Comprehensive Guide to Melanoma Causes and Symptoms: Protect Your Skin Today
This comprehensive guide explores the causes and symptoms of melanoma, emphasizing the importance of early detection and prevention. Learn how UV exposure, skin type, genetics, and lifestyle influence melanoma risk. Recognizing warning signs like unusual moles, persistent wounds, and color changes can save lives. Regular skin checks and sun safety are vital for reducing melanoma risks and ensuring timely medical intervention for better prognosis.
Understanding the Common Causes and Recognizing Melanoma Symptoms
Skin cancer is a diverse group of diseases characterized by abnormal growths of skin cells, with melanoma standing out as the most aggressive and deadly type. Melanoma originates from melanocytes, the specialized pigment-producing cells located in the skin's outer layer, responsible for skin coloration. Despite extensive research, the precise cause of melanoma remains complex and multifactorial, involving a combination of genetic predisposition, environmental exposures, and immune system factors. Recognizing these contributors and understanding the symptoms are essential steps in early detection and effective treatment.
Major Causes of Melanoma
Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation Exposure: Prolonged and intense exposure to ultraviolet rays from the sun is the primary risk factor for melanoma. UV radiation damages the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations that can initiate cancer. People who frequently sunbathe, use tanning beds, or spend a lot of time outdoors without protection are at increased risk. History of sunburns, especially blistering ones in childhood or adolescence, significantly elevates the risk of developing melanoma later in life.
Skin Type and Genetic Factors: Individuals with fair skin, light hair, and blue or green eyes possess less melanin, which offers some protection against UV damage. These skin types are more susceptible to melanoma. Genetics also play a crucial role; a family history of melanoma or other skin cancers increases an individual's risk. Specific gene mutations, such as those affecting the CDKN2A gene, can predispose individuals to melanoma.
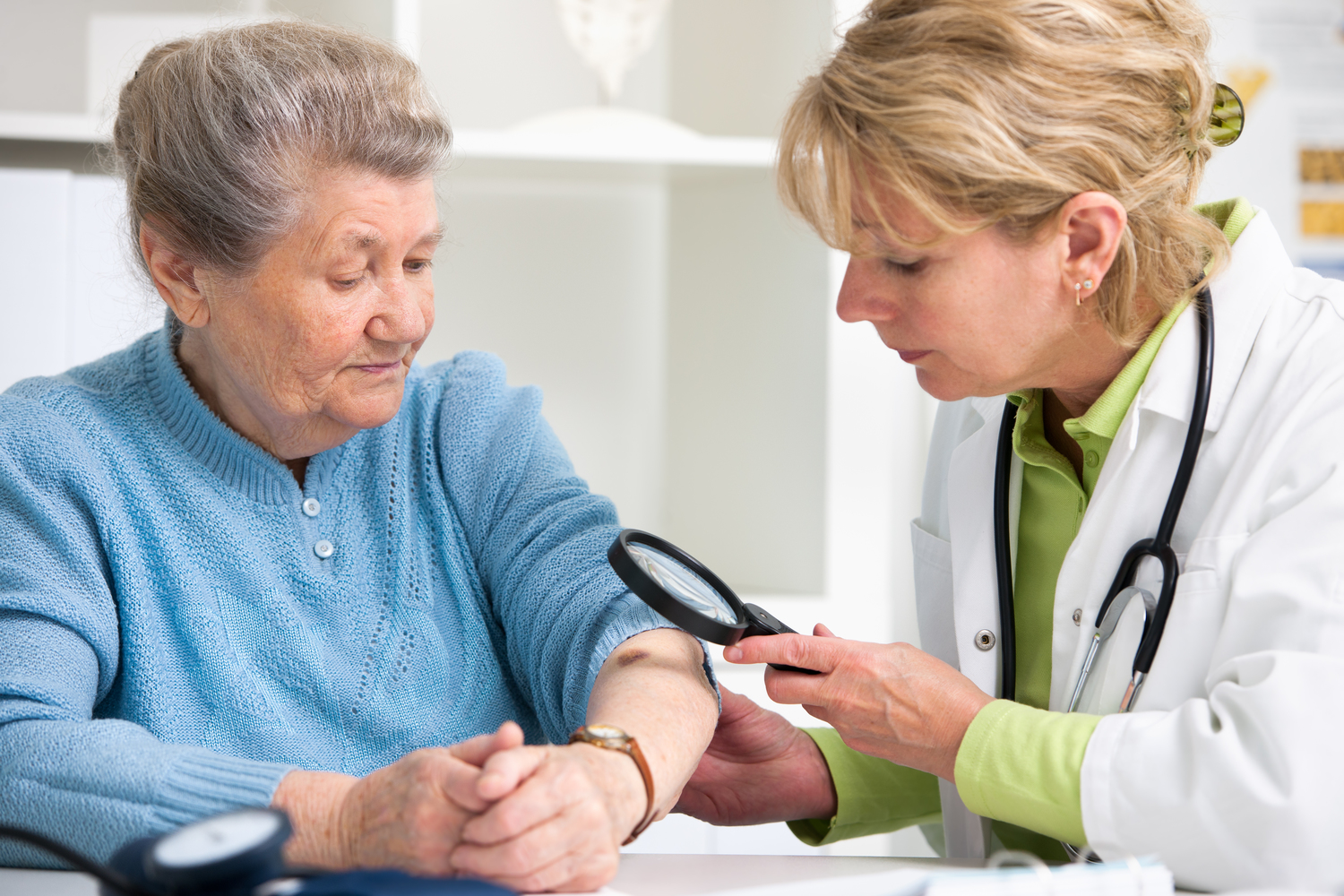
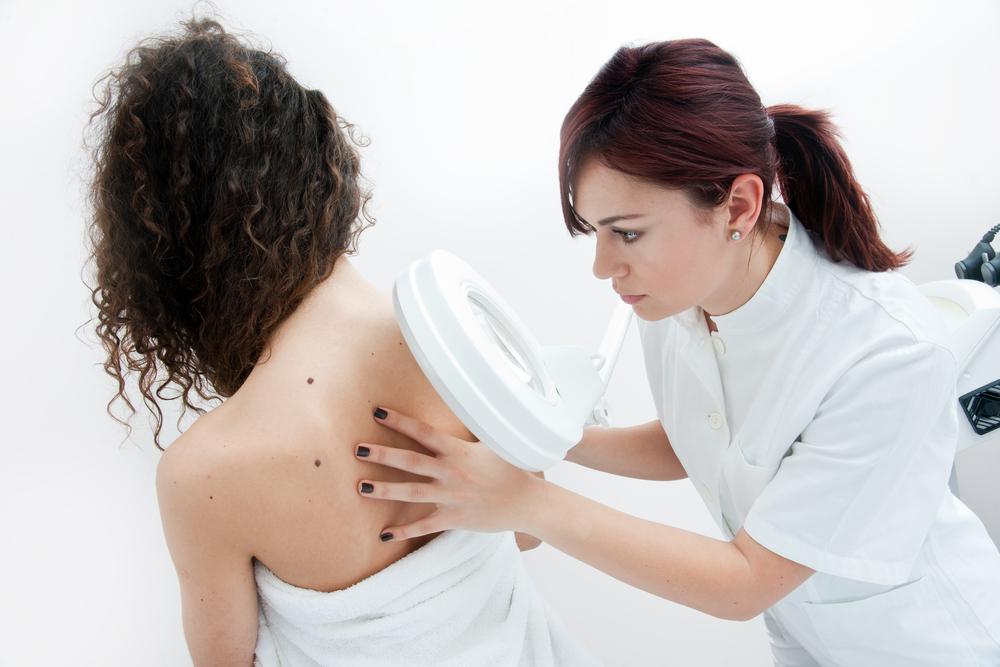
Presence of Moles and Skin Spots: People with numerous moles, atypical or dysplastic nevi (large, irregular moles), or peculiar skin lesions are at greater risk. The ABCDEs of mole examination (Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variation, Diameter over 6mm, and Evolution) help identify moles that warrant medical evaluation.
Immune System Suppression: Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as organ transplant recipients or those on immunosuppressive therapy, face higher risks of melanoma. A weakened immune response hampers the body's ability to detect and destroy abnormal skin cells.
Environmental Factors and Lifestyle
Environmental UV Levels: Living in regions with high UV index levels, such as areas near the equator or at high altitudes, increases exposure to damaging rays. Additionally, reflective surfaces like snow, sand, and water can intensify UV exposure.
Protective Measures and Behavioral Factors: Lack of sun protection, such as sunscreen, protective clothing, or limiting sun exposure during peak hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.), contributes to higher melanoma risk. Indoor tanning, especially during adolescence and young adulthood, significantly raises the chances of developing skin cancer later in life.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Melanoma
Early detection of melanoma can be life-saving. The symptoms may vary, but certain warning signs should prompt immediate medical consultation. Regular self-examinations of the skin are crucial for identifying potential issues early on.
Unusual Moles or Skin Spots: Changes in existing moles, such as rapid growth, irregular borders, uneven coloration, or bleeding, warrant attention. Newly appearing spots that look different from surrounding skin should also be examined.
Persistent Wounds or Sores: Skin wounds that do not heal within four weeks or heal temporarily only to reopen should be checked by a healthcare professional.
Color Changes and Irregular Borders: Melanomas often have uneven color, including shades of black, brown, red, white, or blue. Borders may be ragged, notched, or blurred.
Redness, Tenderness, or Swelling: Persistent redness or tender skin around a mole or lesion can be a sign of melanoma invasion.
Bleeding or Oozing: Any lesion that bleeds or oozes without injury needs urgent evaluation.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Melanoma can spread rapidly if not detected early, leading to advanced stages that are more difficult to treat. Early diagnosis significantly improves the prognosis, with high survival rates when melanoma is identified and removed promptly. Regular skin checks, both by professionals and self-examinations, are vital in catching suspicious changes early.
Anyone noticing unusual skin changes should consult a dermatologist or healthcare provider for proper assessment, which may include biopsy and staging procedures. Prevention strategies, including sun safety behaviors and regular skin monitoring, are essential parts of reducing melanoma risk.
In conclusion, understanding the causes and recognizing the early signs of melanoma are crucial for effective prevention and treatment. By protecting yourself from excessive sun exposure, monitoring your skin for abnormalities, and seeking timely medical advice, you can significantly reduce the risk of melanoma and improve outcomes in case of diagnosis.