Comprehensive Guide to Blood Disorders: Causes, Symptoms, and Risk Factors
This comprehensive article explores the various blood disorders, including their causes, symptoms, and risk factors. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and tailored treatments to manage conditions like anemia, thrombocytopenia, and blood overproduction disorders. Learn how genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors contribute to blood health issues, and discover key signs to watch for. Understanding blood disorders is crucial for effective intervention, reducing complications, and improving quality of life through proper medical care and management strategies.

A Complete Guide to Blood Disorders: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Risk Factors
Blood disorders are a wide range of medical conditions that interfere with the normal functioning of blood components, which include red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, plasma, and other cellular elements. These conditions can significantly impact the body’s ability to circulate blood effectively, leading to a variety of health complications. Blood disorders may reduce the number of vital blood cells, impair nutrient transport, or affect blood clotting mechanisms. They are often categorized based on whether they cause a decrease (deficiency) or an increase (overproduction) of specific blood elements. Understanding these conditions requires awareness of their types, symptoms, causes, and risk factors.
In cases such as anemia, the body does not produce enough red blood cells or hemoglobin, resulting in insufficient oxygen delivery to tissues. Symptoms such as persistent fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, and pale skin are common indicators. Thrombocytopenia, characterized by low platelet count, leads to easy bruising, bleeding gums, and prolonged bleeding after injuries. Leukopenia involves a reduced white blood cell count, which diminishes the body’s ability to fight infections, causing recurrent illnesses and infections.
On the other hand, conditions like erythrocytosis (or polycythemia), leukocytosis, and thrombocythemia involve an overproduction of cells, resulting in blood thickening, increased risk of clot formation, headaches, redness of the skin, and other circulation-related problems. These abnormalities not only compromise blood flow but also escalate the risk of blood clots, strokes, or heart attacks.
Common physical signs associated with various blood disorders include clotting issues, redness and swelling in the legs indicating potential deep vein thrombosis, skin rashes such as petechiae (small skin hemorrhages), enlarged lymph nodes, pallor, and unusual cravings for non-food items, known as Pica. Recognizing these signs early can prompt timely medical intervention and management.
Numerous factors contribute to the development of blood disorders. Genetic predispositions are significant, especially in inherited conditions like sickle cell disease or hemophilia. Age is another crucial factor, with certain disorders becoming more prevalent in older adults due to cumulative cellular damage or age-related changes in blood production. Chronic liver or kidney diseases can disrupt blood cell synthesis, leading to deficiency or overproduction. Poor nutrition, particularly deficiencies in iron, vitamin B12, or folic acid, can cause anemia, while exposure to toxins and chemicals impair blood cell formation.
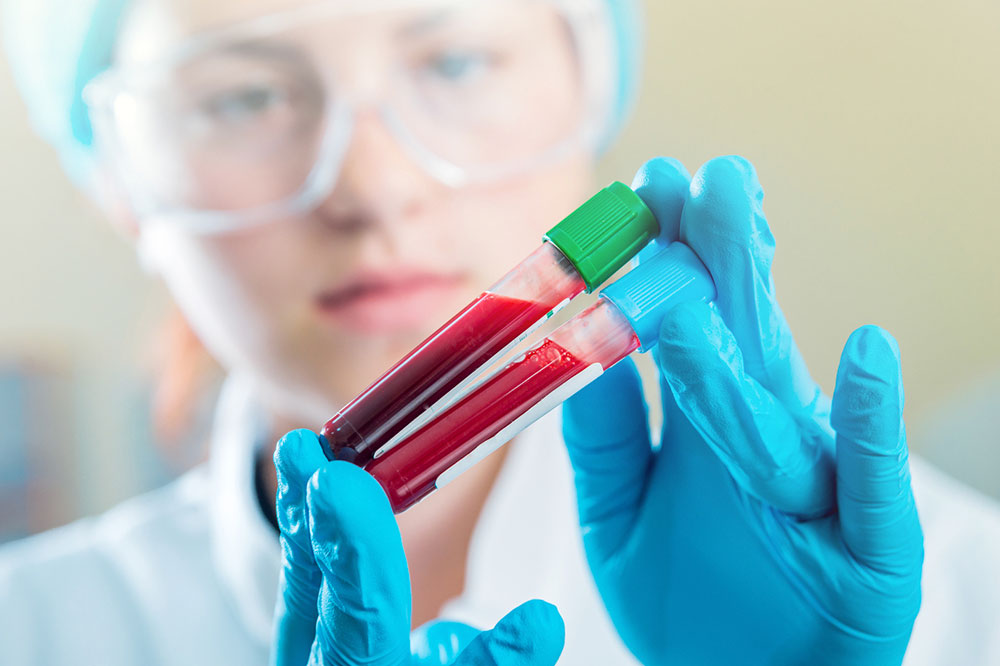
Life events such as pregnancy, trauma, surgeries, or prolonged hospitalizations can also influence the risk of developing blood disorders. Moreover, lifestyle factors like smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug use can damage blood components or interfere with blood production processes. Recognizing the cause behind a blood disorder is essential for effective treatment and management. Diagnostic evaluations typically include blood tests like complete blood count (CBC), bone marrow biopsy, and specialized assays to determine the type and severity of the disorder.
Early diagnosis and tailored treatment plans are vital in managing blood disorders. Treatments may involve medication, blood transfusions, lifestyle modifications, or procedures like chemotherapy or stem cell transplants, depending on the specific condition. A comprehensive understanding of blood disorders helps in better management and improving patients’ quality of life, reducing the risk of severe complications such as stroke, organ damage, or bleeding episodes.