Essential Nutritional Strategies to Reduce Cancer Risk and Promote Prevention
This comprehensive guide highlights key nutritional strategies to lower cancer risk by emphasizing the importance of foods like garlic, broccoli, berries, turmeric, green tea, and tomatoes. Supported by scientific research, these foods possess powerful anti-cancer properties and can be naturally incorporated into daily meals to promote health and prevent cancer. Whether for general health or supporting cancer treatment, understanding the role of diet in cancer prevention is vital for maintaining wellness and reducing vulnerability to this complex disease.

Essential Nutritional Strategies to Reduce Cancer Risk and Promote Prevention
Cancer remains one of the most complex and challenging health conditions worldwide, encompassing numerous types and involving a multitude of biological processes. While genetics play a role, extensive scientific research has increasingly highlighted the significant influence of lifestyle choices, particularly dietary habits, on the development and progression of various cancers. Understanding how specific foods and nutrients can either increase vulnerability or provide protective benefits is essential for those seeking to lower their risk of developing cancer. Incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods into daily meals not only supports overall health but also offers targeted benefits in cancer prevention. This comprehensive guide explores some of the most powerful foods known for their cancer-fighting properties, backed by scientific evidence and nutritional studies.
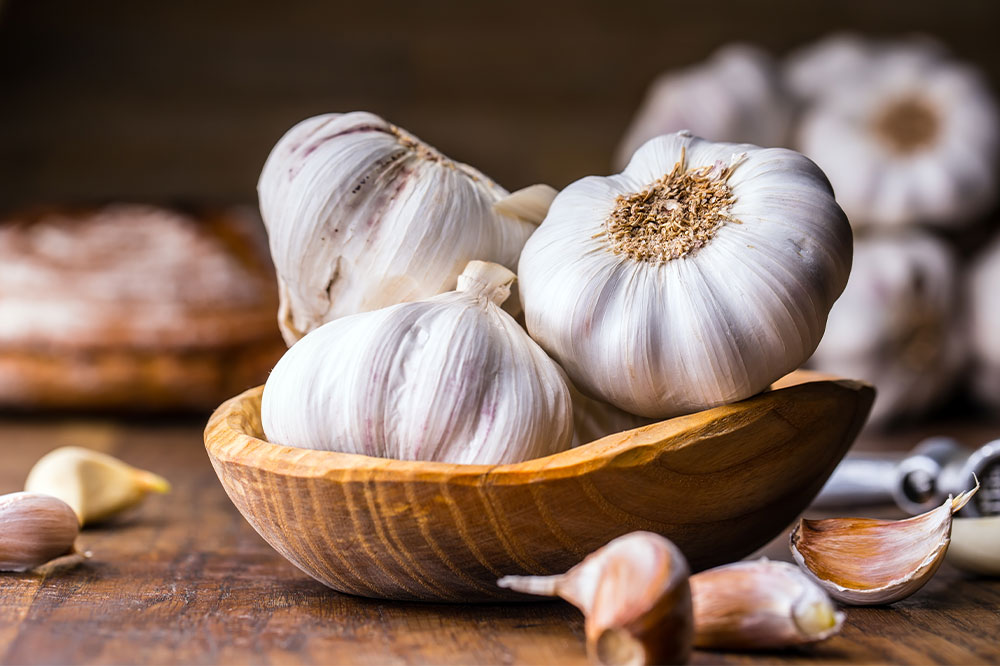
Garlic: Nature’s Anti-Cancer Weapon
Garlic has long been celebrated in traditional medicine for its numerous health benefits, and modern research continues to uncover its potential in fighting cancer. The key bioactive compound in garlic, allicin, is responsible for many of its medicinal properties. Allicin is formed when garlic is chopped, crushed, or chewed, releasing its potent compounds. Scientific studies have demonstrated that garlic's anti-cancer effects may be linked to its ability to stimulate apoptosis (programmed cell death) in abnormal cells, inhibit tumor cell proliferation, and reduce inflammation. Regular consumption of garlic has been associated with a decreased risk of stomach, colorectal, and other gastrointestinal cancers. Including raw or cooked garlic in meals can be a simple yet effective strategy for enhancing your nutritional defenses against cancer.
Broccoli: A Cruciferous Champion Against Cancer
Broccoli belongs to the cruciferous vegetable family, which also includes cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage. These vegetables contain high levels of sulforaphane, a sulfur-containing compound that exhibits powerful anti-cancer properties. Sulforaphane works by activating various detoxification enzymes, inhibiting inflammation, and inducing apoptosis in cancer cells. Studies indicate that regular intake of broccoli and related vegetables can significantly reduce the risk of colorectal, breast, prostate, and other cancers. To maximize benefits, it is recommended to consume broccoli either raw or lightly steamed to preserve its valuable nutrients. Incorporating broccoli into salads, stir-fries, or roasted dishes is a great way to promote cancer prevention through diet.
Berries: Rich in Antioxidants and Phytochemicals
Berries such as raspberries, strawberries, blackberries, and goji berries are renowned for their high antioxidant content. Antioxidants neutralize free radicals, unstable molecules that can damage DNA and trigger cancerous changes in cells. Berries also contain phytochemicals like anthocyanins, ellagic acid, and resveratrol, which have been studied for their anti-cancer effects. Research suggests that regular consumption of berries can help prevent cancers of the colon, esophagus, and other regions. They are versatile, delicious, and easy to include in your diet—add them to smoothies, cereals, yogurts, or enjoy them fresh as a healthy snack.
Turmeric: The Golden Spice with Tumor-Reducing Potential
Turmeric, a bright yellow spice commonly used in Indian cuisine, contains curcumin—an active compound with notable anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties. Curcumin has been shown to inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells, interfere with cancer signaling pathways, slow tumor growth, and induce apoptosis. Laboratory and animal studies support turmeric’s role in reducing the risk of colorectal, pancreatic, breast, and prostate cancers. Combining turmeric with black pepper enhances absorption, making it more effective. Incorporating turmeric into curries, soups, or smoothies can be an easy way to harness its protective effects and support cancer prevention efforts.
Green Tea: A Potent Source of Cancer-Preventive Antioxidants
Green tea is rich in catechins, particularly epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), a powerful antioxidant that has garnered considerable attention in cancer research. EGCG helps protect cells from oxidative damage, inhibit tumor cell growth, and induce cancer cell death. Epidemiological studies have linked regular green tea consumption with a decreased risk of several cancers, including breast, liver, skin, and lung cancers. To incorporate green tea into your daily routine, enjoy a few cups of freshly brewed tea throughout the day. Its antioxidant benefits extend beyond cancer prevention, supporting overall cellular health and immune function.
Tomatoes: The Lycopene-Rich Fruit for Cancer Defense
Tomatoes are globally recognized for their high lycopene content, a potent carotenoid pigment with strong antioxidant properties. Lycopene has been extensively studied for its role in preventing prostate, lung, and other cancers. It works by neutralizing free radicals, reducing inflammation, and modulating cellular growth pathways. Unlike other nutrients, lycopene absorption improves when tomatoes are cooked or processed, making tomato sauces and pastes particularly effective sources. Including tomatoes in salads, sauces, soups, or roasting them intensifies their health benefits and can be a delicious component of a cancer-preventive diet.
For individuals already diagnosed with cancer, dietary strategies that emphasize these nutrient-dense foods can complement medical treatments. Conventional therapies such as Lumakras, Neulasta, Ibrutinib, Venclexta, as well as advanced therapies like CAR T-cell therapy and radiopharmaceuticals, are tailored to specific cancer types and individual patient needs. Combining these treatments with targeted nutritional support can improve outcomes and overall well-being. Consultation with healthcare providers is essential to develop a comprehensive care plan that integrates diet, medical therapy, and lifestyle modifications for optimal results.