Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Stomach Discomfort and Its Underlying Causes
Stomach discomfort can signal various health issues, from indigestion to severe conditions like gallbladder disease. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and when to seek medical help is essential for effective management. This comprehensive guide covers common abdominal pain causes, diagnostics, and treatment options to promote better digestive health and prevent complications.

Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Stomach Discomfort and Its Underlying Causes
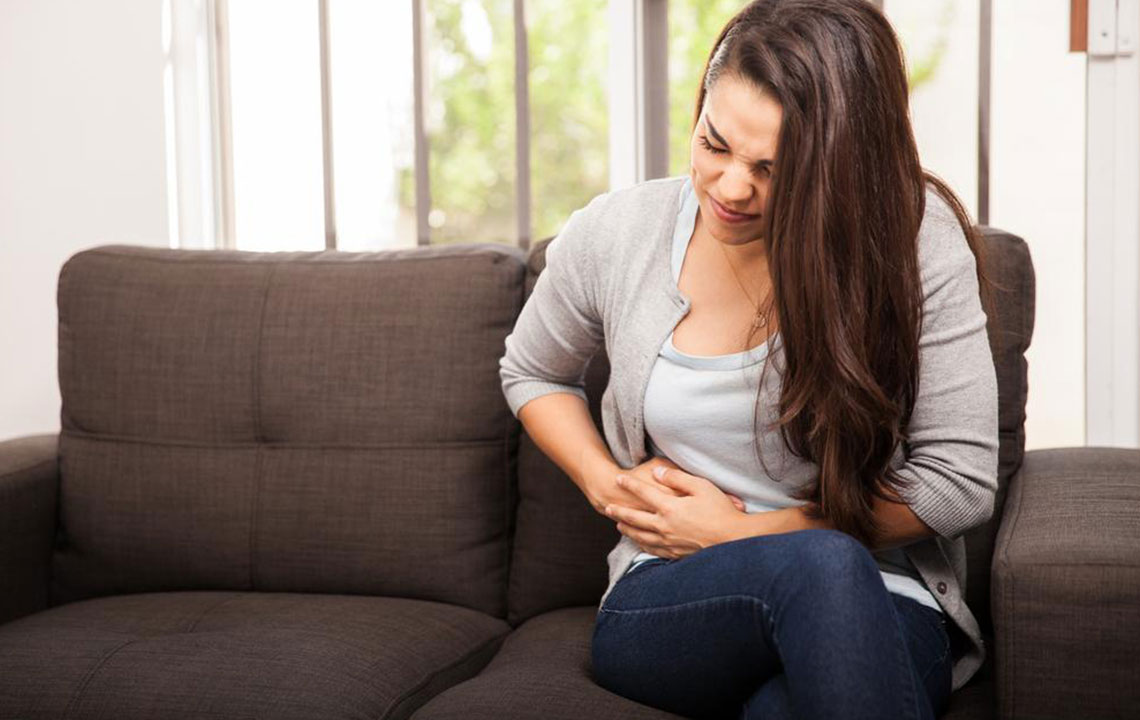
Experiencing stomach discomfort is a common health concern that can significantly impact daily life, causing discomfort not only in the abdominal region but sometimes radiating to the chest and pelvis as well. The intensity and nature of this discomfort can vary widely, ranging from mild dull aches to sharp, excruciating pains. These symptoms often serve as signals of underlying health issues, some of which may require urgent medical intervention. Understanding the various causes of stomach pain is crucial for effective management and treatment, helping individuals seek timely care and prevent complications.
The Significance of Pain Location in Diagnosis
Identifying where the pain occurs in the abdomen is vital for diagnosing the root cause. Common causes of general stomach pain include indigestion, food poisoning, diarrhea, constipation, and excessive gas. Overeating can also cause sudden and intense abdominal discomfort, highlighting the importance of moderation in meals. Rather than consuming large portions at once, adopting smaller, more frequent meals can help prevent indigestion and reduce discomfort. Such dietary adjustments not only promote digestive health but also lessen the likelihood of pain associated with overeating.Pain in the Upper Abdomen and Its Implications
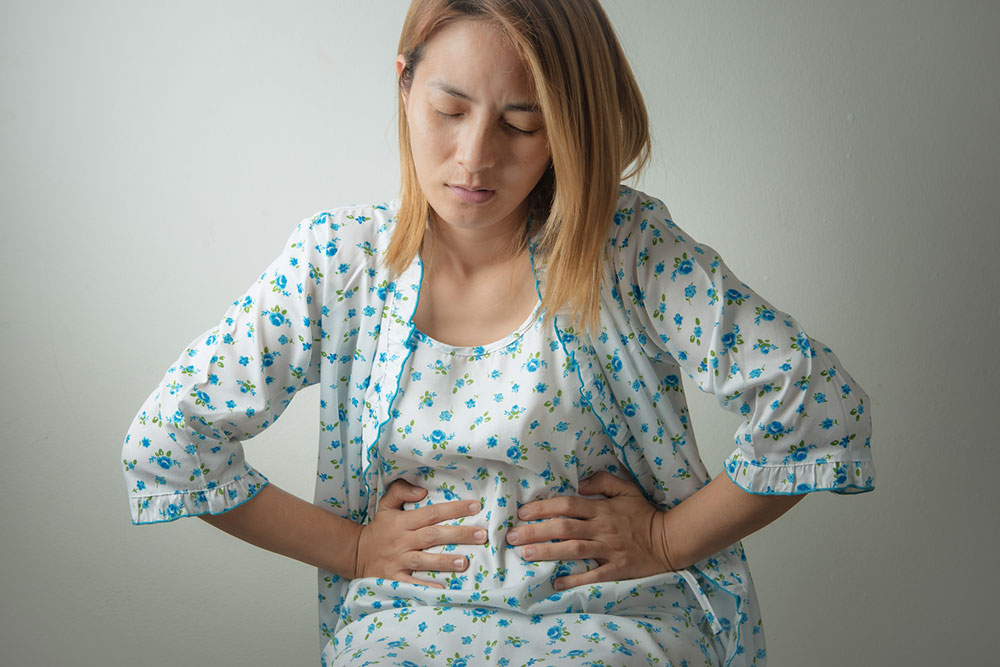
Pain localized in the upper abdomen may indicate serious health problems requiring immediate medical attention. Conditions such as gallbladder inflammation, pancreatitis, liver issues, or even heart-related problems can manifest as upper abdominal pain. Rapid onset or severe pain in this area should never be ignored, and prompt medical evaluation is essential to determine the underlying cause. Diagnostic tests such as ultrasound, CT scans, or blood work may be necessary for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.The recurring discomfort in the upper stomach could also be symptomatic of gallbladder disease, issues in the upper small intestine, or pancreatic disorders. Recognizing the precise location and nature of pain helps healthcare providers narrow down potential causes and initiate appropriate interventions.
Lower and Middle Abdomen Pain: Possible Causes and Associated Conditions
Discomfort around the navel, especially if sudden or sharp, might suggest appendicitis or infections of the small intestine. Pain in the lower and middle regions of the abdomen could point to bowel or colon problems, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), diverticulitis, or inflammatory conditions. For women, reproductive health issues like urinary tract infections (UTIs) or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) are common causes of abdominal pain. Recognizing other accompanying symptoms like bloating, nausea, or changes in bowel habits can assist in accurate diagnosis and prompt treatment.Sudden or sharp pains
Bloating and distention
Gastroenteritis symptoms
Acid reflux and heartburn
Top Causes of Stomach Pain
Several infectious and non-infectious factors contribute to stomach discomfort. Infections caused by viruses, bacteria, or parasites are among the primary culprits, often leading to symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Lifestyle factors such as dietary changes or excessive alcohol consumption can also trigger stomach pain. Chronic inflammatory conditions like ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease further aggravate discomfort and require ongoing management. Viral infections, menstrual cramps, and kidney-related issues are additional contributors to abdominal pain. Recognizing these factors helps in early diagnosis and effective treatment.Common Medical Conditions Leading to Abdominal Pain
Gastroenteritis: This is a prevalent infection of the stomach and intestines, caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Symptoms often include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, cramping, and dehydration. Severe cases may require hospitalization or surgical intervention, and persistent symptoms beyond two days warrant medical attention. Gastroenteritis can sometimes progress to more severe conditions, like inflammatory bowel disease, if untreated.
Indigestion (Dyspepsia): Usually caused by bacteria interfering with digestion in the small intestine, indigestion leads to trapped gases, bloating, pressure, and upper abdominal pain. It is often aggravated by unhealthy eating habits and stress. Managing diet and lifestyle changes can alleviate symptoms.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A chronic functional disorder of the intestines, IBS causes persistent, often cramping or stabbing pain, bloating, nausea, and irregular bowel movements. Stress management, dietary modifications, and medication are common treatments.
Acid Reflux and GERD: When stomach acids escape into the esophagus, they cause a burning sensation known as heartburn, often accompanied by chest pain, bloating, and regurgitation. Lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgical interventions are effective in managing GERD.
Menstrual Cramps and Endometriosis: Women may experience lower abdominal pain, bloating, and cramping during menstruation. Endometriosis, a condition where uterine tissue grows outside the uterus, can lead to chronic pain, inflammation, and discomfort.
Urinary Tract and Bladder Infections: Bacterial infections like E. coli can cause cystitis, leading to lower abdominal pain, urgency, and painful urination. Foul-smelling urine and fever may also be present, requiring antibiotics for treatment.
Recognizing these causes and their associated symptoms is crucial for seeking timely medical care and effectively managing stomach discomfort.