Comprehensive Guide to Relieving Heel Spurs and Managing Heel Pain
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for relieving heel spurs and managing heel pain. It covers treatment methods like cold therapy, supportive footwear, medications, advanced therapies, and surgical options, providing detailed insights to help patients understand their condition and seek appropriate care. Proper management prevents further damage and improves mobility, especially for individuals involved in sports or standing occupations. Early intervention and lifestyle adjustments play a crucial role in heel spur relief, making this article a valuable resource for anyone suffering from heel pain or at risk of developing heel spurs.
Comprehensive Guide to Relieving Heel Spurs and Managing Heel Pain
Heel spurs are bony outgrowths that develop on the underside of the heel bone, often leading to discomfort, inflammation, and impaired mobility. These bony projections can vary in size and may be present without causing symptoms, but when symptoms do occur, they can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life. Heel spurs are frequently associated with plantar fasciitis, a common condition involving inflammation of the plantar fascia ligament that runs along the bottom of the foot. The presence of heel spurs often indicates underlying issues related to strain, overuse, or trauma to the heel area.
Understanding heel spurs is essential for effective management and relief. These calcified deposits typically form over months due to calcium buildup as a response to repetitive stress or injury to the ligaments and foot tissues. Athletes, individuals who stand for long hours, and those with improper footwear are at higher risk of developing heel spurs. Although they can be asymptomatic, for many people, heel spurs cause sharp pain, especially during weight-bearing activities, which can hinder walking, running, or standing for extended periods. Proper diagnosis involves clinical assessment and imaging studies such as X-rays that reveal the bony growths.
While some treatments focus on alleviating symptoms, others aim to address the root causes of heel spur formation. A combination of lifestyle modifications, therapeutic interventions, medications, and, in severe cases, surgical procedures can provide relief. Early intervention often helps prevent the progression of symptoms and supports better recovery outcomes. A comprehensive approach involves both conservative treatments and preventive strategies to promote foot health and reduce the risk of recurring heel spurs.
Effective Treatment Strategies for Heel Spurs
Managing heel spurs effectively requires a multi-pronged approach tailored to the severity of symptoms and underlying causes. Below are some of the most recommended treatment options:
Cold Therapy to Reduce Inflammation
Applying cold therapy is a simple yet effective method to minimize swelling and relieve pain. Use an ice pack wrapped in a towel or cloth to prevent frostbite, and apply it directly to the affected heel for about ten minutes. Repeat this process hourly during the initial stages of pain to help control inflammation. Cold therapy constricts blood vessels, thereby reducing swelling and numbing nerve endings that transmit pain signals. This natural remedy is typically safe and can be used alongside other treatments for better results.
Supportive and Proper Footwear
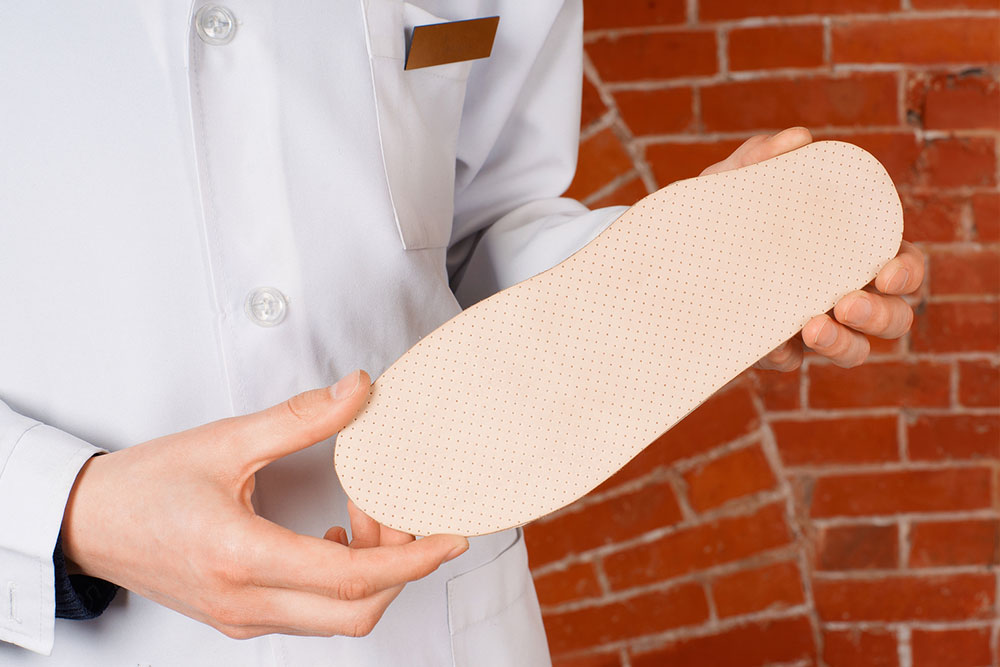
Choosing the right footwear is crucial in managing heel spurs. Shoes with good arch support and a firm heel counter help stabilize the foot and reduce pressure on the heel. Look for shoes that provide cushioning around the heel area and are constructed with supportive insoles or orthotics if necessary. Elevating the heel slightly—up to one inch—can help redistribute weight away from the heel, easing stress on the bony growth. Custom orthotic devices are often prescribed by podiatrists to ensure optimal fit and support, especially for individuals with flat feet or high arches, which can contribute to heel spur development.
Medications for Pain and Inflammation
Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)—such as ibuprofen or naproxen—are commonly used to reduce pain and swelling associated with heel spurs. These medications provide temporary relief and improve mobility during flare-ups. However, it's important to consult a healthcare professional before starting any medication regimen, particularly if you have underlying health conditions like kidney problems, ulcers, or cardiovascular issues. In some cases, doctors may recommend stronger prescription medications or topical anti-inflammatory creams for localized relief.
Advanced Therapies
For persistent heel pain unresponsive to conventional treatments, advanced therapies such as cryoultrasound may be recommended. This technique combines cold therapy with electromagnetic energy to target inflamed tissues effectively. Administered by trained physical therapists or podiatrists, cryoultrasound promotes tissue healing and pain relief without the need for invasive procedures.
Injections and Medical Interventions
In cases of severe pain, corticosteroid injections can provide temporary pain relief by reducing inflammation around the heel spur. These injections must be administered under medical supervision, and their use should be limited to prevent adverse effects like tissue degeneration or nerve damage. It's important to note that injections do not eliminate the bone spur but help manage symptoms during flare-ups. For some patients, if conservative measures prove ineffective after several months, surgical options may be considered.
Surgical Options for Heel Spur Removal
Surgery is typically reserved for cases where nonsurgical treatments have failed to provide adequate relief. The most common surgical procedure involves removing the heel spur and releasing tension in the plantar fascia, which may involve detaching part of the fascia. Post-surgical recovery can take several weeks, during which patients are advised to limit weight-bearing activities and follow a physical therapy program to restore foot function and prevent complications. Like all surgeries, heel spur removal carries risks such as nerve damage, infection, or recurrence of the bony growth, making careful medical evaluation essential before proceeding with an operation.
Prevention strategies include maintaining a healthy weight to reduce stress on the heels, wearing supportive footwear, stretching the foot and calf muscles regularly, and avoiding excessive activity that strains the plantar fascia. For athletes and active individuals, understanding proper training techniques and using appropriate footwear can minimize the risk of heel spur development. Early treatment of heel pain symptoms can prevent progression to more severe conditions and improve overall foot health.





