Comprehensive Guide to the Top 5 Medications for Effective Gout Management
Learn about the top five medications for managing gout symptoms effectively. This comprehensive guide covers NSAIDs, uric acid reducers, corticosteroids, and specific gout treatments, providing insights into their usage, costs, and benefits. Proper medication management, combined with dietary and lifestyle changes, can significantly improve quality of life for gout sufferers. Understand how these drugs work and what to expect for long-term control and relief from gout pain and flare-ups.

Your Complete Guide to the Top 5 Medications for Managing Gout Symptoms Effectively
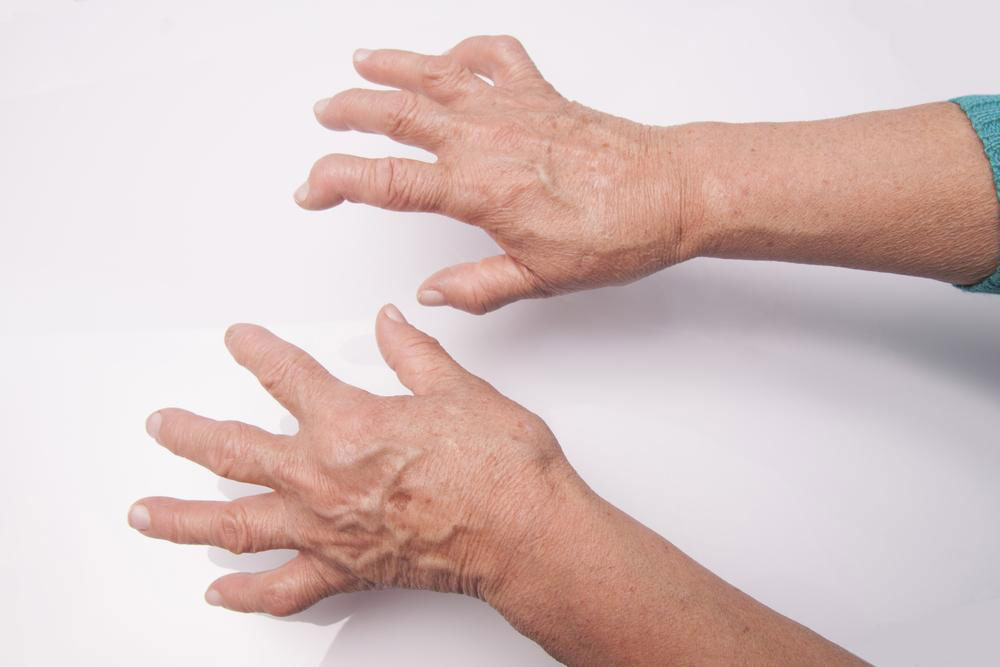
Gout is a well-known form of arthritis that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by sudden, severe episodes of joint pain accompanied by redness, swelling, and warmth in the affected areas. If not managed properly, gout can lead to chronic joint damage and reduce quality of life. This condition is primarily caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood, which leads to the formation of urate crystals within the joints. Understanding the most effective medications designed to control and alleviate gout symptoms is essential for anyone dealing with this painful condition.
Gout develops predominantly due to the buildup of uric acid, a waste product formed when the body breaks down purines—substances found naturally in certain foods like red meats, shellfish, and alcohol, especially beer. When uric acid levels rise beyond the body’s ability to eliminate it efficiently, crystals deposit in joints, triggering acute flare-ups. These attacks can be excruciating, often occurring suddenly during the night, and can persist for several days. Therefore, medications that reduce inflammation, lower uric acid levels, and prevent flare-ups are vital in effective gout management. Alongside maintaining a gout-friendly diet—rich in anti-inflammatory foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains—and avoiding purine-rich foods, pharmacological treatments play a pivotal role.
1. Naprosyn (Naproxen) – The Anti-Inflammatory Ally
Naprosyn, known generically as Naproxen, is one of the most widely prescribed NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) for gout pain relief. This medication is praised for its ability to significantly reduce joint pain, swelling, and inflammation associated with gout attacks. Available in various strengths, Naproxen requires a healthcare provider’s prescription, but it is highly effective at managing acute flare-ups and chronic symptoms alike. The medication works by inhibiting cyclooxygenase enzymes (COX-1 and COX-2), which play a central role in producing inflammatory prostaglandins. Patients often find relief in doses ranging from 250mg to 500mg, taken every 12 hours, with adjustments based on severity and tolerability.
From a financial perspective, Naprosyn offers affordable options, with generic versions costing approximately $16.13 for a standard 30-count pack of 500mg tablets. For those seeking additional savings, medication discounts are available through platforms like GoodRx Gold, which can offer discounts of up to 76%. Pharmacies often provide coupons and discounts that make regular use of Naproxen accessible for most patients, making it a practical choice in gout management. It’s important to remember that NSAIDs are typically used for short-term management of flares because prolonged use can pose gastrointestinal and cardiovascular risks.
2. Zyloprim (Allopurinol) – The Uric Acid Reducer
Preventing gout attacks over the long term requires reducing uric acid levels in the bloodstream. Zyloprim, known generically as Allopurinol, is a cornerstone medication in chronic gout management. It functions as a xanthine oxidase inhibitor, which blocks the enzyme responsible for converting purines into uric acid. By lowering uric acid production, Zyloprim effectively prevents the formation of urate crystals and subsequent joint attacks. This medication is usually prescribed for patients with frequent or severe gout episodes or those who exhibit elevated uric acid levels despite dietary modifications.
In terms of cost, Zyloprim averages around $19.62 for a 30-tablet pack of 300mg tablets, making it a cost-effective long-term solution. With significant discounts of up to 69% available through GoodRx Gold, patients have access to affordable treatment options. Consistent dosing is crucial to achieve optimal results, with typical regimens involving daily intake of 300mg to 600mg depending on individual needs. Regular monitoring of uric acid levels and kidney function is recommended during treatment to avoid potential side effects like hypersensitivity reactions or renal issues.
3. Dexamethasone (Taperdex) – The Corticosteroid for Acute Relief
When gout attacks become severe or do not respond adequately to NSAIDs, corticosteroids such as Dexamethasone are often prescribed to rapidly control inflammation and pain. Dexamethasone, marketed under the brand Taperdex, is a potent corticosteroid that reduces inflammation in joints and other tissues. It’s particularly useful for patients who cannot tolerate NSAIDs or for cases where rapid symptom control is necessary. The medication is usually administered in small, short-term courses—typically in doses of 1.5mg for 6 to 12 days, depending on severity—to minimize side effects inherent in steroid therapy.
For cost-conscious patients, Dexamethasone is economical, with a typical package of 10 tablets of 4mg costing up to $10, especially when purchased through discount programs like GoodRx Gold, which can offer savings of up to 58%. While corticosteroids are effective in controlling acutely inflamed joints, they are not suitable for long-term use due to potential side effects such as weight gain, osteoporosis, and suppression of the body’s own steroid production.
4. Prednisone – The Versatile Corticosteroid
Prednisone is another corticosteroid often used in gout treatment, especially when inflammation is intense or persistent. It is available in generic form in numerous formulations, including tablets, oral solutions, and dose packs, offering flexibility for various patient needs. Prednisone is favored for its rapid onset of action and affordability, with an average cheap price of approximately $9.73 for a pack of 10 tablets at 20mg each. Like Dexamethasone, it effectively diminishes joint inflammation and pain during acute gout attacks, and it can be used in longer courses if necessary.
Patients benefit from discounts through GoodRx Gold, which can provide savings of up to 78% on prescriptions. However, healthcare providers usually recommend tapering the dose gradually to prevent withdrawal symptoms and to avoid flare-ups during cessation. Long-term or high-dose use warrants careful monitoring due to risks such as osteoporosis, hyperglycemia, and increased infection susceptibility. Prednisone’s versatility makes it a mainstay in gout treatment protocols, especially in complex cases or when other treatments are contraindicated.
5. Colchicine (Mitigare, Colcrys) – The Gout-Specific Symptom Manager
Colchicine is a unique medication specifically targeting gout flare-ups. Originally derived from the Colchicum autumnale plant, it remains a vital option for managing acute gout symptoms and preventing recurrent attacks. Colchicine does not affect uric acid levels directly but works by reducing inflammation caused by urate crystal deposits in joints. It’s commonly prescribed during the early stages of gout attacks or as a prophylactic measure in patients prone to frequent episodes.
This medication is available as tablets or capsules, typically in doses of 0.6mg. It’s generally prescribed in short-term courses during acute flare-ups, with dosing regimens often involving 1.2mg initially, followed by smaller doses to minimize side effects. Cost-wise, colchicine can be economical, with discounts of up to 26% available through GoodRx Gold for 30 tablets. Prices vary based on the brand and dosage, but it remains an essential part of any comprehensive gout treatment plan.
Some common side effects include gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea, and diarrhea—especially at higher doses. Long-term use should be closely monitored by healthcare providers to avoid toxicity. When used appropriately, colchicine can significantly reduce the severity and frequency of gout attacks, improving patients’ quality of life over time.
Managing gout effectively involves a combination of medication, lifestyle, and dietary adjustments. The medications highlighted here—Naproxen, Allopurinol, Dexamethasone, Prednisone, and Colchicine—form the core arsenal that healthcare providers use to help patients control symptoms, prevent flare-ups, and minimize long-term joint damage. Patients should always consult their healthcare provider before starting, stopping, or adjusting any medication to ensure safe and effective treatment tailored to their specific health needs. Staying informed about new developments and staying compliant with prescribed regimens can make a significant difference in living well with gout.