Comprehensive Guide to Botox Treatment for Chronic Migraine Management
Explore the comprehensive benefits, procedure details, and safety considerations of Botox therapy for chronic migraine relief. This detailed guide covers who is a suitable candidate, how Botox works to reduce migraine frequency, and what patients can expect during and after treatment. Ideal for those seeking long-term headache management options, Botox offers significant relief for persistent migraine sufferers, with proper medical supervision and follow-up. Learn about potential side effects, injection procedures, and ways to maximize treatment success for a better quality of life.

Comprehensive Guide to Botox Treatment for Chronic Migraine Management
In recent years, Botox has become increasingly popular not only for cosmetic enhancements but also as an effective therapy for chronic migraines. Originally recognized for its wrinkle-reducing properties, Botox has shown promising results as a preventive treatment for individuals suffering from persistent and debilitating migraines. Chronic migraines, characterized by frequent and severe headache episodes, can significantly impair daily life, prompting many to seek alternative treatments. Among these, Botox stands out as a noteworthy option backed by clinical research and FDA approval for migraine prevention. If you're one of the many who experience relentless migraine episodes and are looking for a proactive, long-term solution, understanding Botox's role and application is essential.
Before deciding on Botox as a treatment option, it is crucial to comprehend how the procedure works, its benefits, potential risks, and what to expect during and after the treatment process. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on all aspects of Botox therapy for chronic migraines, helping patients make informed decisions.
Understanding the Botox Migraine Treatment Process
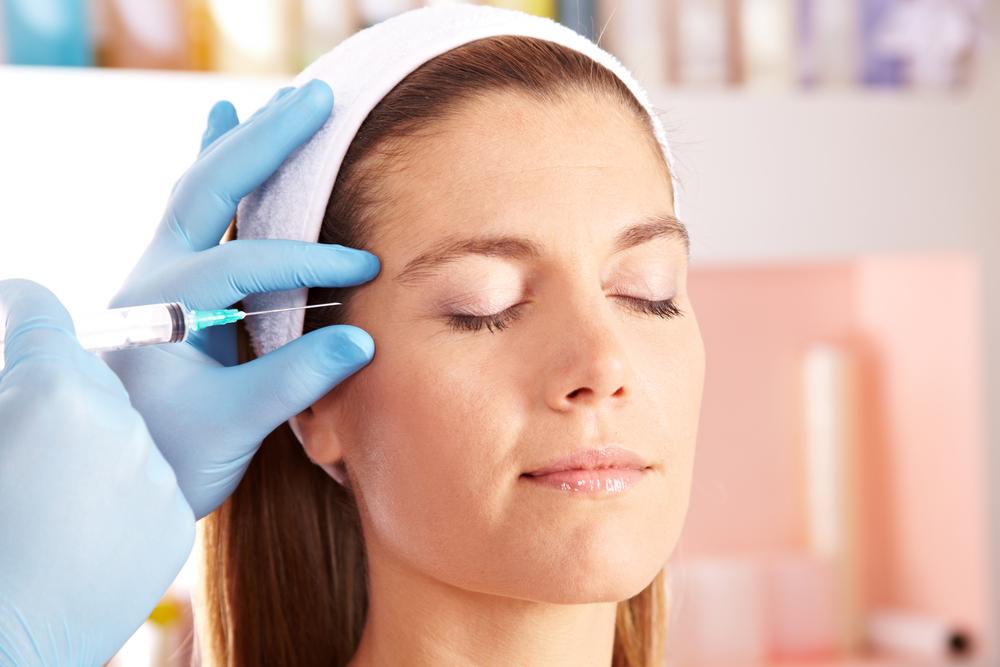
Botox, scientifically known as botulinum toxin type A, is administered through precise injections targeted at specific areas around the head and neck. This procedure is performed by trained medical professionals, usually neurologists specializing in headache medicine. The goal is to relax certain muscles and inhibit nerve signaling pathways that contribute to migraine pain.
During a typical treatment session, patients receive between 30 to 40 small injections distributed across multiple injection sites on both sides of the head and neck. These injections are carefully placed around key muscles such as the forehead, temples, back of the head, and neck muscles. The number of shots and targeted areas may vary depending on the severity and location of the patient's migraines. The injections are generally spaced approximately every 12 weeks to maintain effectiveness, making it a long-term preventive approach rather than a one-time remedy.
Patients are advised to arrive with a clean face and should inform their healthcare provider about any allergies, medication use, or underlying health conditions before the procedure. The injection process itself usually takes about 15 to 30 minutes, making it a relatively quick outpatient procedure. Most individuals tolerate the injections well, though some may experience minor discomfort or localized pain during the process.
In terms of results, many patients begin to notice fewer migraine episodes and reduced severity within two to three weeks after their initial treatment. The full benefits tend to accumulate over successive treatments, especially in those with chronic, frequent migraines. Consistent follow-up sessions are essential to sustain relief and assess ongoing needs.
Who Should Consider Botox for Migraine Relief?
Botox is primarily recommended for adults suffering from chronic migraines—defined as having at least 15 headache days per month, with each episode lasting four hours or more. It is particularly beneficial for patients who have not responded well to traditional preventive medications or who experience intolerable side effects from oral medications.
It is important to understand that Botox is not suitable for everyone. For example, it has not been proven effective for episodic migraines that occur less frequently than 15 days a month. Additionally, pregnant or breastfeeding women are generally advised to avoid Botox until further safety data is available. Consulting with a qualified neurologist will help determine if Botox therapy is appropriate based on your specific health profile and migraine pattern.
How Does Botox Alleviate Migraine Symptoms?
Botox works by blocking specific nerve signals involved in transmitting pain. When injected, it prevents the release of certain neurotransmitters responsible for sending pain signals to the brain. This chemical interference reduces nerve excitability and muscle contractions that typically exacerbate migraine pain. By calming hyperactive nerves and relaxing tense muscles, Botox reduces both the frequency and severity of migraine episodes.
Scientific studies confirm that Botox can significantly decrease the number of headache days experienced by those with chronic migraines. Many patients report longer pain-free periods and improved overall quality of life after undergoing treatment.
Side Effects and Precautions
While Botox is generally safe when administered by trained professionals, like all medical treatments, it carries potential side effects. Common temporary side effects include mild neck pain, stiffness, or tenderness at injection sites. Some individuals may experience mild headaches shortly after the procedure.
More severe but rare adverse reactions include allergic responses such as hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the face and lips. It is vital to inform your healthcare provider immediately if any allergic symptoms develop.
Injected toxins can sometimes cause unintended muscle weakness, drooping eyelids (ptosis), double vision, changes in voice, or swallowing difficulties. Patients should be vigilant about these symptoms and seek medical attention promptly if they occur.
Pre-treatment consultation with a healthcare professional helps minimize risks. Patients are advised to avoid alcohol and blood-thinning medications before injections to reduce bruising and bleeding complications.
Post-Treatment Expectations and Long-Term Outlook
After the Botox injections, some people may experience minor side effects such as bruising, fatigue, or a sensation of heaviness in the head. These effects are temporary and typically resolve within a few days. It is common to notice some facial weakness or tenderness, especially after initial treatments, but these usually improve over time.
Many patients find that their migraine frequency decreases substantially after a few treatment cycles, leading to fewer days of pain and a better quality of life. It is important to have regular follow-up appointments to assess the effectiveness and determine whether additional sessions are necessary.
It’s worth noting that Botox functions primarily as a preventive measure rather than an immediate pain relief treatment. Results tend to improve cumulatively over multiple sessions, making it an ongoing management strategy rather than a quick fix. Patients should maintain realistic expectations and continue other recommended lifestyle modifications to optimize results.
In summary, Botox provides a viable and scientifically supported option for managing chronic migraines, especially for those who have exhausted other preventive measures. Consulting experienced headache specialists can help tailor a treatment plan that maximizes benefits while minimizing risks. With continued advancements and research, Botox remains a promising tool in the comprehensive management of chronic migraine suffering, offering hope for a more comfortable and functional life.