Comprehensive Guide to Mesothelioma Cancer: Key Facts You Need to Know
This comprehensive guide offers essential information on mesothelioma cancer, including its causes, symptoms, stages, treatment options, and dietary tips. Understanding this rare but aggressive disease can aid in early detection and improve management strategies. Learn about the risk factors, signs to watch for, and how medical professionals approach treatment at various stages to enhance patient outcomes and quality of life.
In-Depth Overview of Mesothelioma: What You Should Know
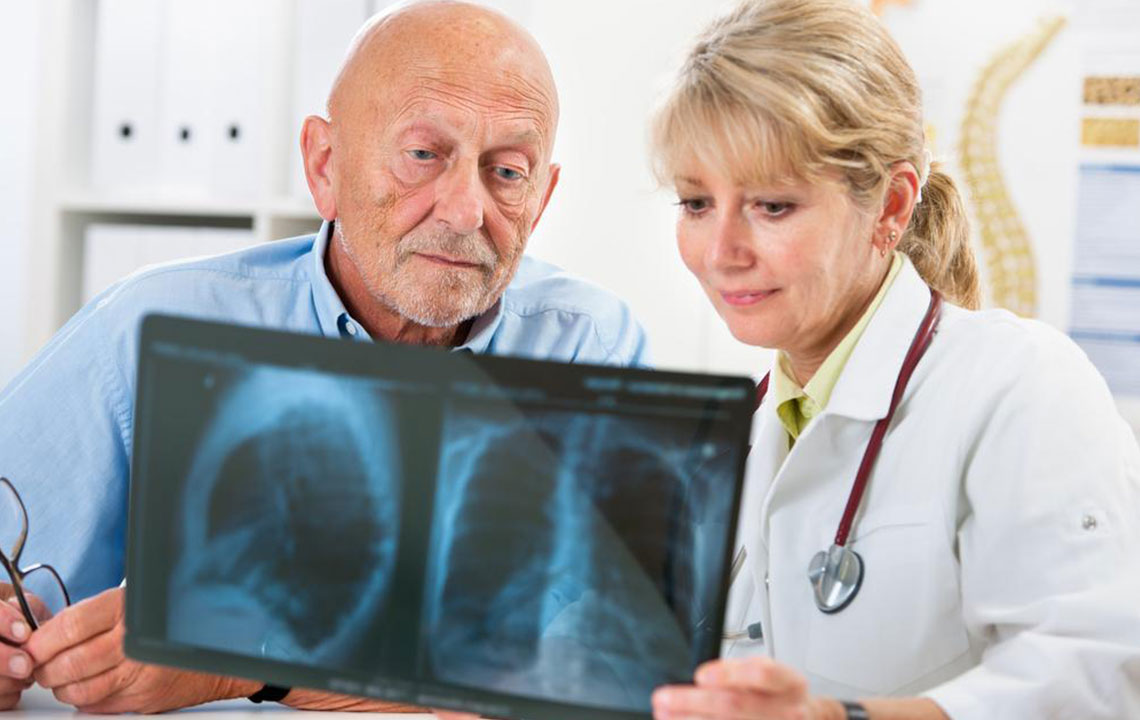
Mesothelioma is a rare but highly aggressive form of cancer that primarily affects the mesothelium, which is the protective lining covering many of the body's internal organs. This disease is predominantly linked to exposure to asbestos fibers, which are microscopic and can be inhaled or ingested. The high propensity of mesothelioma to develop in the chest cavity makes it a significant concern in occupational health, especially for workers exposed to asbestos in industries such as construction, shipbuilding, and manufacturing.
While pleural mesothelioma, which affects the lining of the lungs, is the most common form, accounting for approximately 75% of all cases, the disease can also develop in other parts of the body, including the peritoneum (abdominal cavity), the pericardium (the lining around the heart), and rarely, the testes. The pathogenesis involves asbestos fibers that are inhaled or swallowed, settling in tissue layers, causing chronic inflammation, cellular damage, and eventually tumor formation. Besides asbestos, other less common risk factors include exposure to specific mineral fibers like zeolites, certain viral infections such as SV40, exposure to radiation, and genetic predispositions that elevate individual susceptibility.
Identifying the Symptoms of Mesothelioma
Pleural mesothelioma: manifests as persistent chest pain, severe coughing, shortness of breath, lumps or swelling under the skin of the chest or abdomen, and unexplained weight loss.
Peritoneal mesothelioma: causes abdominal pain, swelling or bloating, nausea, significant weight loss, persistent fatigue, and indigestion.
Pericardial mesothelioma: presents with difficulty breathing, chest discomfort or pain, fatigue, fever, and irregular heartbeats.
Testicular mesothelioma: is characterized by fluid buildup in the scrotum, lumps on the testicles, or swelling.
Understanding the Stages of Mesothelioma
Stage 1: Tumors are confined to the original site with no evidence of spread to neighboring tissues or organs.
Stage 2: The cancer begins to invade nearby structures, such as the diaphragm or chest wall, and may involve regional lymph nodes.
Stage 3: Tumors extend to involve adjacent tissues, more lymph nodes, and distant organs within the chest or abdominal cavity.
Stage 4: The most advanced stage, where the cancer has metastasized to distant organs, lymph nodes, and tissues, making treatment more challenging.
Treatment Options and Outlook
Stage 1: Treatment typically involves aggressive methods such as surgical removal of tumors, combined with radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. At this stage, patients may expect survival times exceeding 21 months with optimal care.
Stage 2: Similar multimodal treatments are employed, aiming to control disease progression. Average survival ranges around 19 months, depending on individual health and treatment response.
Stage 3: Focus shifts more towards relieving symptoms and improving quality of life. Survival time averages approximately 16 months, emphasizing palliative care strategies.
Stage 4: The emphasis is on palliative and supportive care to maximize comfort. Estimated survival time is about one year, and treatment is tailored to alleviate pain and symptoms rather than cure.
Dietary and Lifestyle Recommendations
Include omega-3 rich fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines to help reduce inflammation.
Eat high-fiber foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and legumes to support overall health and immune function.
Incorporate herbs with anti-inflammatory properties such as turmeric, basil, mint, and rosemary into daily meals.
Consume sources of Coenzyme Q10—found in organ meats, fatty fish, and nuts—to support cellular energy production.
Drink green and herbal teas, which contain antioxidants that can help combat cellular stress.
It is important to remember that this article provides general informational content. For accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment options, always consult qualified healthcare professionals and specialists in oncology and pulmonology.