Comprehensive Approaches to Effectively Manage Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST)
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) are rare but treatable cancers requiring a multidisciplinary approach. This article explores comprehensive management strategies, including targeted therapies, surgery, nutrition, lifestyle changes, and emotional support, to improve patient outcomes and quality of life. Early diagnosis and personalized care plans are essential for effective GIST control and long-term health maintenance.
Comprehensive Approaches to Effectively Manage Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST)
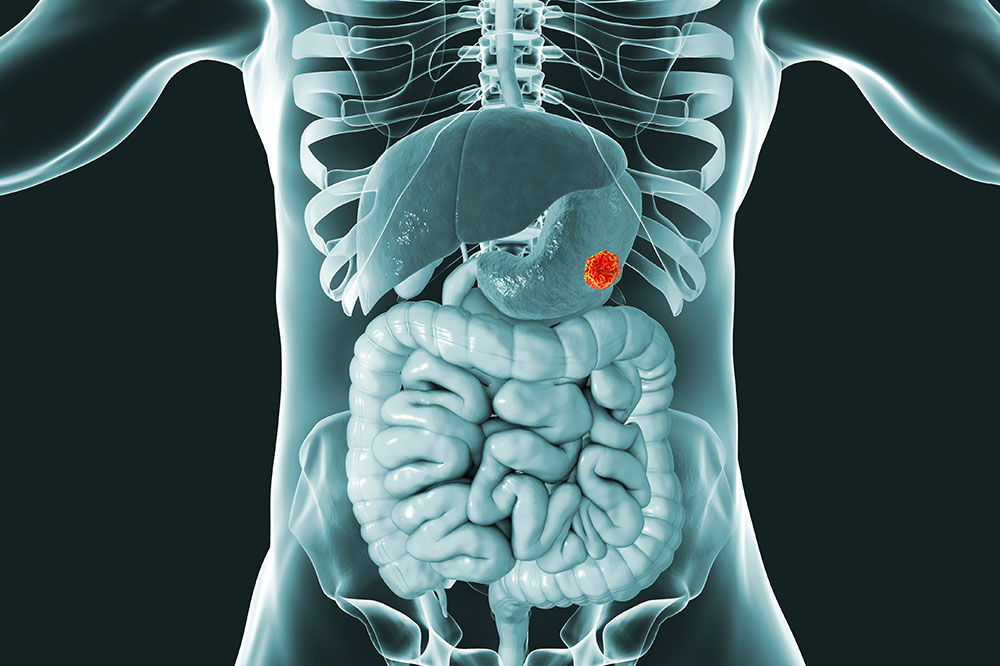
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors, commonly known as GIST, are a rare form of cancer that presents unique challenges in diagnosis and treatment. These tumors originate from the interstitial cells of Cajal — the nerve cells in the digestive tract responsible for coordinating motility. Although relatively uncommon, GIST can significantly impact a patient's quality of life due to symptoms like anemia, persistent abdominal discomfort, nausea, vomiting, and weight loss. Early detection and a well-rounded management plan are crucial for improving prognosis and enhancing life quality for those affected.
Understanding GIST begins with awareness of its causes, symptoms, and progression. While the exact origin of GIST remains unclear, genetic mutations, particularly in the KIT and PDGFRA genes, play a significant role in its development. These mutations lead to abnormal cell growth in the digestive tract’s wall, often resulting in tumors that vary in size and potential for malignancy. Accurate diagnosis involves imaging studies such as CT scans and PET scans, coupled with biopsy procedures to confirm the presence of GIST and identify specific genetic mutations.
Developing an effective management strategy for GIST hinges on a multidisciplinary approach, incorporating medical treatments, nutritional guidance, lifestyle adjustments, and emotional support. Medical intervention often includes targeted therapies such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) like imatinib, which have revolutionized GIST treatment by specifically targeting the mutated genes involved in tumor growth. Surgical removal remains a vital option for localized tumors, especially when they are operable and accessible. In certain cases, combining surgery with targeted therapy offers the best chance for remission or long-term control.
Beyond medication and surgery, nutritional management and lifestyle modifications are vital to support patients. Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber helps strengthen the immune system and manage symptoms like anemia and gastrointestinal discomfort. Patients are encouraged to consume smaller, more frequent meals to ease digestion and improve nutrient absorption. Gentle physical activity, tailored to individual ability, can improve overall well-being, boost energy levels, and reduce stress. Adequate rest is equally important for recovery and emotional resilience.
Psychological and emotional support play a key role in coping with GIST. Patients may experience anxiety, depression, or emotional distress due to diagnosis and treatment demanding ongoing adjustments in their daily routines. Connecting with support groups, counseling services, and healthcare professionals can provide reassurance and practical advice to navigate these challenges. Open communication with the medical team ensures that treatment plans are continually optimized and side effects are managed effectively.
Early consultation with healthcare professionals, including oncologists, nutritionists, and mental health counselors, is essential for crafting personalized treatment plans. Regular monitoring through imaging and blood tests help to assess treatment efficacy and detect any recurrence early. Advances in medical research continue to improve therapeutic options, offering hope for more targeted, less invasive, and more effective treatments in the future.
In conclusion, managing GIST requires a holistic, patient-centered approach that combines medical treatments with lifestyle modifications, nutritional support, and emotional care. By staying informed, engaging actively with healthcare professionals, and adopting a proactive attitude toward health and wellness, patients can better control symptoms, reduce tumor progression risks, and significantly improve their quality of life. As research progresses, the outlook for GIST patients continues to improve, paving the way for more precise and effective management strategies in the future.