Comprehensive Guide to Celiac Disease: Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Management Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores celiac disease, highlighting its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and the importance of a gluten-free diet. Early detection and proper management are essential to prevent complications and maintain overall health, making awareness crucial for those affected. Advances in research offer hope for improved treatment options in the future.

Comprehensive Guide to Celiac Disease: Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Management Strategies
Celiac disease is a complex autoimmune disorder that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It is characterized by an adverse immune response to gluten, a protein found primarily in wheat, rye, barley, and their derivatives. This condition leads to damage to the lining of the small intestine, specifically the villi—tiny finger-like projections responsible for nutrient absorption. When these villi become damaged or flattened, the body’s ability to absorb essential nutrients diminishes, resulting in malnutrition and a range of associated health problems.
Understanding the intricacies of celiac disease involves exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management. Despite extensive research, the exact triggers of celiac disease remain somewhat elusive, but it is known to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and possibly infectious factors. Individuals with a family history of celiac disease or other autoimmune disorders are at higher risk, emphasizing the genetic component. High gluten consumption can also exacerbate the condition, making dietary management a cornerstone of treatment.
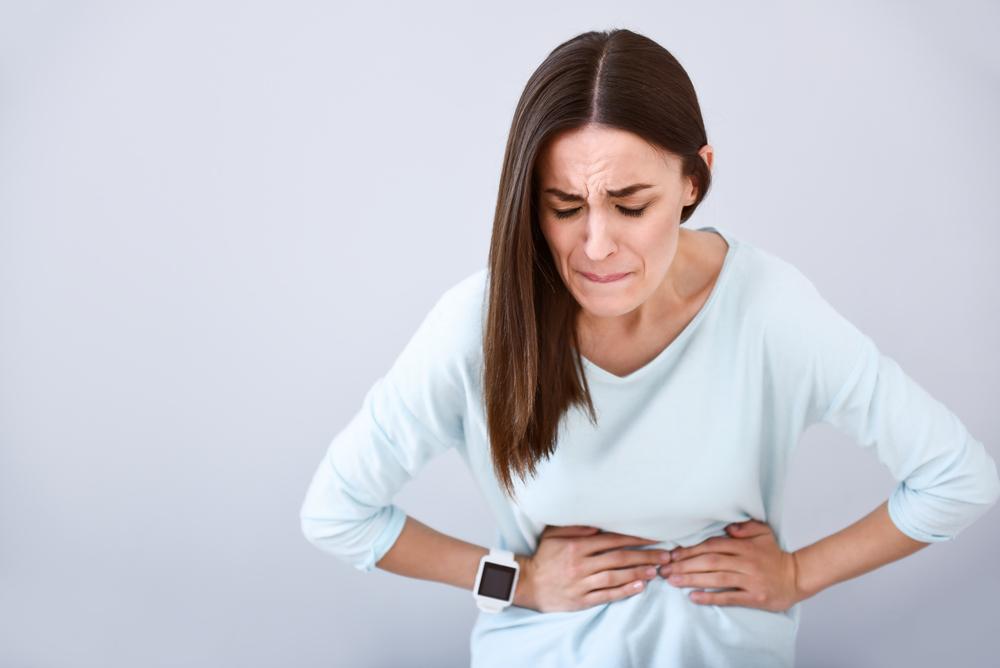
Furthermore, celiac disease can be triggered or worsened by various factors such as certain surgical procedures, infections, pregnancy, or stressful life events. Recognizing the symptoms early is crucial for diagnosis and management. Symptoms may manifest differently across age groups, with children experiencing growth delays, diarrhea, and abdominal distension, while adults may report chronic fatigue, anemia, skin rashes (notably dermatitis herpetiformis), joint pain, or osteoporosis.
The diagnosis of celiac disease involves a combination of serological blood tests and a small intestine biopsy conducted by a healthcare professional. Once diagnosed, the most effective management strategy is adhering to a strict gluten-free diet. Eliminating gluten allows the intestinal mucosa to heal, alleviating symptoms and preventing long-term complications. Additionally, nutritional supplementation and regular follow-up are essential to address deficiencies and monitor recovery.
Living with celiac disease requires ongoing education about gluten sources, careful reading of food labels, and awareness of cross-contamination risks. Emerging therapies aim to modify immune responses or develop enzyme treatments to break down gluten, but currently, diet remains the primary treatment. Support from dietitians, patient support groups, and medical professionals plays a vital role in managing this lifelong condition effectively.
In summary, celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder triggered by gluten intake, causing intestinal damage and diverse symptoms. Early diagnosis and strict dietary management are key to maintaining health and improving quality of life. As research continues, new treatments and diagnostic tools are anticipated, providing hope for better management options in the future.
Gluten-free diet
Celiac disease symptoms
Autoimmune disorder
Nutrition management