Comprehensive Guide to Whooping Cough (Pertussis): Causes, Symptoms, and Preventive Measures
This comprehensive guide covers the causes, symptoms, and prevention of pertussis, also known as whooping cough. It highlights the importance of vaccination, early diagnosis, and public health measures to prevent the spread of this highly contagious respiratory disease. The article provides detailed insights into transmission routes, disease progression, vulnerable populations, and current global trends, emphasizing proactive health strategies to combat pertussis effectively.

Comprehensive Guide to Whooping Cough (Pertussis): Causes, Symptoms, and Preventive Measures
Whooping cough, medically termed pertussis, is a highly contagious respiratory disease that primarily affects the upper respiratory tract. Despite being well-known and preventable through vaccination, pertussis continues to pose health risks worldwide, especially in communities with low immunization rates. Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms early, and adopting effective prevention strategies are crucial to controlling the spread of this disease.
**Pertussis: An Overview**
Pertussis is caused by a pathogenic bacteria called Bordetella pertussis. This bacteria infects the mucous membranes of the throat and nose, leading to inflammation and severe coughing fits. The bacteria are highly transmissible, making pertussis a significant public health concern, particularly among infants, unvaccinated children, and vulnerable adults.
**Transmission and Infection Routes**
Bacterial Infection Transmission: The primary mode of transmission is through respiratory droplets expelled when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Close contact, such as living in the same household, attending daycare, or being in crowded areas, increases the likelihood of infection.
Exposure to infected individuals or epidemic zones significantly raises the risk of contracting pertussis, especially if preventive measures are not taken.
**Role of Immunization in Prevention**
The most effective way to prevent pertussis is through vaccination. The Tdap vaccine, which combines protection against tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis, is recommended for children, teens, and adults to maintain herd immunity and reduce disease outbreaks.
**Early Symptoms and Disease Progression**
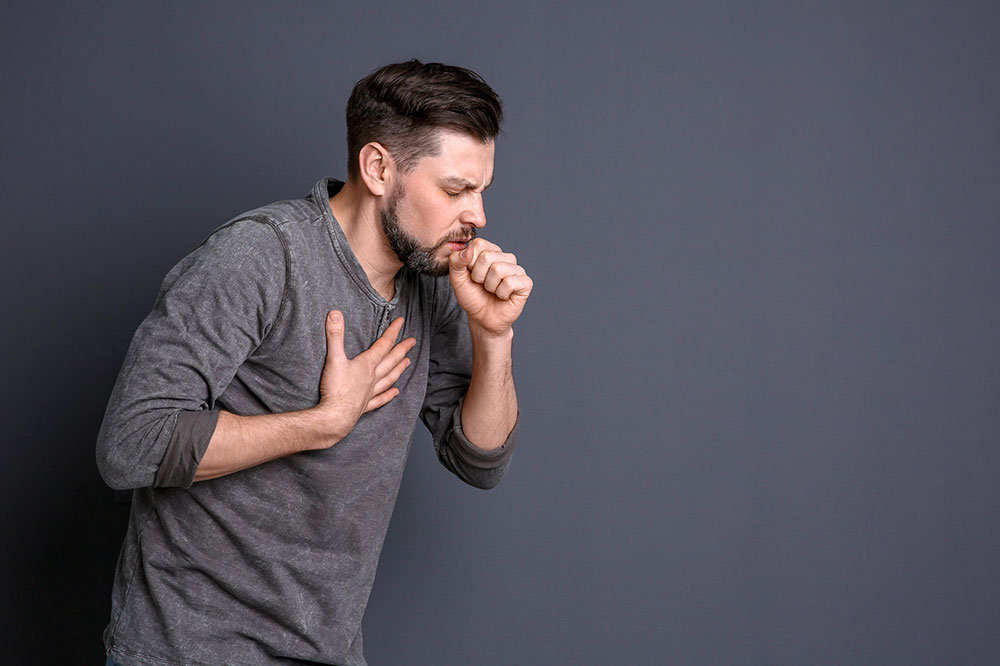
Initially, pertussis symptoms resemble a mild cold: rhinitis, low-grade fever, and a mild cough. As the disease progresses, symptoms intensify, especially in infants and young children. They may experience apnea, a dangerous pause in breathing, which requires immediate medical attention.
Later stages are characterized by severe fatigue, vomiting, and distinctive coughing episodes. These episodes include a series of rapid, forceful coughs followed by a high-pitched inspiratory sound known as the ‘whoop,’ which gives the disease its common name. Such intense coughing can last for weeks, significantly impacting quality of life.
**Complications and Vulnerable Populations**
Infants under one year old are most vulnerable to severe complications, including pneumonia, seizures, and brain damage. Unvaccinated individuals and those with compromised immune systems are also at higher risk for severe disease and hospitalization.
**Diagnosis and Treatment**
Diagnosis is typically confirmed through a combination of clinical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests such as PCR or bacterial cultures. Antibiotics like azithromycin or erythromycin can help reduce bacterial load if administered early, thereby limiting disease severity and transmission.
**Prevention Strategies and Public Health Measures**
Ensuring timely vaccination schedules are followed and booster doses are administered.
Promoting awareness about the importance of vaccination and hygiene practices, such as covering coughs and frequent handwashing.
Isolating infected individuals to prevent further spread during outbreaks.
**Global Perspective and Current Trends**
Although widespread immunization dramatically decreased pertussis prevalence in many regions, outbreaks still occur, often due to waning immunity or vaccine hesitancy. Ongoing surveillance, booster immunizations, and public health initiatives remain vital to controlling pertussis globally.
In summary, pertussis remains a preventable yet potentially severe respiratory illness. Early recognition, vaccination, and public health interventions are crucial to protecting vulnerable populations and reducing disease transmission worldwide.