Comprehensive Guide to Contraceptive Options for Breastfeeding Mothers
This comprehensive guide explores various effective and safe contraceptive options for breastfeeding mothers. From natural methods like lactational amenorrhea to long-term solutions like IUDs and implants, learn how to choose the right method that supports your health, breastfeeding, and family planning needs. Consultation with healthcare providers is highly recommended to tailor contraception choices to individual circumstances, ensuring safety and peace of mind. This detailed overview empowers nursing mothers with the knowledge to make informed decisions about birth control during breastfeeding.

Comprehensive Guide to Contraceptive Options for Breastfeeding Mothers
Balancing the responsibilities of caring for a newborn while planning for future pregnancies can be quite demanding. For new mothers, especially those who are breastfeeding, choosing an appropriate and effective birth control method is critical to ensuring overall health, family planning goals, and the well-being of both mother and child. Medical experts generally advise waiting at least a year postpartum before attempting to conceive again, allowing the mother sufficient time to recover physically and emotionally from childbirth, while also reducing potential health risks associated with closely spaced pregnancies.
Once couples resume intimacy after childbirth, selecting the right method of contraception becomes essential to prevent unplanned pregnancies and support a healthy breastfeeding journey. The choice of birth control for nursing mothers involves considering factors such as hormone safety, impact on milk supply, duration of effectiveness, and personal preferences. This comprehensive guide highlights the most reliable and safe contraceptive options specifically suitable for breastfeeding women, offering insights into each method's benefits and considerations.
Lactational Amenorrhea: Nature’s Own Contraceptive
One of the natural methods of contraception available to breastfeeding mothers is known as lactational amenorrhea. This phenomenon occurs because breastfeeding stimulates high prolactin levels in the body, which in turn suppresses the ovulation process. When ovulation is suppressed, the chances of becoming pregnant decrease significantly.
However, the lactational amenorrhea method (LAM) is most effective during the first six months postpartum, particularly when the mother is exclusively breastfeeding her infant on demand, including nighttime feeds. To maximize effectiveness, the mother should breastfeed frequently (at least every four hours during the day and every six hours at night), and the infant should be under six months old. Once menstruation resumes or breastfeeding frequency diminishes, the likelihood of ovulation—and thus pregnancy—increases, making this method less reliable beyond this period.
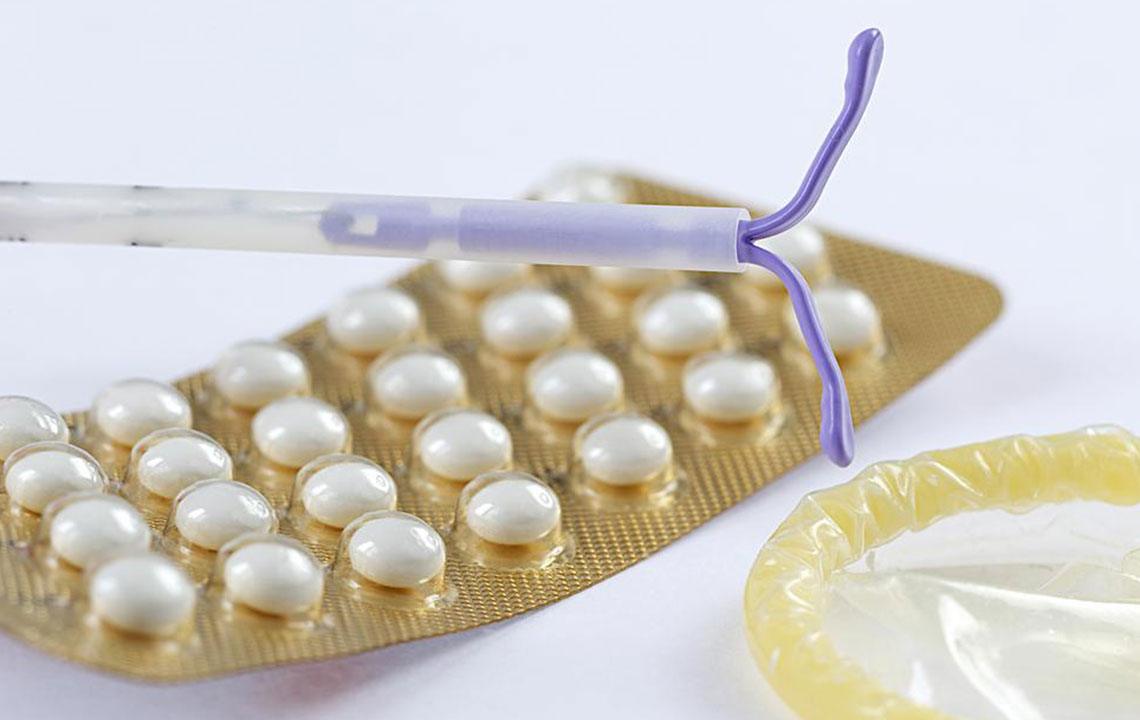
Condoms
Condoms remain a popular choice for breastfeeding mothers seeking a hormone-free, reliable form of contraception. They are about 98% effective when used correctly and also provide protection against sexually transmitted infections (STIs), adding an extra layer of safety. Both male condoms and female barrier devices are suitable options during breastfeeding. Condoms are easy to use, do not interfere with breastfeeding, and are accessible worldwide, making them an excellent first-line contraceptive method.
Progestin-Only Pills (Mini Pills)
Unlike combined oral contraceptives that contain estrogen and progestin, progestin-only pills contain only progestin. They work by thickening cervical mucus to prevent sperm penetration and may also suppress ovulation in some cases. Taken daily at the same time, these pills are safe for breastfeeding women because they do not interfere with milk production and do not contain estrogen, which could potentially affect the infant. However, adherence is crucial for efficacy, and some women may experience irregular bleeding as a side effect.
Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
IUDs are among the most effective long-term contraceptive methods available. There are two main types: hormonal IUDs, which release small amounts of progestin to thicken cervical mucus and sometimes inhibit ovulation; and copper IUDs, which create a hostile environment for fertilization and implantation through copper ions. Both types are highly effective—over 99%—and can last anywhere from three to ten years depending on the specific device. IUD insertion requires a healthcare professional’s expertise, and most women can safely use them while breastfeeding without affecting milk supply.
Contraceptive Implants
Subdermal implants are small, flexible rods inserted under the skin of the upper arm. They release steady doses of progestin, providing reliable contraception for up to three years. This method is particularly appealing to women who prefer a set-it-and-forget-it approach, as it requires no daily attention. Implants are safe to use during breastfeeding and generally do not impact milk volume or composition. Some women may experience changes in menstrual bleeding patterns, but overall, this is a highly effective and discreet option.
Birth Control Shots (Injectables)
Injectable contraceptives, commonly administered every three months, contain progestin and work by preventing ovulation. The most well-known option is depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA). These injections are approximately 94% effective when used correctly. They are convenient for women who prefer not to handle daily pills or barrier methods. However, some studies suggest that prolonged use can result in a temporary reduction in breast milk supply, especially in the initial months after starting. Fertility typically returns gradually, often taking over ten months after the last injection, so planning for future pregnancies should be considered.
Each of these contraceptive options offers distinct advantages and considerations. Therefore, it’s essential for breastfeeding mothers to consult with healthcare providers to determine the most suitable method tailored to their health profile, breastfeeding status, lifestyle, and family planning goals. Proper counseling ensures safe and effective contraception, enabling mothers to enjoy optimal health while nurturing their newborns.