A Comprehensive Guide to Managing Uric Acid Levels: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Reduction Strategies
Explore a detailed guide on uric acid, including its causes, symptoms, and proven strategies to effectively manage and reduce uric acid levels. Learn about dietary adjustments, hydration tips, and lifestyle changes to prevent gout and kidney stones. This comprehensive article offers insights into maintaining optimal uric acid for overall health and wellness.
A Comprehensive Guide to Managing Uric Acid Levels: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Reduction Strategies
Uric acid is a naturally occurring chemical compound in the human body, playing a vital role in various metabolic processes. Composed of carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, and oxygen, uric acid’s molecular structure includes six carbon atoms, four hydrogen atoms, four nitrogen atoms, and three oxygen atoms. It is primarily excreted through urine, maintaining a balanced internal environment. However, when the production of uric acid exceeds the body’s ability to eliminate it efficiently, health issues may arise. This article explores the causes of elevated uric acid, symptoms associated with abnormal levels, and effective strategies to manage and reduce uric acid for optimal health.
Uric acid originates from the breakdown of purines—substances found naturally in many foods. Normally, the body maintains uric acid levels through a delicate balance between production and excretion. However, when this equilibrium is disrupted, uric acid can accumulate in the bloodstream—a condition known as hyperuricemia. Elevated uric acid levels are linked to various health problems including kidney stones and gout, an inflammatory joint condition that causes sudden and severe pain. Understanding the dietary and physiological factors that influence uric acid levels is crucial for effective management.
Understanding the Causes of Elevated Uric Acid
Multiple factors contribute to high uric acid levels, including dietary habits, genetic predisposition, obesity, dehydration, certain medications, and underlying health conditions such as metabolic syndrome and kidney dysfunction. Foods rich in purines—like fatty fish (mackerel, sardines), organ meats (liver, kidneys), dried beans, shellfish, and alcoholic beverages—are primary dietary sources of uric acid precursors. Lifestyle choices such as excessive alcohol consumption, high sugar intake, and a sedentary lifestyle can exacerbate the problem, leading to increased production of uric acid.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Abnormal Uric Acid Levels
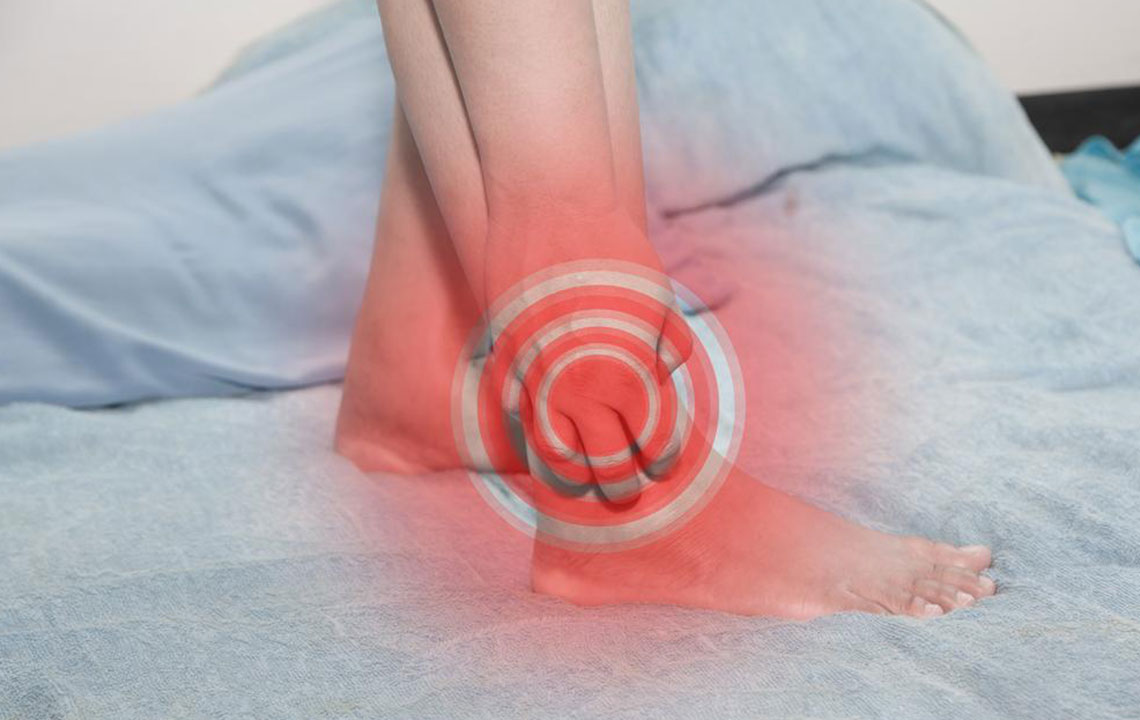
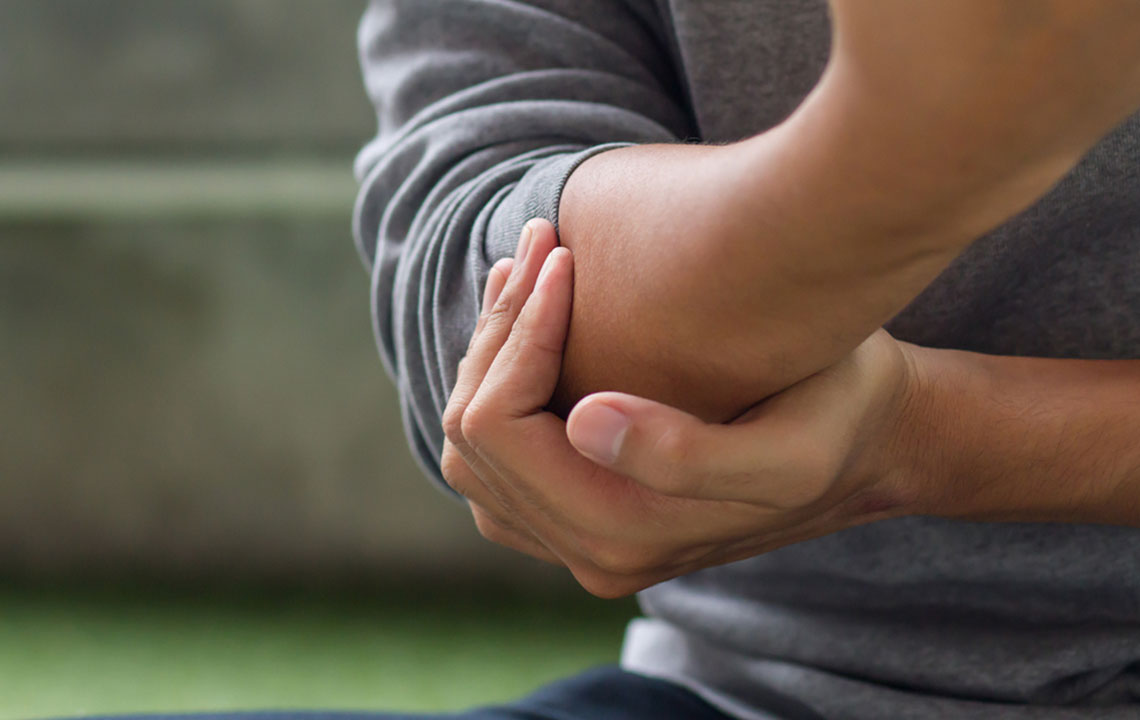
High uric acid levels often produce distinctive symptoms, with gout being the most well-known condition associated with hyperuricemia. Gout manifests as sudden and intense joint pain, swelling, redness, and warmth, typically affecting the big toe but also impacting other joints like the ankles, knees, wrists, and elbows. Recurrent gout attacks can lead to joint damage if untreated. Additionally, elevated uric acid can lead to the formation of kidney stones, which cause severe pain during urination, hematuria, and risk of kidney infections. Conversely, low uric acid levels, or hypouricemia, are less common and often less noticeable, but may be associated with symptoms such as weakness, bone pain, dehydration, and in certain cases, neurological issues.
Effective Strategies to Reduce Uric Acid Levels
Maintaining optimal uric acid levels—generally between 3.5 to 7.2 mg/dL—is essential to prevent associated health risks like gout and kidney stones. Here are comprehensive methods to control and lower elevated uric acid levels:
Prioritize Hydration: Adequate water intake is vital for diluting uric acid in the bloodstream and enhancing its excretion via the kidneys. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day, complemented by beverages such as coconut water, lemon water, and green tea, helps prevent crystal formation and promotes detoxification.
Adopt a Uric Acid-Friendly Diet: Limit foods high in purines like red meats, organ meats, certain seafood (anchovies, sardines), mushrooms, and lentils. Instead, increase consumption of vitamin C-rich foods such as citrus fruits, bell peppers, strawberries, and gooseberries, which aid uric acid excretion. Incorporate more whole grains, fresh vegetables, and fiber-rich fruits to foster better digestion and promote uric acid elimination. Avoid alcohol—especially beer—and limit caffeine intake, as these can hinder uric acid clearance.
Reduce Sugar Intake and Use Natural Remedies: Cutting back on sugary foods and beverages decreases the risk of gout attacks. Natural remedies like apple cider vinegar, which contains acetic acid, can help balance blood pH, reduce joint inflammation, and support circulation. Mixing a small amount of apple cider vinegar with water and consuming it daily may aid in lowering uric acid levels naturally.
Maintain a Healthy Weight and Active Lifestyle: Weight management through balanced diet and regular exercise reduces uric acid production. Excess body weight is a significant risk factor for hyperuricemia. Engage in moderate physical activities such as walking, swimming, or yoga to improve circulation, promote metabolic health, and support uric acid metabolism.
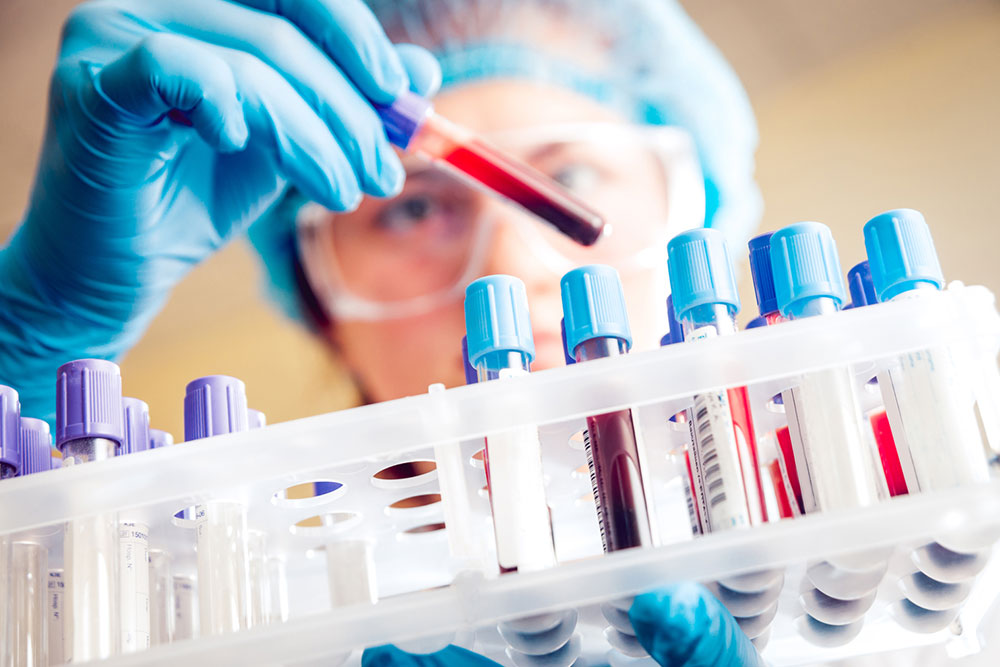
Medical Treatment and Lifestyle Adjustments: For persistent hyperuricemia, physicians may prescribe medications like allopurinol or febuxostat to regulate uric acid production. Regular check-ups and blood tests are essential to monitor levels. Combining medication with lifestyle modifications offers the best approach to preventing gout crises and kidney issues.
Managing uric acid levels through dietary modifications, hydration, and lifestyle changes is crucial for preventing related health complications. Long-term adherence to these strategies can lead to improved quality of life and overall health stability. If you experience recurrent joint pain or other symptoms associated with high uric acid, consult a healthcare professional for personalized evaluation and treatment plans.