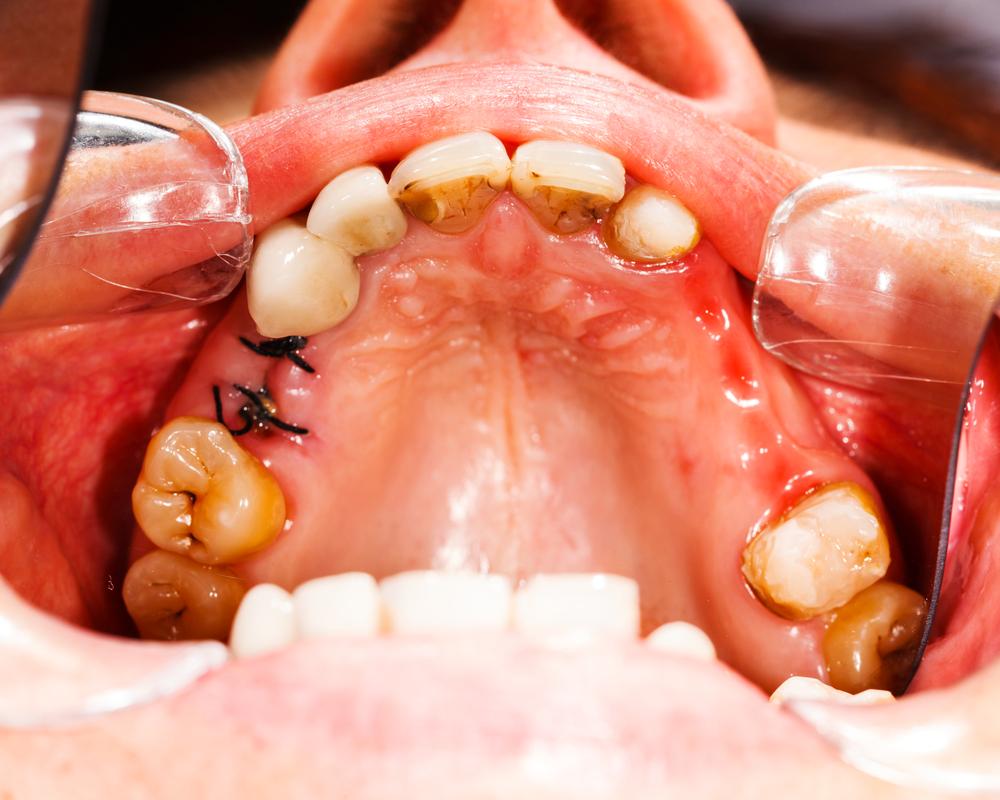
Comprehensive Guide to Tooth Decay: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment
Understanding tooth decay is essential for maintaining oral health. This comprehensive guide covers causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment options for cavities. Regular dental care and good hygiene practices are crucial in preventing cavities, saving you from pain and costly procedures. Learn how early signs can be identified and how simple daily habits can protect your teeth. By following expert advice, you can keep your teeth healthy and avoid the complications associated with untreated decay, ensuring a confident smile for life.
Are you noticing a dark spot or a small hole forming on your tooth and unsure about what to do next? Don’t be alarmed—dental cavities or tooth decay are very common conditions that can often be effectively managed with timely action. Understanding the fundamentals of tooth decay, recognizing early signs, and knowing how to prevent it are crucial steps towards maintaining excellent oral health.
Understanding Tooth Decay and Its Causes
Tooth decay, medically referred to as dental caries, is a progressive deterioration of the tooth structure caused mainly by acids produced by bacteria living in your mouth. These bacteria feed on the sugars and carbohydrates you consume, leading to the production of acids that attack the enamel—the hard, protective outer layer of your teeth. Over time, this acid erosion results in small holes or cavities forming in the enamel.
This process is cumulative and influenced by several factors, including poor oral hygiene, frequent snacking on sugary foods, and inadequate fluoride exposure. If left untreated, these cavities can grow larger and penetrate deeper into the tooth, affecting the dentin and pulp. This can lead to severe pain, infections, and eventual tooth loss, impacting your overall health and quality of life.
Recognizing the Signs of Tooth Decay
Early detection often occurs during routine dental visits: Dentists can identify initial signs of decay before symptoms manifest, through X-rays and visual examinations.
Visible symptoms include: Black, brown, or white spots on the teeth, small holes, or rough areas that feel different when touched with your tongue.
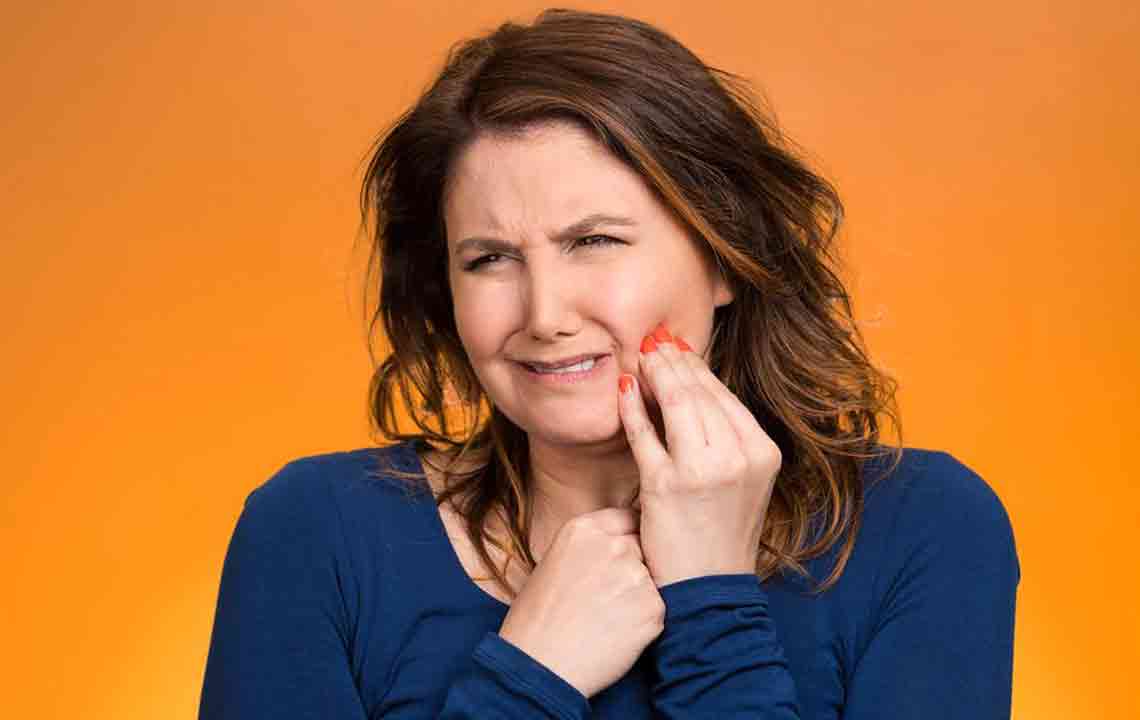
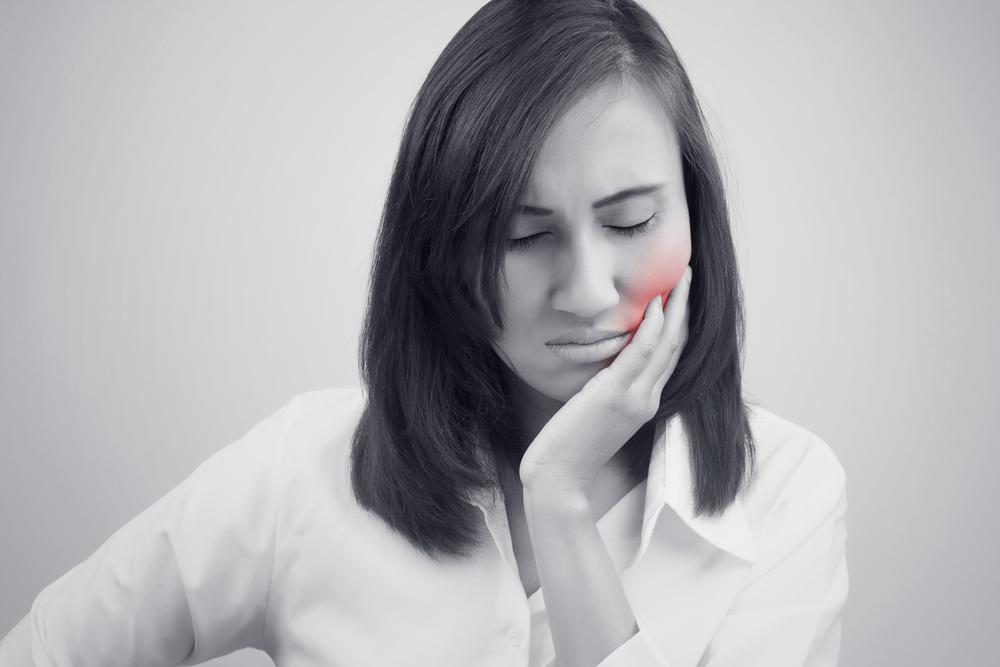
Persistent toothache or sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks is a common indicator of underlying decay that needs immediate attention.
Changes in tooth appearance: Uneven surfaces, discoloration, or a rough texture on the affected tooth may be visible signs of decay progression.
Effective Treatment Options for Tooth Decay
Addressing cavities promptly can save your tooth and prevent further complications. The choice of treatment depends largely on the extent of the decay:
Dental Fillings: For small to moderate cavities, the decayed tissue is removed, and the resulting cavity is filled with durable materials like amalgam, composite resin, porcelain, or gold. Dental fillings restore the tooth's function and prevent further decay.
Crowns: When decay is extensive and weakens the tooth significantly, a crown, or cap, may be placed over the tooth after removing the decayed portions. Crowns provide structural support and restore the tooth’s shape and function.
Root Canal Therapy: If decay has reached the pulp or nerve of the tooth, a root canal procedure becomes necessary. This involves removing infected tissue from the root canal, disinfecting, and sealing it, often followed by placing a crown for reinforcement.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Tooth Decay
Preventing cavities is easier than treating them. Essential oral hygiene practices, combined with lifestyle considerations, can significantly reduce your risk:
Brush thoroughly twice a day: Use fluoride toothpaste to remove plaque and strengthen enamel.
Floss daily: Clean between teeth to eliminate plaque and food particles missed by brushing.
Limit sugary snacks and drinks: Reduce frequent consumption of candies, sodas, and other sugary foods, which fuel bacterial acid production.
Eat a balanced diet: Incorporate foods rich in vitamins and minerals, especially calcium and phosphate, to support tooth remineralization.
Schedule regular dental checkups: Visit your dentist at least twice a year for screenings, cleanings, and early intervention if necessary.
Use fluoride products and mouth rinses: Fluoride strengthens enamel and protects against acid attacks.
Consider dental sealants: Sealants are protective coatings applied to the chewing surfaces of back teeth, creating a barrier against decay.
By integrating these habits into your daily routine, you can effectively safeguard your teeth against cavities and maintain a healthy, bright smile for years to come. Remember, early detection and intervention are key to avoiding more invasive treatments and preserving your oral health.