Comprehensive Dietary Strategies for Managing ADHD: Foods to Incorporate and Avoid
Discover effective dietary strategies for managing ADHD by incorporating nutrient-rich foods like proteins, herbs, and vitamins, while avoiding processed sugars and artificial additives. This comprehensive guide highlights key foods to include and avoid to support focus, reduce hyperactivity, and improve mental clarity, providing practical tips for healthier living with ADHD.

Effective Dietary Approaches to ADHD Management: Essential Foods to Embrace and Reconsider
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental condition that impacts how the brain functions, leading to challenges with maintaining attention, controlling impulses, and staying focused. It is a prevalent condition, affecting about 11% of children and around 5% of adults globally each year. The manifestation of ADHD symptoms often includes hyperactivity, inattentiveness, difficulty in concentrating, and impulsive behaviors. While medication and behavioral therapy are common treatments, increasing evidence suggests that diet and nutrition play a crucial role in managing symptoms effectively. Making informed dietary choices—emphasizing beneficial foods and reducing intake of foods that exacerbate symptoms—can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with ADHD. This comprehensive guide explores the key foods to include and avoid, supported by nutritional science and clinical findings.
Implementing specific dietary strategies can help in stabilizing mood, improving concentration, and reducing hyperactivity. Here are the essential foods to prioritize:
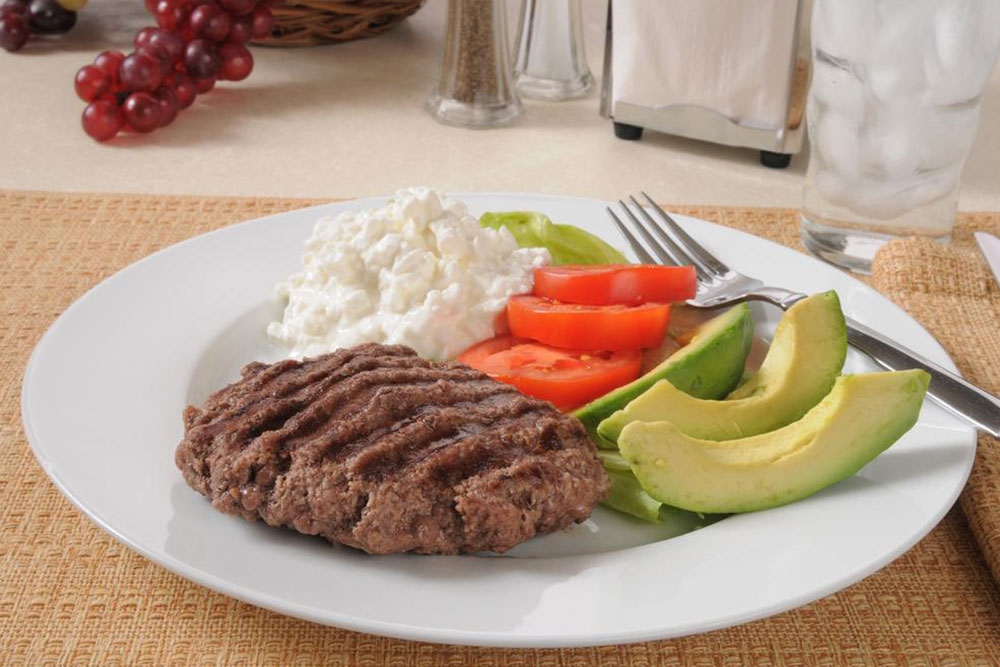
Protein-rich foods: Consuming a variety of high-protein foods such as lean meats, eggs, beans, lentils, nuts, and seeds can support neurotransmitter synthesis, which is vital for brain function. Proteins help stabilize blood glucose levels, reducing the likelihood of mood swings and hyperactivity. Including adequate protein in each meal is especially beneficial for children with ADHD, as it promotes sustained energy and focus throughout the day.
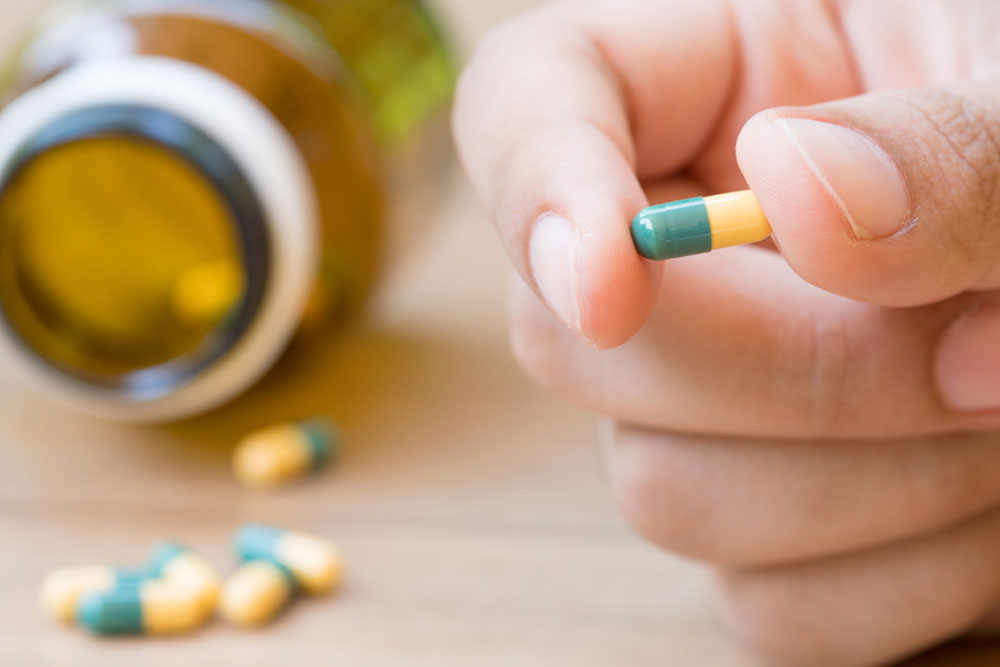
Herbal supplements and natural remedies: Certain herbal supplements such as Ginkgo biloba and ginseng are known to enhance cognitive function, memory, and mental clarity. These herbal options are used traditionally to support brain health and may complement other treatment strategies for ADHD. However, it’s important to consult health professionals before adding herbal supplements to your routine.
Vitamins and minerals: Proper intake of essential vitamins and minerals is key. B vitamins, particularly B6 and B12, are crucial for neurological function. Minerals like zinc, magnesium, and iron are involved in neurotransmitter production and brain health. Deficiencies in these nutrients can worsen ADHD symptoms, so focusing on a nutrient-dense diet or supplementation can make a significant difference.
Polyphenol supplements: Pycnogenol, an extract derived from pine bark, is rich in antioxidants and has been studied for its neuroprotective effects. It helps protect brain cells from oxidative stress, which can improve attention span, reduce impulsiveness, and decrease hyperactivity. Incorporating foods rich in polyphenols, such as berries, dark chocolate, and green tea, can also provide similar benefits.
In addition to emphasizing beneficial foods, it is equally important to avoid foods that can worsen ADHD symptoms. The following are foods to limit or eliminate from your diet:
Foods with high added sugars or processed sugars, which can cause blood sugar spikes followed by crashes leading to irritability and inattention.
Products containing artificial food colors and preservatives—such as synthetic dyes, flavorings, and chemical additives—that have been linked to increased hyperactivity in sensitive individuals.
Highly processed foods, including fast foods, chips, and sugary snacks, which are often rich in unhealthy fats, sodium, and artificial additives.
Junk foods and fast foods that provide little nutritional value and can contribute to behavioral issues.
Spicy or greasy snacks that can upset stomach and exacerbate focus issues.
Foods known to cause allergies or sensitivities, such as dairy, gluten, or certain additives, which can trigger behavioral changes or worsen symptoms in some individuals.
Adopting an ADHD-friendly diet requires careful monitoring of the foods consumed. Keeping a food diary can help identify personal triggers and patterns, improving management strategies. It’s essential for individuals and caregivers to work closely with healthcare professionals, including dietitians and physicians, when making significant dietary changes. With proper guidance, nutrition can serve as a powerful tool in alleviating ADHD symptoms, enhancing cognitive function, and promoting overall mental health.