Comprehensive Guide to Heart and Pulse Rates: Key to Heart Health and Fitness Optimization
This comprehensive guide explains the importance of understanding normal heart and pulse rates, how to measure them correctly, and how to interpret the results for improved heart health. Whether you're an athlete or managing health issues, monitoring your heart rate is essential for maintaining cardiovascular wellness and early detection of potential problems.

Comprehensive Guide to Heart and Pulse Rates: Key to Heart Health and Fitness Optimization
The rate at which your heart beats, often measured through your pulse, provides crucial insights into your cardiovascular health. Your pulse rate indicates how many times your heart contracts during a minute, serving as an accessible indicator of your heart’s efficiency and overall health condition. Understanding normal ranges of heart and pulse rates is vital for early detection of potential health issues and for tracking fitness progress. This comprehensive guide delves into what constitutes a normal heart rate, how to measure it accurately, and how to interpret your readings to maintain optimal heart health.
Understanding the Basics of Heart Rate and Pulse
Your heart rate is essentially the number of heartbeats per minute. It varies according to factors such as age, fitness level, activity, and overall health status. The pulse, on the other hand, is the palpable throbbing of an artery caused by the heartbeat, often measured at specific locations like the wrist or neck. Knowing what is considered a normal pulse rate can help you assess your cardiovascular health and identify early signs of potential health problems.
For most adults, a normal resting heart rate ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute (bpm). Athletes and highly fit individuals often have resting heart rates below 60 bpm, sometimes even as low as 40 bpm, indicating efficient heart function and good cardiovascular conditioning. Conversely, higher resting heart rates may be linked to stress, dehydration, illness, or underlying cardiovascular issues. In children, the normal range tends to be higher due to faster metabolism and growth processes.
Maintaining a healthy heart rate is fundamental for overall well-being. Errors in heart rate—either too high or too low—can signal health problems that may require medical attention. Regular monitoring of your pulse and understanding the normal ranges can help you detect anomalies early. This proactive approach is especially important for individuals with existing health conditions or those engaged in regular physical activity aiming to optimize cardiovascular efficiency.
What Constitutes a Normal Heart Rate?
A normal resting heart rate falls between 60 and 100 bpm for most adults. Rates consistently exceeding 100 bpm or falling below 60 bpm while at rest warrant further evaluation by a healthcare professional. For example, a persistently high resting heart rate could signify stress, dehydration, or underlying cardiovascular problems, whereas a very low rate might indicate an efficient heart function, common among athletes. Regular health check-ups and heart rate monitoring are essential for maintaining a healthy cardiovascular profile.
Lower resting heart rates are generally associated with better cardiovascular health. Athletes, for instance, often have resting heart rates around 40 bpm, indicating their hearts are both strong and efficient. Children usually have higher resting heart rates—typically between 70 and 100 bpm—due to rapid growth and higher metabolic rates. Maintaining your heart rate within a healthy range is critical; too high or too low can expose you to health risks.
How to Measure Your Heart and Pulse Rate Correctly
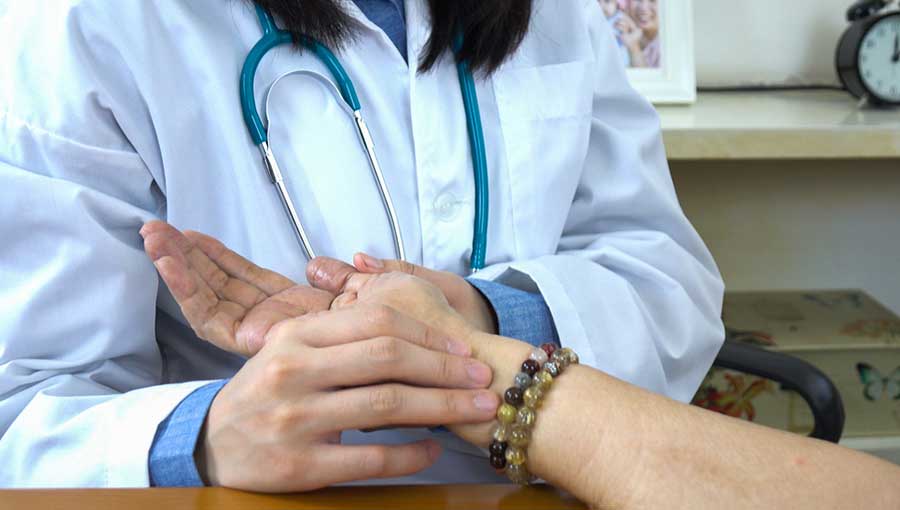
Monitoring your pulse at home is straightforward, practical, and invaluable for keeping track of your cardiovascular health. If you are on medication, regularly checking your pulse can provide important insights to your healthcare provider about your treatment's effectiveness. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to measure your pulse accurately:
Locate your pulse points: The most common sites are your wrist (radial artery) and neck (carotid artery). To find your wrist pulse, place your index and middle fingers on the underside of your wrist, below your thumb. For neck, gently press on either side of your windpipe.
Apply gentle pressure until you feel your heartbeat clearly.
Count the number of beats you feel in 15 seconds. Use a stopwatch or count aloud.
Multiply the total count by 4 to determine your beats per minute.
It’s recommended to take multiple readings at different times to get an accurate assessment of your heart health. If your pulse rate consistently deviates from the normal range or if you experience symptoms such as dizziness, chest pain, or irregular heartbeat, seek medical advice immediately.
Understanding and monitoring your heart and pulse rates empower you to take charge of your cardiovascular health. Whether you are an athlete aiming to optimize your fitness or someone managing a health condition, maintaining a normal heart rate is a cornerstone of good health. By staying informed about your heart’s activity, identifying abnormal signals early, and consulting healthcare professionals when necessary, you can ensure better heart health and overall well-being.