Comprehensive Guide to Preventing Gout Attacks: Key Factors and Practical Tips
This comprehensive guide explores the top factors to prevent gout attacks, including medication influences, lifestyle choices, diet, hydration, and proper footwear. Preventing gout involves understanding how excess uric acid builds up due to various triggers. The article offers detailed insights into managing weight, avoiding high-purine foods, staying well-hydrated, and choosing appropriate shoes—all vital steps to reduce flare-ups. With practical tips and expert advice, individuals affected by gout can effectively control their condition and improve their quality of life by adopting a multi-faceted prevention approach.

Comprehensive Guide to Preventing Gout Attacks: Key Factors and Practical Tips
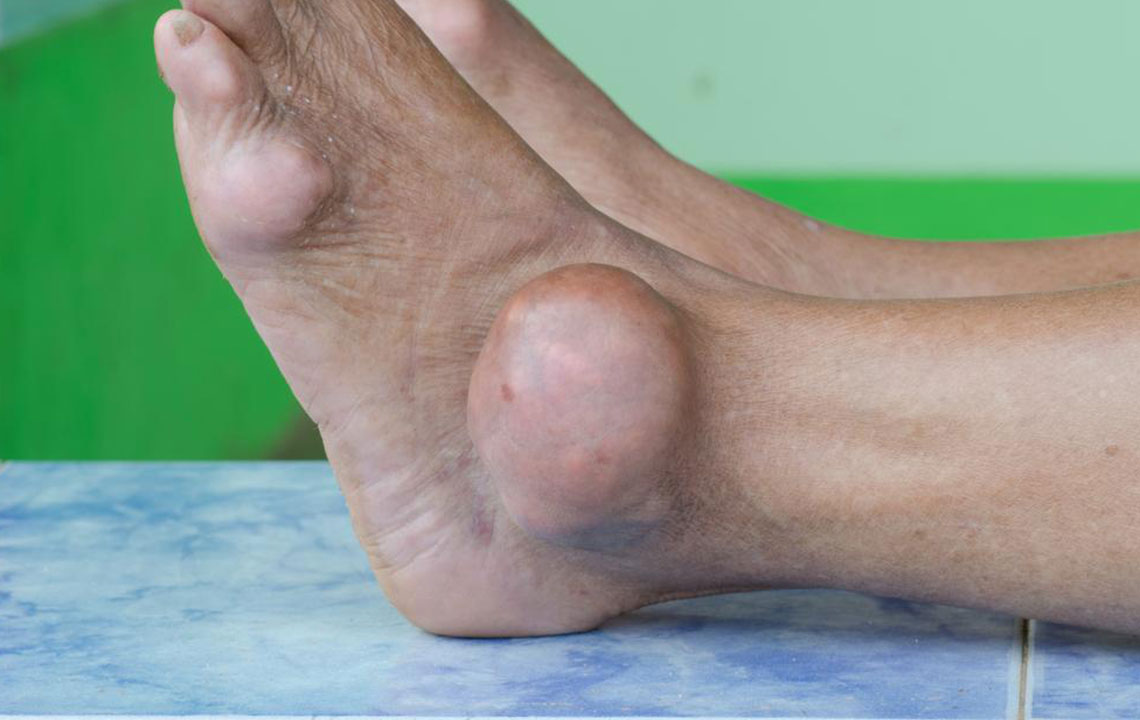
Gout is a complex and often debilitating form of arthritis that primarily affects the joints, causing intense burning pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness. It is widely recognized as a chronic condition that can significantly impair quality of life if not properly managed. The episodes of gout attacks can be unpredictable, making understanding the underlying causes and prevention strategies essential for those affected.
Understanding what triggers gout attacks provides a foundation for effective management. Gout develops due to the accumulation of uric acid in the bloodstream, a condition known as hyperuricemia. When uric acid levels become excessive, they tend to crystallize in the joints, leading to painful inflammation characteristic of gout. By identifying and modifying various risk factors, individuals can reduce the frequency and severity of attacks, improving their overall well-being.
Uric acid is a waste product generated from the natural breakdown of purines—compounds found ubiquitously in many foods and beverages. Normally, uric acid dissolves in the blood and is eliminated through the kidneys via urine. However, when there’s an overproduction of uric acid or the kidneys fail to excrete it efficiently, excess uric acid accumulates. This surplus then forms sharp, needle-like crystals within the joints, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness. The big toe is often the first joint affected, but gout can also involve other parts of the foot, ankles, knees, elbows, and wrists.
Interestingly, certain medications and substances can influence uric acid levels, either elevating them or impairing their clearance. Recognizing these factors is crucial to preventing gout attacks effectively.
Medications and Substances That Impact Gout Risk
Various drugs can influence uric acid levels either directly or indirectly, increasing the likelihood of gout flare-ups. For example, aspirin, especially in low doses, can raise uric acid levels by reducing renal clearance. This is particularly noteworthy in women, where low-dose aspirin use for cardiovascular prevention may inadvertently elevate gout risk. Diuretics such as hydrochlorothiazide, metolazone, and chlorothiazide are commonly prescribed for conditions like hypertension and heart failure—yet they can impair kidney function and decrease the excretion of uric acid, thereby elevating blood levels.
Other medications, including immunosuppressants like cyclosporine, certain blood pressure medicines such as ACE inhibitors, and some chemotherapy agents, may also contribute to increased uric acid levels. If you are on such medications, consulting with your healthcare provider to balance treatment benefits with potential gout risks is essential.
Understanding these medication effects allows for better management strategies, such as adjusting dosages or exploring alternative treatments that have minimal impact on uric acid levels.
Excess Body Weight and Its Role in Gout Development
Obesity is a significant risk factor for developing gout. Excess weight impacts uric acid levels in multiple ways. Firstly, adipose tissue (body fat) produces more uric acid, contributing to hyperuricemia. Secondly, obesity often correlates with insulin resistance, which can hinder the kidneys' ability to excrete uric acid efficiently. Furthermore, fat deposits around joints can increase the mechanical stress on these areas, making them more susceptible to crystal formation and inflammation.
Carrying extra weight also makes physical activity more challenging, which could exacerbate joint problems and limit mobility during gout attacks. Weight management through a combination of healthy eating and regular exercise is one of the most effective strategies to lower gout risk. Even modest weight loss can significantly reduce uric acid levels, leading to fewer flare-ups.
Dietary Factors and Their Impact on Gout
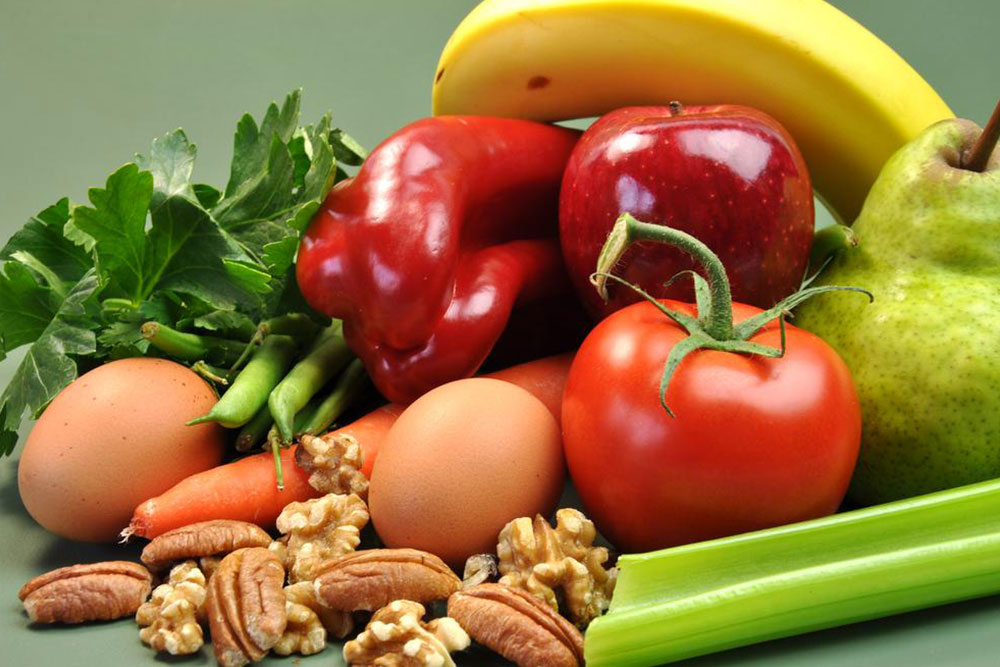
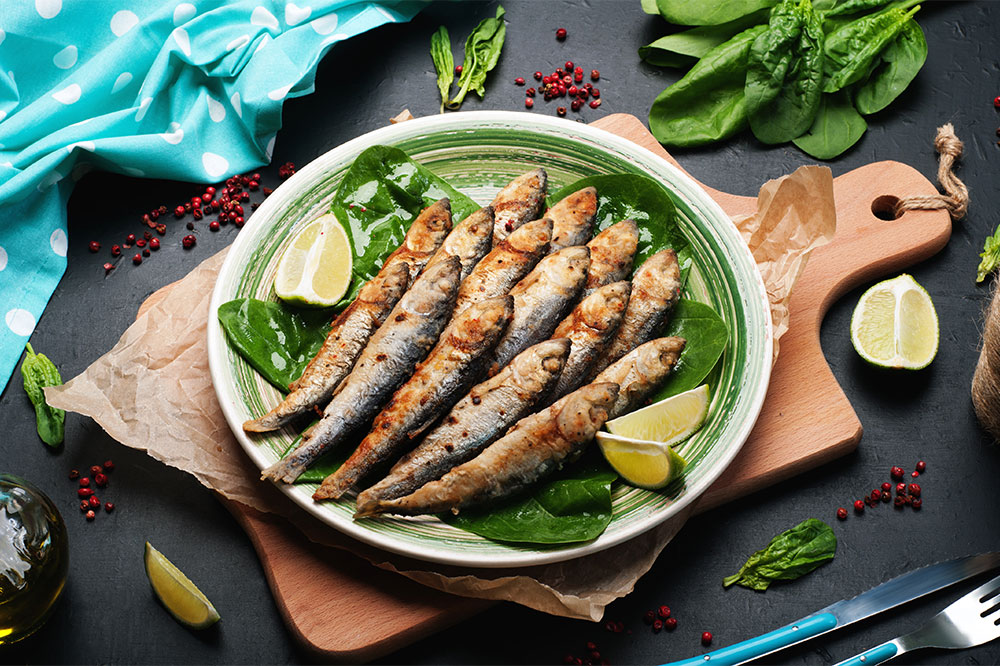
Diet plays a pivotal role in either preventing or provoking gout attacks. Foods high in purines—the building blocks that produce uric acid—should be consumed judiciously. Key high-purine foods include organ meats such as liver and kidneys, shellfish and certain types of seafood like sardines, anchovies, and mackerel, as well as high-fat fish such as salmon. Other culprits are processed meats like bacon, ham, and sausage, along with red meats like mutton and turkey.
In addition to purine-rich foods, sugary drinks — especially those sweetened with high-fructose corn syrup — significantly raise uric acid levels. Alcohol, particularly beer and spirits, is also a major contributor due to its purine content and dehydration effects. Limiting or avoiding these foods and beverages can greatly reduce the risk of gout attacks.
Choosing healthier options like vegetables, low-fat dairy, and whole grains can help manage uric acid levels. For instance, cherries and berries contain antioxidants that may reduce inflammation and lower gout risk. Staying mindful of your diet and making informed food choices are fundamental steps towards effective gout management.
Hydration and Fluid Intake
Dehydration is a silent yet significant trigger for gout attacks. When the body lacks sufficient fluids, uric acid becomes more concentrated in the blood, increasing the chances of crystal formation. Adequate hydration aids the kidneys in flushing out excess uric acid more effectively, thereby reducing blood levels and preventing crystal deposits in the joints.
The general recommendation is to drink at least six to eight glasses of water a day, or roughly 1.5 to 2 liters. During hot weather, physical activity, or illness, ensuring additional fluid intake is vital to compensate for fluid loss. Avoid sugary drinks and alcohol, as they can contribute to dehydration and elevate uric acid levels. Consistent hydration is a simple, yet powerful tool in the prevention of gout attacks and maintaining overall health.
Choosing Proper Footwear to Prevent Joint Stress
Gout commonly affects the big toe joint, causing significant discomfort and difficulty in walking. Wearing appropriate footwear can alleviate pressure on the affected joints and prevent gout flare-ups. Shoes that are tight, narrow, or cause friction can exacerbate symptoms by putting extra stress on the joint, leading to increased inflammation.
Opt for comfortable, well-fitting shoes that provide ample room for the toes. Women should consider lower-heeled options to minimize stress on the toe joint, whereas for men and women, supportive footwear with cushioned soles can help absorb impact and reduce joint strain. Custom orthotics or insoles may also provide additional support.
Good footwear choices are especially crucial during gout attacks, but they also serve as a preventive measure to avoid triggering episodes. Proper footwear not only aids in pain relief but also promotes overall joint health and mobility, making daily activities more manageable for gout sufferers.
In conclusion, preventing gout attacks involves a comprehensive approach that addresses medication effects, lifestyle, dietary habits, hydration, and footwear. By understanding these key factors and actively managing them, individuals can drastically reduce the frequency and severity of gout episodes, leading to a healthier and more comfortable life. If you are prone to gout, consult your healthcare provider for personalized strategies and treatment options to keep this painful condition at bay.