Early Detection and Symptoms of Liver Cancer: What You Need to Know
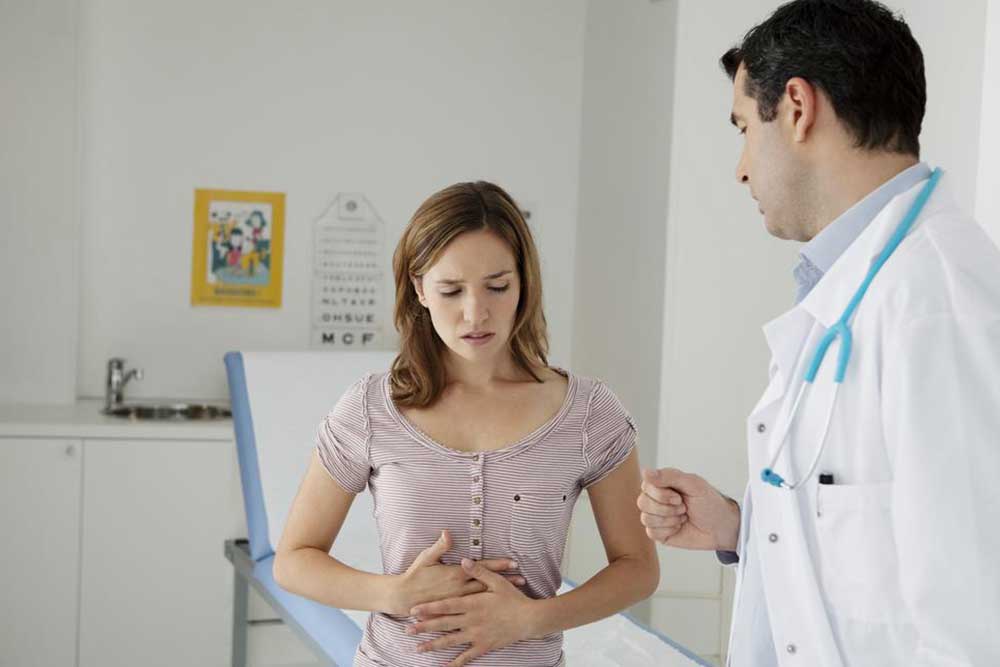
Liver cancer remains a silent threat with subtle early symptoms making detection challenging. Recognizing key signs such as jaundice, abdominal pain, and unexpected weight loss is crucial for early diagnosis. This comprehensive guide explains the primary types of liver cancer and highlights critical symptoms that should prompt immediate medical consultation. Understanding these warning signs can lead to earlier intervention, improving treatment success and survival rates. Regular screening and awareness are vital, especially for high-risk individuals, to catch liver cancer at an early stage and prevent its progression.

Early Detection and Symptoms of Liver Cancer: What You Need to Know
Liver cancer poses serious health risks and often develops silently, making early diagnosis crucial. Recognizing the early signs can significantly improve treatment outcomes and survival rates.
Liver cancer occurs when abnormal growths develop within the liver tissue, forming malignant tumors that progressively impair liver function. These tumors can invade nearby tissues and, in advanced cases, metastasize to other organs via the bloodstream. Understanding the main types of liver cancer is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment:
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): This is the most common type, originating within the primary liver cells, called hepatocytes. It accounts for approximately 75% of all liver cancers.
Cholangiocarcinoma: This type develops in the bile ducts within the liver, leading to bile flow obstruction and other complications.
Metastatic liver cancer: Tumors that originate from cancers elsewhere in the body, such as the colon, breast, pancreas, kidney, ovary, or lungs, and spread to the liver. These secondary tumors are classified based on their primary location.
Early-stage liver cancer often presents with subtle or nonspecific symptoms, which makes early detection a challenge. As the disease progresses, however, symptoms become more noticeable and can vary depending on individual health and tumor progression. Being aware of these signs can prompt timely medical attention. Here are some of the most common symptoms associated with liver cancer:
Loss of appetite: An early sign, often presenting as a feeling of fullness after minimal eating, which can lead to weight loss over time. This decrease in appetite is typically caused by tumor growth affecting digestion or hormonal changes.
Unintentional weight loss: Rapid and unexplained weight reduction is common as cancer advances, often linked to decreased food intake and metabolic changes caused by the tumor.
Persistent fatigue: Patients frequently report ongoing tiredness and weakness that do not improve with rest, significantly impacting daily life and activity levels.
Abdominal pain and discomfort: Discomfort located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen or extending to the back and shoulder blade area may indicate tumor growth and liver inflammation.
Jaundice: The yellowing of the skin and eyes is a hallmark sign of liver dysfunction caused by high bilirubin levels, often resulting from bile duct obstruction or liver cell damage.
Enlarged liver (hepatomegaly): A palpable mass or swelling below the right rib cage can be a sign of a significantly enlarged liver due to tumor growth or tissue damage.
Abdominal swelling: Ascites, or fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity, can lead to noticeable swelling and discomfort. This occurs because of increased pressure within blood vessels or liver failure.
Spleen enlargement (splenomegaly): Swelling of the spleen may accompany liver disease and is often related to blood flow issues or infections related to liver pathology.
While these symptoms can be caused by other less serious conditions, their presence warrants prompt medical evaluation. Early diagnosis is key to effective treatment options and improving prognosis. If you notice any of these signs, it is essential to seek medical advice without delay, as timely intervention can be life-saving.