Comprehensive Guide to Identifying Early Signs of Immune Thrombocytopenia
Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is a blood disorder marked by low platelet levels, leading to bleeding risks. Recognizing early symptoms like petechiae, purpura, unexplained bruising, and bleeding gums is essential for prompt diagnosis. This comprehensive guide explains ITP features, causes, and why early medical intervention can significantly improve health outcomes. Understanding these signs helps patients seek timely treatment, preventing complications such as internal bleeding or anemia, especially in vulnerable groups like children and women with heavy menstrual bleeding. Early detection plays a vital role in managing this autoimmune blood disorder effectively.

Comprehensive Guide to Identifying Early Signs of Immune Thrombocytopenia
Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP), also known as idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, is a hematological disorder characterized by an abnormally low number of platelets — the blood components responsible for clotting. This condition can manifest suddenly, termed acute ITP, or persist over time as chronic ITP. Understanding how to recognize early symptoms is vital for timely intervention, which can prevent serious complications and improve prognosis. While children tend to recover without significant treatment, adults often need ongoing medical management. Recognizing the hallmark signs early on ensures prompt diagnosis and effective treatment strategies.
Major Symptoms and Their Significance
1. Petechiae (Tiny Red or Purple Spots)
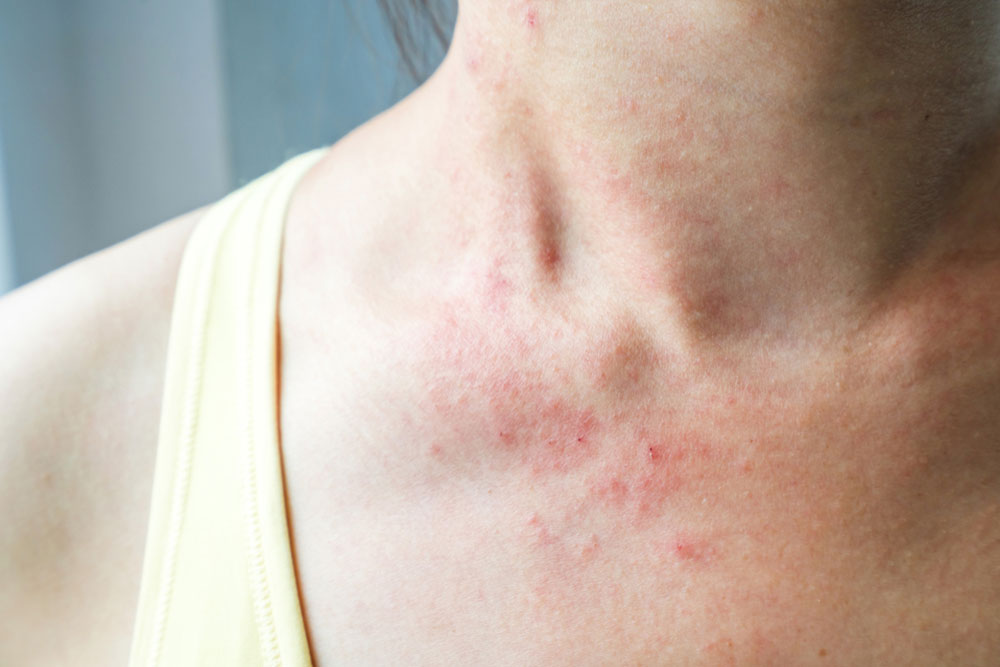
One of the earliest indicators of ITP is the appearance of petechiae—small, pinpoint hemorrhages that appear as red, purple, or brown spots. These spots are often found just beneath the skin or mucous membranes, particularly around the eyelids, arms, legs, or inside the mouth and stomach area. They are flat and not itchy or raised, making them easy to mistake for allergic reactions or minor skin irritations. However, their presence warrants immediate medical assessment to rule out blood clotting issues, especially if multiple spots appear suddenly or worsen over time.
2. Purpura (Larger Blood Lesions)
Purpura refers to larger patches of bleeding that occur when numerous petechiae merge together, forming broader, more noticeable purple or brownish discolorations on the skin or mucous membranes. These patches often indicate more extensive bleeding from small blood vessels and are frequently seen on areas like the mouth, throat, or on exposed skin. The presence of purpura signifies a higher bleeding risk and should prompt urgent medical consultation to determine if thrombocytopenia is the underlying cause.
3. Sudden & Unexplained Bruising
Bruising that appears inexplicably and frequently—without any recent trauma—is another hallmark symptom. Such bruises typically vary in color from yellowish to purple and tend to develop quickly. Low platelet levels impair normal clot formation, making even minor bumps cause significant bruising. Recurrent unexplained bruises should always be evaluated by healthcare professionals for potential blood disorders like ITP.
4. Bleeding Gums and Oral Hemorrhages
Gums that bleed easily, especially during routine activities like brushing or flossing, may signal a platelet deficiency. Swollen or inflamed gums that bleed spontaneously, even without apparent injury, are common signs of thrombocytopenia. This symptom often overlooked, can be an early warning sign of ITP and warrants prompt dental or medical evaluation.
5. Blood in Urine or Stool
Unexpected bleeding in the form of blood in urine (hematuria) or stool (hematochezia or melena) indicates internal bleeding from the gastrointestinal or urinary tract. These symptoms, particularly if persistent or accompanied by other signs like fatigue or easy bruising, require immediate medical investigation. They highlight the severity of low platelet counts and the potential for life-threatening bleeding episodes.
6. Persistent Fatigue and Weakness
Chronic fatigue is a common symptom of ITP, often stemming from anemia caused by ongoing blood loss. When platelet destruction leads to a reduction in red blood cells, the body’s oxygen-carrying capacity diminishes, resulting in tiredness, weakness, and reduced energy levels. Over time, untreated anemia can significantly impair daily functioning and quality of life.
7. Abnormal Menstrual Bleeding
Women with ITP may notice increased menstrual flow or longer-lasting periods. Heavy bleeding occurs because low platelet counts impair the blood’s ability to clot efficiently. If menstrual bleeding becomes unusually heavy or prolonged, it’s crucial for women to seek medical advice promptly, as unchecked bleeding can lead to anemia and other complications.
8. Frequent Nosebleeds (Epistaxis)
Repeated or prolonged nosebleeds that occur without apparent cause—such as dry air or recent injury—are indicative of decreased blood platelet levels. Persistent nosebleeds should be evaluated by healthcare providers, especially when they happen frequently, as they can be a significant sign of underlying thrombocytopenia, including ITP.
Understanding the Causes of ITP
Although the exact cause of immune thrombocytopenia remains uncertain, it is widely believed to be an autoimmune disorder. In ITP, the immune system—specifically, antibodies—mistakenly targets and destroys platelets, mistaking them for harmful invaders. This immune-mediated destruction leads to a significant reduction in platelet count, impairing the blood's ability to clot properly. As a result, even minor injuries can cause excessive bleeding, or bleeding may occur spontaneously from internal blood vessels. Certain infections, autoimmune diseases, or even certain medications can trigger or exacerbate ITP, but often the cause remains idiopathic. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial, as they can help prevent severe bleeding episodes and improve patient outcomes.