Comprehensive Guide to Foods to Avoid for Effective Arthritis Relief
Learn about the top foods that worsen arthritis symptoms and discover effective dietary strategies to manage joint pain. This detailed guide highlights foods to avoid, including red meats, processed foods, sugars, and gluten, offering practical tips for a healthier, inflammation-reducing diet suitable for arthritis sufferers.
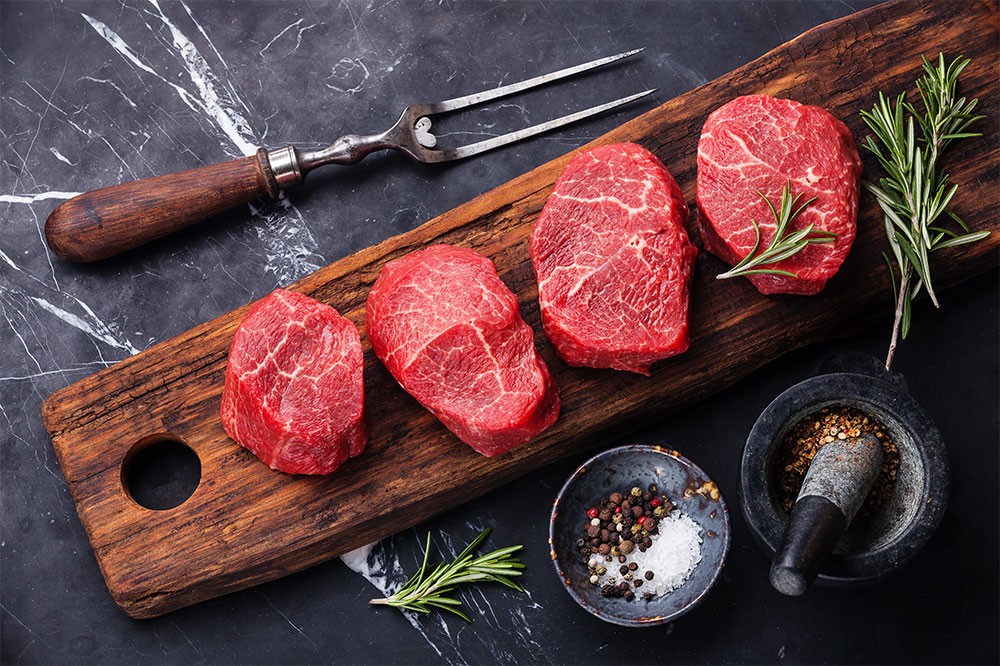

Essential Foods to Avoid When Managing Arthritis Symptoms Effectively
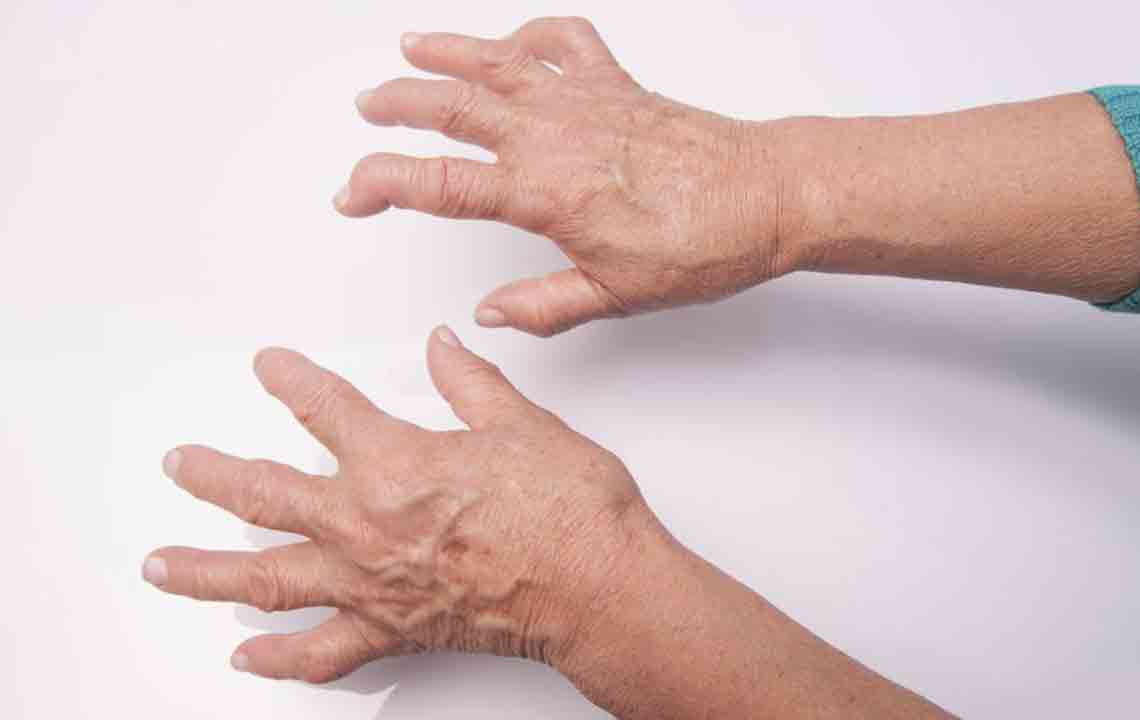
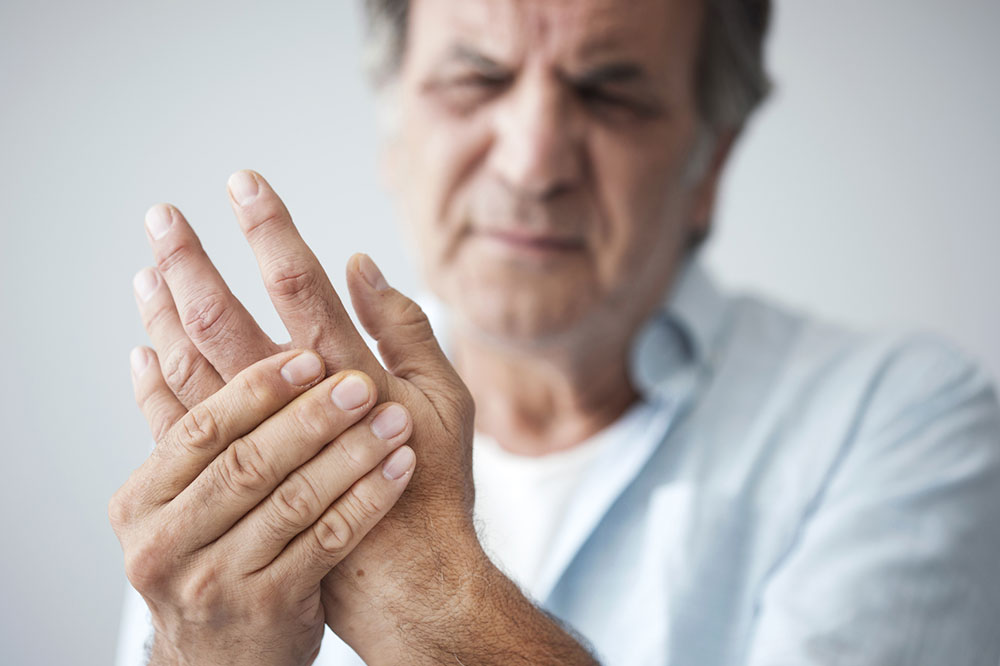
Arthritis is a widespread and often debilitating chronic joint condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by symptoms such as persistent joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and decreased mobility, arthritis can significantly impair daily activities and overall quality of life. While there is no complete cure for arthritis, managing its symptoms through lifestyle modifications, especially dietary changes, plays a crucial role in improving patient outcomes. Among various factors influencing the progression of arthritis, diet stands out as a key aspect that can either exacerbate or alleviate symptoms. Certain foods, particularly those that promote inflammation, should be avoided or minimized to help control joint discomfort and inflammation.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the top 8 foods that individuals with arthritis should consider excluding from their diet. Understanding which foods are inflammatory and why they impact arthritis symptoms can empower patients to make informed dietary choices. This approach not only helps reduce joint pain but also supports overall health and wellness.
1. Red and Processed Meats
Red meats, including beef, lamb, and pork, are known for their high saturated fat content. Diets rich in saturated fats have been linked to increased inflammation levels in the body, aggravating arthritis symptoms. When these meats are cooked at high temperatures—such as grilling or frying—they release harmful compounds like advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which can further promote inflammation and oxidative stress within joint tissues. This inflammatory response exacerbates pain, swelling, and stiffness in affected joints.
To minimize these risks, individuals with arthritis should consider reducing their intake of red and processed meats. Opting for leaner protein sources like poultry, fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, or plant-based proteins can provide necessary nutrients without inflaming joints. Incorporating fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines can be particularly beneficial as they contain anti-inflammatory omega-3s that may help reduce joint swelling and pain.
2. Refined Carbohydrates and Grains
Refined grains, including products like white rice, white bread, and white flour-based baked goods, are processed to remove fiber and nutrients. These foods contain simple carbohydrates that cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, which in turn trigger an inflammatory response. High blood sugar levels promote the release of inflammatory cytokines, chemicals that can worsen joint pain and stiffness in arthritis patients.
Switching to whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole wheat products provides fiber and nutrients that help stabilize blood sugar and reduce inflammation. Maintaining balanced blood sugar levels is essential for controlling arthritis symptoms effectively.
3. Processed and Packaged Foods
Many processed foods contain artificial additives, preservatives, flavor enhancers like MSG, excess salt, and artificial sweeteners. These ingredients have been associated with increased systemic inflammation, which can intensify joint pain and damage in arthritic conditions. Consuming a diet high in processed foods often leads to weight gain, which adds strain to already inflamed joints, worsening symptoms.
To alleviate these issues, patients should prioritize whole, minimally processed foods such as fresh vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, and lean proteins. Reading labels carefully and reducing intake of processed snacks, ready-made meals, and fast foods helps minimize inflammation-triggering ingredients.
Sugary Snacks and Drinks
Items like candies, baked goods, and snack foods loaded with added sugars contribute significantly to joint inflammation. Excess sugar consumption leads to increased production of inflammatory mediators known as cytokines, which aggravate joint pain. Moreover, high sugar intake can impair immune function, impairing the body’s ability to repair joint tissues effectively. Sugary beverages such as soda, sweetened teas, and flavored drinks are particularly problematic due to their high fructose content.
Switching to water, herbal teas, or infused water with fresh fruit can satisfy sweet cravings without exacerbating arthritis symptoms. Additionally, reducing or eliminating sugary snacks and beverages from the diet can lead to noticeable improvements in joint comfort and overall health.
Canned and Preserved Foods
Canned fruits and vegetables often contain added salts, sugars, and preservatives, which increase their inflammatory potential. These additives can cause blood sugar spikes and promote systemic inflammation, aggravating joint symptoms. Moreover, many canned products are processed with unhealthy levels of sodium, which can contribute to water retention and swelling in joints.
Opting for fresh, frozen, or minimally processed produce is a healthier choice for managing arthritis. Reading product labels carefully and choosing options without added sugars or salts can significantly reduce the risk of inflamed joints.
Full-Fat Dairy Products
Regular consumption of full-fat dairy items like whole milk, cheese, and sweetened yogurts has been linked to increased inflammation due to their high saturated fat content. These fats can stimulate the production of inflammatory chemicals, leading to joint flare-ups and worsening of arthritis symptoms.
Switching to low-fat or fat-free dairy options, such as skim milk, or choosing plant-based alternatives like almond or soy milk can provide necessary nutrients while reducing inflammation. Incorporating dairy alternatives rich in calcium and vitamin D supports joint health without triggering inflammation.
Sugar-Laden Beverages
Soft drinks, flavored waters, and sweetened teas are loaded with added sugars, including high levels of fructose. These drinks can cause rapid blood sugar increases, promoting inflammation and joint pain. Furthermore, excessive sugar intake may impair immune function, potentially hindering the body's ability to repair damaged joint tissues.
Replacing sugary drinks with water, herbal infusions, or natural fruit-infused water helps keep hydration levels up without contributing to inflammation. Limiting these beverages can lead to reduced joint pain and improved mobility over time.
Gluten-Containing Foods
Foods containing gluten, such as wheat, barley, and rye, can aggravate symptoms in individuals sensitive or intolerant to gluten. For some people with arthritis, especially those with autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, gluten can increase joint inflammation and pain.
Adopting a gluten-free diet, or at least reducing gluten intake, may alleviate symptoms for sensitive individuals. Consulting with a healthcare provider or dietitian can help determine if gluten elimination is beneficial.
By understanding which foods can worsen arthritis symptoms, patients can take proactive steps towards dietary modifications that help reduce inflammation and improve joint health. Combining these dietary strategies with appropriate medical treatment, physical activity, and weight management forms a comprehensive approach to managing arthritis effectively.