Effective Approaches for Rapid Relief from Gout Pain and Long-Term Management
This comprehensive guide details effective strategies for rapid gout pain relief and long-term management. It covers immediate treatment options such as medications, cold therapy, hydration, and lifestyle changes, alongside natural remedies and dietary adjustments for prevention. Regular medical monitoring is emphasized for sustained health and minimizing flare-ups. Implementing these approaches can help gout sufferers reduce pain, prevent future episodes, and maintain overall joint health, leading to a better quality of life.

Effective Approaches for Rapid Relief from Gout Pain and Long-Term Management
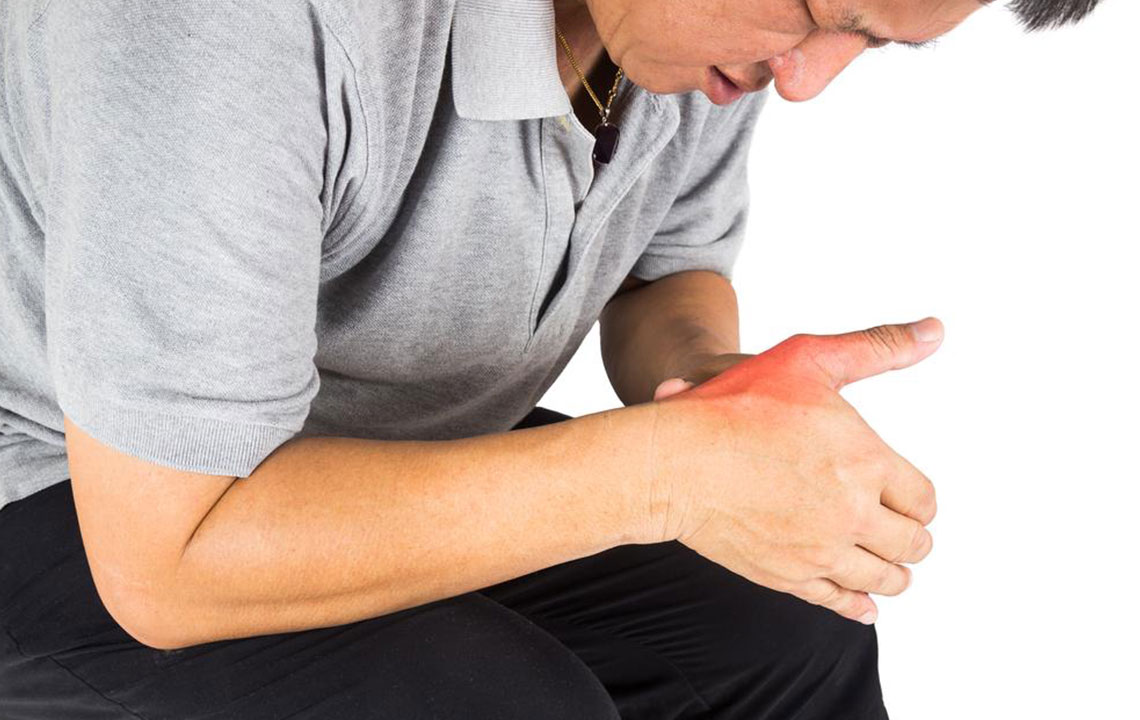
Gout is a common form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by sudden, intense episodes of pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in the affected joints, most frequently the big toe. These gout attacks can significantly impair daily functioning and quality of life if not managed properly. Recognizing the symptoms early and adopting appropriate treatment strategies are essential to alleviate suffering quickly and prevent future flare-ups. Combining medication, lifestyle modifications, dietary adjustments, and natural remedies can effectively control the condition and promote overall joint health.
Understanding the primary symptoms of gout is the first step toward effective management. These symptoms typically include an abrupt onset of severe joint pain, swelling, redness, warmth, and tenderness in the affected joint. The pain can be excruciating, often awakening individuals from sleep. Early detection and intervention are vital to minimizing joint damage and speeding recovery. Therefore, learning about immediate relief methods, lifestyle changes, and long-term prevention tactics can empower sufferers to manage gout more efficiently and maintain a better quality of life.
Immediate Strategies to Relieve Gout Pain
1. Use Appropriate Medications Promptly
The cornerstone of acute gout treatment involves the use of anti-inflammatory medications. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as naproxen, ibuprofen, or indomethacin are commonly used to reduce pain and inflammation during a flare-up. These medications should be taken as soon as symptoms appear to suppress the inflammatory response effectively. It’s crucial to follow dosage instructions carefully and consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
It’s important to avoid aspirin during gout attacks, as aspirin can increase uric acid levels and worsen symptoms. If you are already prescribed uric acid-lowering drugs, continue their use as directed by your doctor. Adjusting medication based on your previous response can help expedite relief and prevent complications.
2. Apply Cold Therapy
Applying ice or a cold pack directly to the affected joint can significantly reduce inflammation, swelling, and pain. For best results, use an ice pack wrapped in a cloth and apply it for 20-30 minutes at a time, several times a day. This cold compress works by constricting blood vessels, decreasing blood flow to the area, and numbing nerve endings, thus providing quick relief from severe pain.
3. Maintain Proper Hydration
Staying well-hydrated is essential for managing gout flare-ups. Drinking at least 2 liters of water daily helps dilute uric acid levels in the blood and promotes its elimination through urine. Adequate hydration can prevent the formation of uric acid crystals in the joints and reduce the risk of kidney stones associated with gout. Fresh water is best, and sugary beverages should be avoided as they can increase uric acid production.
4. Avoid Alcohol and Purine-Rich Foods
Alcohol consumption, particularly beer and spirits, can elevate uric acid levels by impairing its excretion through the kidneys. It is advisable to abstain from alcohol during a gout attack and limit or avoid it altogether to prevent triggering future episodes. Additionally, foods high in purines—such as red meats, organ meats, shellfish, and certain fish—should be minimized in the diet. Reducing intake of these foods can lower uric acid production and decrease the likelihood of flares.
5. Elevate and Protect the Affected Limb
Proper positioning of the affected joint can aid in reducing swelling and pain. Elevate the limb on pillows to promote fluid drainage and decrease inflammation. For example, if the gout attack involves the foot or ankle, keep it elevated above heart level whenever possible. Additionally, wearing loose, comfortable footwear and avoiding tight socks or shoes can reduce pressure and strain on the joint.
6. Rest and Keep the Joint Warm
Rest is vital during a gout flare-up. Minimize weight-bearing activities and avoid unnecessary movements that can aggravate the pain. Wearing soft, warm socks and keeping the affected area warm can help soothe the joint and promote relaxation. Stress management and gentle joint support can also help minimize severity and duration of attacks.
Long-Term Strategies for Managing Gout
Effective long-term management involves more than just immediate relief. Lifestyle and dietary modifications, natural remedies, and regular medical monitoring are essential to controlling uric acid levels and preventing recurring gout episodes.
1. Incorporate Natural Remedies
Several natural substances have been traditionally used to manage gout symptoms and reduce uric acid levels. Celery seed extract, black cherry juice, and nettles are among the most popular. Celery seed extract contains compounds that may help lower uric acid and reduce inflammation. Black cherry juice is rich in antioxidants and anthocyanins that can decrease uric acid formation and support joint health. Nettle tea or supplements may help improve kidney function and promote uric acid excretion. These natural remedies can serve as complementary strategies alongside medical treatments.
2. Dietary Modifications for Prevention
Adopting a gout-friendly diet is crucial for long-term management. Focus on reducing high-purine foods and increasing intake of low-purine options. Emphasize fresh fruits and vegetables, complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products. Consuming foods rich in vitamin C can also help lower uric acid levels.
Limit or avoid alcohol, sugary drinks, and processed foods high in saturated fats. Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular exercise can significantly reduce the risk of gout attacks. Weight loss helps lower uric acid levels and decreases joint stress, further preventing flare-ups.
3. Regular Medical Monitoring
Routine check-ups with your healthcare provider facilitate the monitoring of uric acid levels and overall health. Blood tests and joint assessments help tailor treatment plans and make necessary adjustments. Maintaining a record of flare-up frequency, severity, and triggers can help identify patterns and refine management strategies.
4. Medications for Chronic Control
For individuals with recurrent gout or persistently high uric acid levels, long-term medication may be prescribed. These include urate-lowering drugs such as allopurinol, febuxostat, or probenecid. Adherence to prescribed therapies can prevent future attacks, joint damage, and associated complications. Always follow your physician’s advice and report any side effects promptly.
Conclusion
Managing gout requires a comprehensive approach that combines immediate symptom relief with long-term lifestyle adjustments. Early intervention with appropriate medications, cold therapy, hydration, and diet plays a vital role in reducing pain and preventing complications. Incorporating natural remedies and maintaining regular medical check-ups further enhance disease control. By adopting these strategies, gout sufferers can effectively manage flare-ups, improve their quality of life, and enjoy healthier, pain-free joints.