Comprehensive Guide to Scalp Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Strategies
This comprehensive article explores scalp psoriasis, detailing its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and the most effective treatment options. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and ongoing management to control flare-ups and improve quality of life. Learn how topical therapies, lifestyle changes, and advanced treatments help manage this common skin disorder. Suitable for individuals seeking in-depth understanding and effective strategies to combat scalp psoriasis and its symptoms.
Comprehensive Guide to Scalp Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Strategies
Scalp psoriasis is a prevalent chronic inflammatory skin disorder that predominantly affects the scalp but can sometimes extend to adjacent areas such as the forehead, behind the ears, the sides of the nose, and the back of the neck. Despite its visibility and discomfort, it is often misunderstood, leading to confusion about its causes and management options. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the intricacies of scalp psoriasis, including its underlying causes, manifestation symptoms, diagnosis procedures, and the most effective treatment approaches currently available.
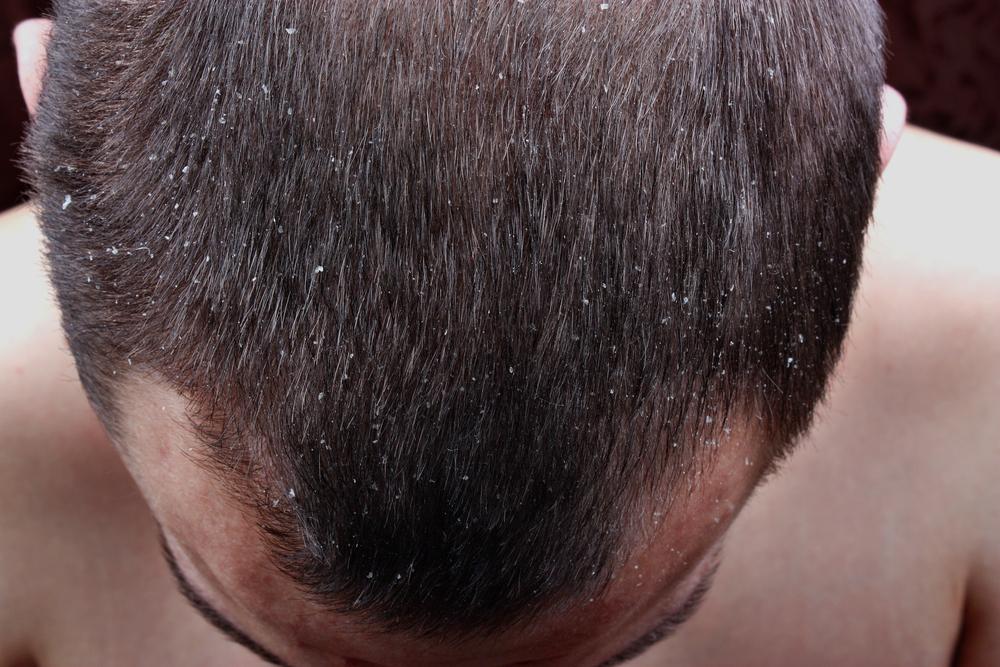
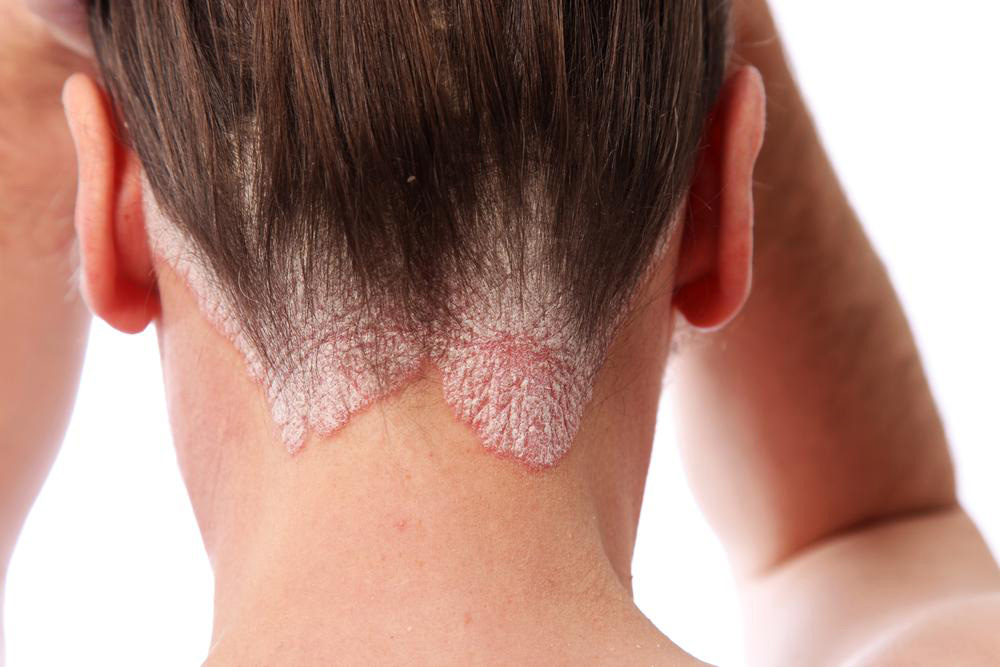
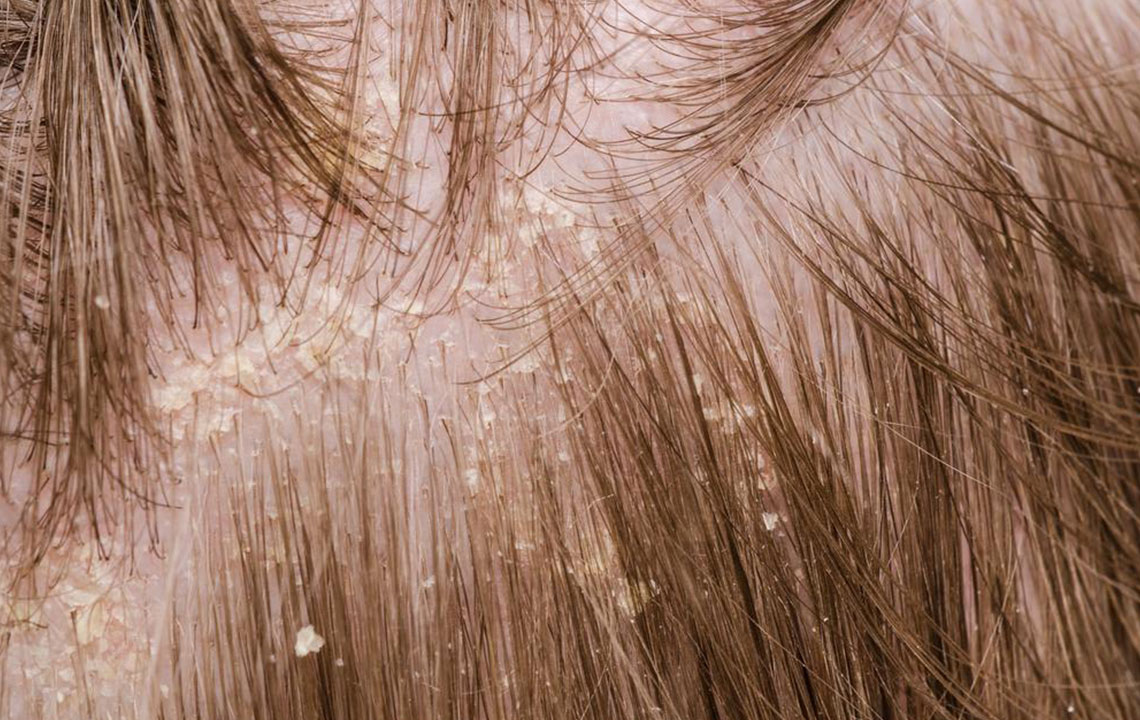
Understanding the nature of scalp psoriasis is essential for effective management. This condition manifests through the appearance of abnormal skin patches that are red, raised, and covered with silvery-white scales. These patches are not only cosmetically distressing but can also cause significant discomfort, including itching, soreness, and in some cases, hair loss. The severity of symptoms varies from person to person, ranging from mild scaling with minimal irritation to severe, widespread plaques that can impair quality of life.
It is important to note that scalp psoriasis is an immune-mediated condition. It results from a disruption within the immune system, which causes skin cells to regenerate at an abnormally rapid pace. Instead of the normal 28-30 days, skin cells in affected areas turn over within just a few days, leading to the buildup of thick, scaly plaques. Unlike contagious skin diseases, scalp psoriasis is not spread through contact, making it a non-infectious disorder that patients cannot pass to others.
The role of genetics is significant, as individuals with a family history of psoriasis are at a higher risk of developing the condition. Studies suggest that about 30% of psoriasis patients report at least one relative with the disease. This hereditary predisposition is thought to involve multiple genes that influence immune responses and skin cell production.
The most common form of scalp psoriasis is chronic plaque psoriasis, characterized by well-defined, raised, and silvery-scaled patches. These can extend beyond the scalp to involve the elbows, knees, and other parts of the body. Other variants include guttate psoriasis, which presents as small droplet-shaped spots, and pustular psoriasis, which involves white pustules surrounded by inflamed skin. The distribution and severity of psoriasis vary widely among individuals.
Symptoms are diverse but generally include:
Mild to severe scaling and flaking of the scalp
Persistent dryness and itching
Soreness or irritation
Hair thinning or temporary hair loss, often due to scratching or skin inflammation
Formation of bumpy patches or plaques
Appearance of dandruff flakes that are more pronounced than regular dandruff
While many associate scalp psoriasis directly with hair loss, most medical evidence indicates that the condition itself does not cause permanent hair loss. However, excessive scratching and inflammation can damage hair follicles, potentially leading to hair thinning over time. Additionally, psychological stress induced by visible scalp lesions can contribute to temporary hair shedding, further complicating the patient’s emotional well-being.
Early diagnosis is critical for effective management. Dermatologists typically perform a clinical examination complemented by a skin biopsy if needed. A small skin sample examined microscopically can rule out other skin conditions, such as seborrheic dermatitis or fungal infections, which may mimic psoriasis symptoms.
Fundamental to psoriasis management are topical treatments, which aim to reduce inflammation, normalize cell growth, and alleviate symptoms. The most widely used topical therapies include:
**Corticosteroids:** Powerful anti-inflammatory medications that help reduce redness and scaling. Available in various forms such as lotions, creams, foams, or sprays.
**Vitamin D Analogs:** Calcipotriene and calcitriol help slow skin cell growth and are often used alongside corticosteroids.
**Coal Tar Shampoos:** Known for their anti-inflammatory and anti-scaling properties, coal tar shampoos are a traditional and effective treatment for scalp psoriasis.
**Retinoids:** Derivatives of vitamin A that help normalize skin cell production but may cause skin irritation.
**Antimalarial Agents (like Anthralin):** Used to reduce plaques, particularly in resistant cases.
Because topical medications can sometimes be insufficient or challenging to use over large areas, dermatologists may recommend adjunct therapies such as medicated solutions, foams, lotions, or sprays for targeted application, making treatment more manageable and effective.
For more persistent or severe cases, systemic treatments or phototherapy might be considered. Systemic therapies include biologic agents that target immune pathways, while phototherapy involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet light under medical supervision. These options are typically reserved for patients who do not respond to topical therapies or have extensive disease.
It is crucial to understand that, currently, there is no cure for psoriasis, including scalp psoriasis. The goal of treatment is symptom control, reduction of flare-ups, and prolonged remission periods. Patients must adhere to their prescribed routines and maintain regular consultations with their dermatologists to optimize disease management.
Alongside medical treatments, lifestyle modifications such as stress management, avoiding skin trauma, and maintaining scalp hydration can significantly improve outcomes. Also, using gentle shampoos and avoiding harsh chemical treatments can help minimize flare-ups. Recognizing early signs of exacerbation ensures timely intervention and helps prevent the progression of the disease.
In conclusion, scalp psoriasis is a manageable chronic condition that affects millions worldwide. While it can cause discomfort and cosmetic concerns, understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options empowers patients to take control of their health. With ongoing medical advancements and consistent care, many individuals experience significant symptom relief and improved quality of life.