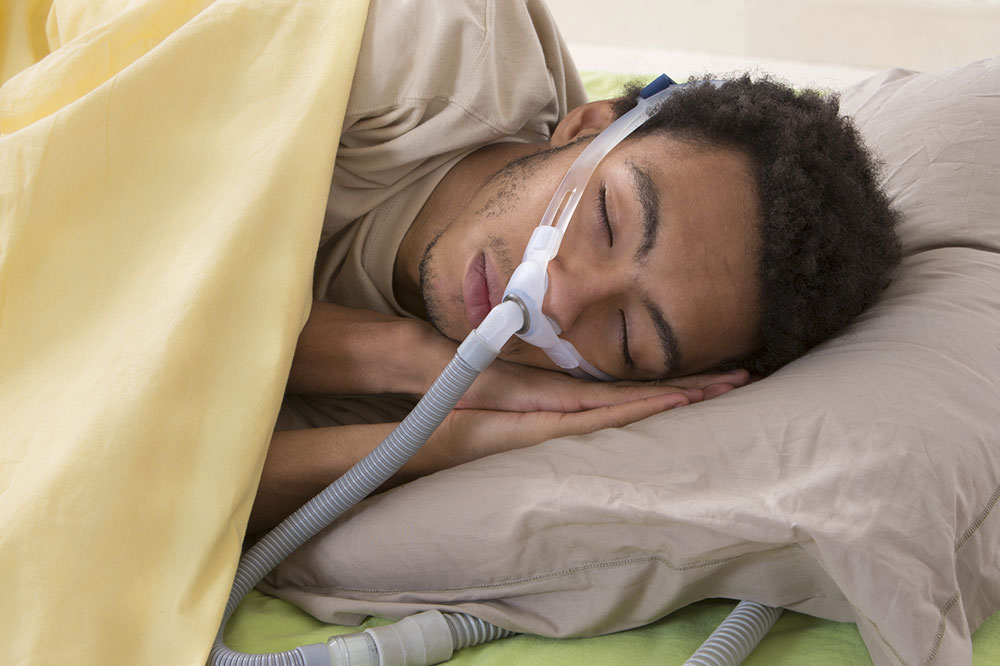
Comprehensive Guide to Managing Sleep Apnea Effectively
Discover comprehensive strategies to manage sleep apnea effectively, including lifestyle changes, medical options, and behavioral adjustments. Learn how weight management, proper sleep positioning, and medical devices like CPAP can improve sleep quality and reduce health risks. This in-depth guide provides essential insights for those seeking long-term relief from sleep-disordered breathing and aims to enhance overall health and well-being.
Comprehensive Strategies for Managing and Treating Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a pervasive sleep disorder characterized by repetitive episodes of breathing cessation during sleep. These episodes can occur dozens of times each night, sometimes exceeding 80 interruptions, which severely impair restful sleep and have profound impacts on overall health. When breathing temporarily stops, the brain and body are deprived of vital oxygen, increasing the risk of serious health complications if the condition remains untreated. While symptoms may seem mild initially, long-term effects such as cardiovascular disease, cognitive impairment, and metabolic issues can develop, making effective management crucial.
Addressing sleep apnea requires a multifaceted approach combining lifestyle adjustments, medical interventions, and sometimes specialized equipment. The goal is to reduce the frequency and severity of apnea episodes, improve sleep quality, and protect long-term health. Below, we explore comprehensive strategies known to be effective in managing sleep apnea, covering dietary considerations, physical activity, behavioral modifications, and medical options.
1. Achieving and Maintaining a Healthy Weight
One of the most significant risk factors for sleep apnea is excess body weight, especially fat deposits around the neck area. These deposits can constrict the airway, making it more likely to collapse or become obstructed during sleep. Therefore, weight management is often the first step in controlling the disorder. Adopting a nutritious, balanced diet fosters weight loss and improves overall health, which can dramatically lessen sleep apnea symptoms.
Focus on foods high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, which promote satiety and aid digestion. Incorporating healthy fats from sources like olive oil, coconut oil, and fatty fish supports metabolic health. Combining dietary changes with regular physical activity enhances weight loss efforts and strengthens respiratory muscles, leading to better airflow during sleep.
Implementing small, sustainable changes such as portion control, meal planning, and avoiding processed foods can make a substantial difference. Consulting nutritionists or dietitians can provide personalized advice to help achieve and maintain a healthy weight, ultimately reducing sleep apnea severity.
2. Incorporating Regular Physical Activity
Physical activity should be a cornerstone of sleep apnea management. Regular exercise not only supports weight loss but also improves cardiovascular health, which is often compromised in sleep apnea patients. Engaging in activities such as brisk walking, running, swimming, or cycling can elevate overall health metrics and enhance respiratory function.
Additionally, specific exercises like yoga and breathing routines can strengthen the diaphragm and chest muscles, promoting more efficient breathing during sleep. Mindfulness-based breathing exercises and meditation can also help in reducing stress levels, which may exacerbate sleep disturbances.
Setting attainable exercise goals—such as 30 minutes of moderate activity most days of the week—can lead to significant health improvements. Maintaining consistency is key, and integrating activity into daily routines ensures long-term adherence and benefits.
3. Eliminating Unhealthy Habits That Trigger Sleep Disruption
Certain lifestyle choices can aggravate sleep apnea symptoms. Alcohol consumption, smoking, and sedative use are notable contributors. Alcohol relaxes throat muscles, increasing airway collapsibility, while smoking inflames and irritates the airway tissues, narrowing the passages. Sedatives reduce muscle tone, deepening airway obstruction risks.
Ceasing alcohol intake, quitting smoking, and avoiding sedatives, especially close to bedtime, can substantially decrease the severity of sleep apnea episodes. Support programs, counseling, and medical guidance may assist in overcoming these habits. Incorporating healthier routines, such as relaxation techniques or alternative sleep aids, can facilitate better sleep quality without compromising airway health.
4. Managing Underlying and Coexisting Conditions
Conditions such as acid reflux, nasal congestion, allergies, or chronic cough can worsen sleep apnea symptoms. Addressing these underlying issues with appropriate medical treatment alleviates some of the strain on the respiratory system during sleep.
Hypothyroidism, nasal polyps, or deviated septum may require medical intervention, including medications or surgical procedures, to improve airflow. An ENT specialist can evaluate structural abnormalities and recommend corrective options like septoplasty or sinus surgery.
Collaborating with healthcare professionals for comprehensive management ensures that all contributing health factors are properly addressed, providing a more effective overall treatment plan for sleep apnea.
5. Enhancing Breathing with Humidification and Positioning
Adding a humidifier to the bedroom can make breathing more comfortable by maintaining optimal humidity levels. Dry air may cause nasal dryness, congestion, and irritation, which can worsen apnea symptoms. Humidification can soothe airways, reduce snoring, and ease breathing during sleep.
Adjusting sleep position is another simple yet effective strategy. Elevating the head with additional pillows or adjusting bed angles can prevent airway collapse. Sleeping on your side—especially the left side—is recommended as it helps keep the airway open, reducing the number of apnea episodes. Avoiding sleeping on the back prevents gravity from pulling the tongue and soft tissues into the airway, which can cause obstruction.
Consistency in sleep schedule and ensuring at least 7–8 hours of restful sleep each night help improve overall health and reduce symptoms of sleep-disordered breathing.
6. Practicing Breathing Exercises and Relaxation Techniques
Strengthening respiratory muscles and promoting relaxed breathing can be highly beneficial. Techniques such as diaphragmatic breathing, deep-breathing exercises, and mindfulness meditation can help regulate breathing patterns, making apnea episodes less frequent and intense.
Regular practice of these techniques has been shown to improve lung capacity and reduce stress-related sleep disturbances. Learning proper breathing habits from trained professionals can optimize results. Over time, these skills can become a natural part of bedtime routines, contributing to healthier sleep cycles.
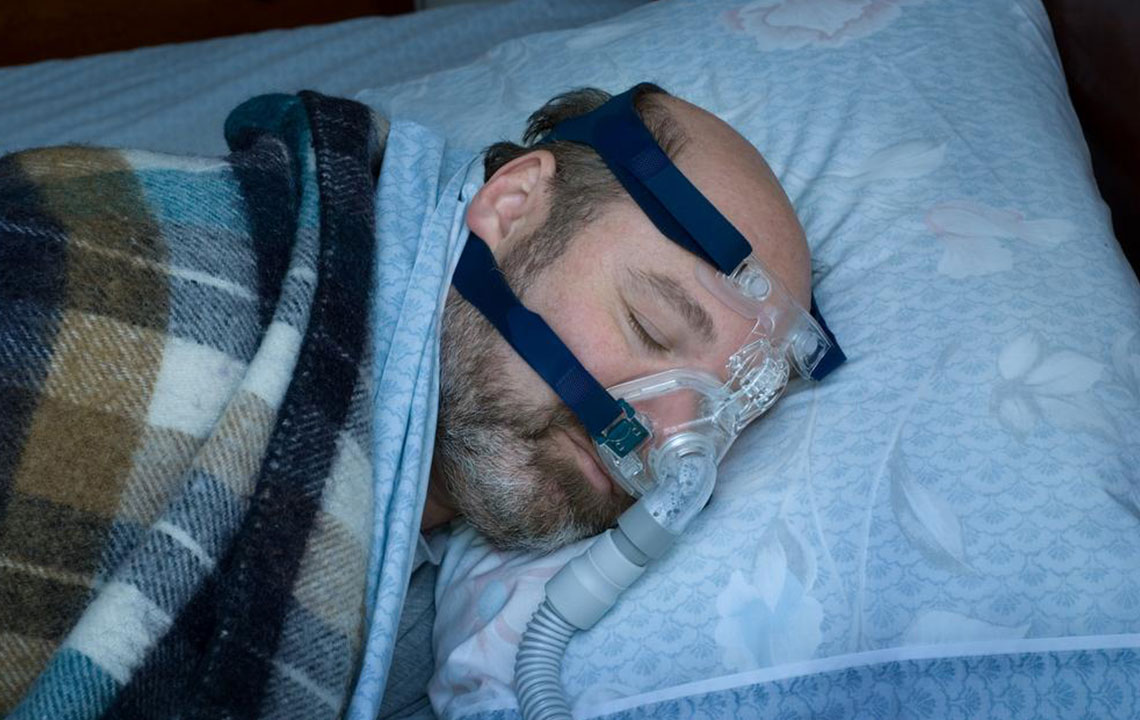
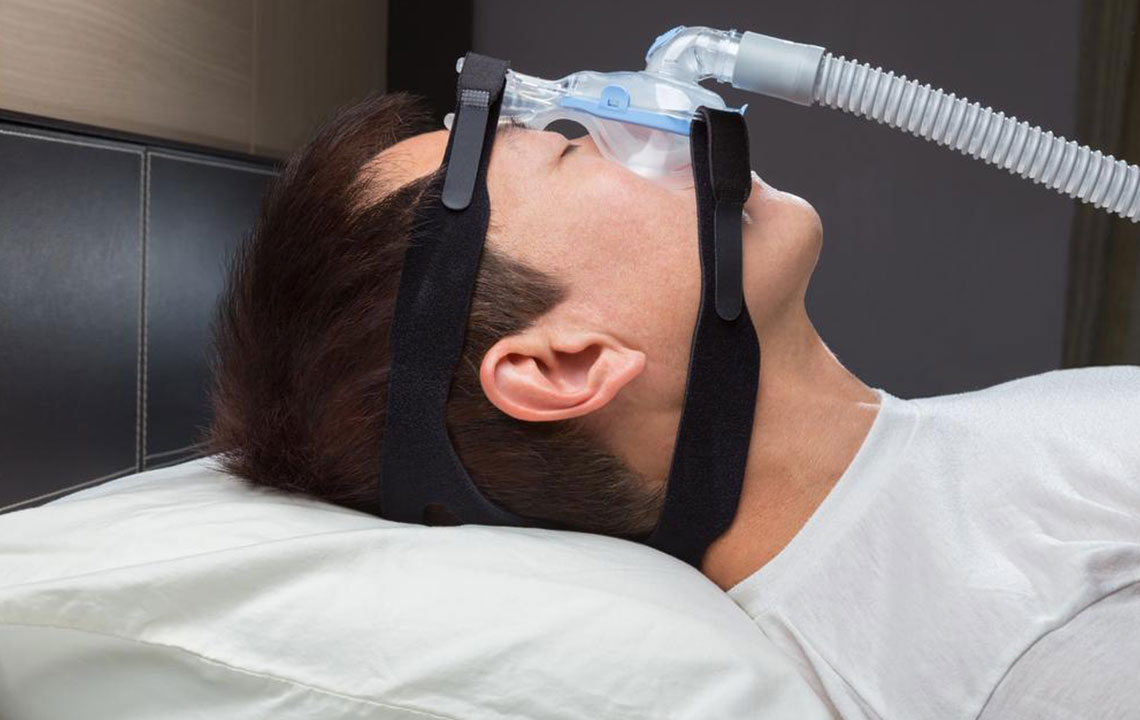
7. Utilizing Medical Devices and Therapies
When lifestyle modifications are insufficient, medical treatments become necessary. The most common and effective intervention is Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy. This device delivers a steady stream of pressurized air through a mask, keeping the airway open during sleep.
Additional options include mandibular advancement devices, which reposition the jaw to prevent airway blockage, or surgical procedures to correct structural abnormalities. Weight loss surgeries, nasal surgeries, or uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) may be considered in severe cases.
Choosing the appropriate intervention should involve consultations with sleep specialists and healthcare providers to tailor solutions based on individual needs and the severity of the disorder.
8. Regular Monitoring and Follow-Up
Managing sleep apnea is an ongoing process. Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential to monitor treatment efficacy and make necessary adjustments. Sleep studies (polysomnography) can evaluate progress and determine if additional treatments are needed.
Patients should also report new or worsening symptoms promptly. Adherence to prescribed therapies, lifestyle changes, and ongoing medical care form the backbone of effective long-term management.
Conclusion
Sleep apnea is a complex but manageable condition. Combining lifestyle modifications such as weight management, physical activity, and the elimination of harmful habits with medical interventions provides the best chance for effective control. Practicing good sleep hygiene, using supportive devices, and maintaining regular health check-ups enhance overall sleep quality and reduce health risks associated with untreated sleep apnea. Early diagnosis and comprehensive treatment plans are key to leading a healthier, more restful life.