-Rich Foods: Foods such as oats, barley, beans, lentils, and fruits like strawberries and apples are rich in soluble fiber. This type of fiber binds cholesterol in the digestive system, helping to remove it from the body and lowering LDL cholesterol levels.
Choose Whole Grains: Opt for whole-grain bread, brown rice, quinoa, and barley instead of refined grains. Whole grains contain more fiber and nutrients that support cardiovascular health.
Eat Heart-Healthy Fats: Use healthy fats like extra virgin olive oil, avocados, and nuts. These sources contain monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats that help improve HDL levels while reducing LDL cholesterol.
Limit Saturated and Trans Fats: Reduce intake of red meats, full-fat dairy products, and processed foods that contain trans fats. These fats can raise LDL cholesterol and lower HDL cholesterol, increasing cardiovascular risk.
Include Legumes and Pulses: Beans, lentils, and peas are excellent sources of soluble fiber and help control blood cholesterol. They also promote satiety, making them a valuable part of a heart-healthy diet.
Lifestyle Modifications for Better Heart Health
Beyond diet, lifestyle choices dramatically influence cholesterol levels and heart health:
Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, per week can elevate HDL cholesterol and help lower LDL and triglycerides.
Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Smoking damages blood vessels and decreases HDL cholesterol, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Moderate alcohol consumption might have some heart benefits, but excessive drinking can raise triglycerides and blood pressure.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Losing excess weight, especially around the abdomen, can significantly improve your cholesterol profile and reduce cardiovascular risk.
Manage Stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact cholesterol levels and overall heart health. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can help manage stress effectively.
Medical Interventions and When to Seek Help
While lifestyle and dietary changes are fundamental, some individuals may require medications to control high cholesterol. Doctors may prescribe statins, ezetimibe, or PCSK9 inhibitors in cases where lifestyle modifications do not sufficiently lower cholesterol levels or if there is a strong family history of heart disease. Regular check-ups and blood tests are essential to monitor progress and adjust treatments accordingly.
It is vital to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized plan that fits your health profile and lifestyle. In addition to medication, follow-up care includes maintaining healthy habits, monitoring for side effects, and adjusting treatment as needed.
In conclusion, managing cholesterol effectively requires a comprehensive approach that combines balanced nutrition, physical activity, avoiding harmful habits, and adhering to medical advice. These strategies can significantly lower your risk of cardiovascular disease, improve your health, and enhance your quality of life. Take proactive steps today to safeguard your heart’s future.