Comprehensive Guide to Foods to Avoid for Effective Diabetes Management
This comprehensive guide highlights the key foods that individuals with diabetes should avoid or limit to maintain optimal blood sugar levels. From sugary drinks to processed meats and refined carbs, learn how dietary choices impact diabetes management and discover healthier alternatives to support overall well-being. Effective diet management can reduce complications, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote heart health, essential for a balanced diabetic lifestyle.

Key Foods to Restrict or Eliminate for Better Blood Sugar Control in Diabetes
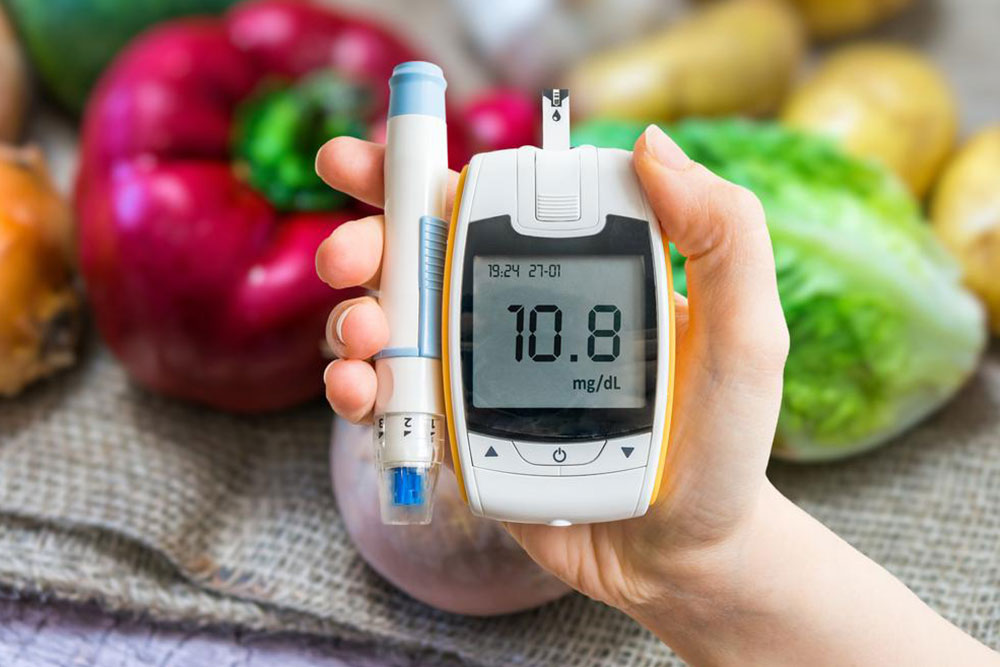
Maintaining stable blood glucose levels is a vital aspect of managing diabetes effectively. Nutrition plays a critical role, and while a balanced diet including carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats is essential, certain foods can adversely affect blood sugar control. Consuming specific items excessively or regularly can lead to unwanted spikes or dips, complicating diabetes management. This comprehensive guide outlines the foods that individuals with diabetes should consider limiting or avoiding to optimize their health and prevent complications.
Sugary Beverages
Beverages such as sodas, sweetened iced teas, lemonades, and commercial fruit drinks are high in added sugars and simple carbohydrates. These drinks rapidly elevate blood glucose levels and contribute to increased insulin demand. The high fructose content in these drinks can lead to insulin resistance, weight gain, and accumulation of visceral fat. Furthermore, excessive consumption is associated with a higher risk of fatty liver disease and metabolic syndrome. Instead of sugary drinks, opt for healthier alternatives like infused water with fresh cucumber and mint, sparkling water flavored naturally with lemon or lime, or herbal teas. These drinks provide hydration without causing blood sugar spikes and support overall health.
Refined Carbohydrates and Their Impact
Foods made from refined grains, such as white bread, regular pasta, and standard white rice, are quickly absorbed by the body, leading to rapid increases in blood glucose levels. These foods are stripped of their fiber content, which normally helps slow down glucose absorption and stabilizes blood sugar. Consuming refined carbs regularly can impair insulin sensitivity over time. To enhance glycemic control, diabetics should prioritize whole grains like brown rice, steel-cut oats, barley, whole-wheat bread, and quinoa. These options are rich in dietary fiber, which not only moderates blood sugar levels but also promotes gut health and supports weight management.
Full-Fat Dairy Products and Heart Health
Many dairy products available on the market are full of saturated fats, which can worsen insulin resistance and raise LDL cholesterol levels, thereby increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease—a common concern among diabetics. Items such as full-fat cheeses, ice cream, creamy yogurt, and butter should be consumed in moderation or replaced with healthier options. Unsweetened, plain, low-fat or fat-free dairy products like plain yogurt, skim milk, and cottage cheese provide essential nutrients without adding unhealthy fats. These choices support better blood sugar control and heart health.
Fatty and Processed Meats
Processed and fatty meats such as bacon, sausages, ribs, and high-fat cuts like marbled beef contain significant amounts of saturated fats that contribute to increased cholesterol levels and systemic inflammation. Regular intake of these foods elevates the risk of cardiovascular complications common in diabetics. A better approach is to select lean protein sources, including skinless poultry, lean cuts of beef, fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, shellfish, and plant-based proteins like legumes and tofu. Incorporating these healthier options supports heart health, reduces inflammation, and maintains stable blood sugar levels.
Dried Fruits and Sugar Concentration
While fresh fruits are a nutritious source of vitamins, minerals, and fiber, dried fruits like raisins, apricots, and dates are highly concentrated sources of natural sugars and carbohydrates. For instance, a single serving of dried raisins can contain over 115 grams of carbs, enough to cause significant blood sugar spikes. Consuming dried fruits frequently can make glycemic control challenging. Instead, opt for fresh fruits like berries, apples, pears, and high-fiber options, which provide essential nutrients without the high sugar load. Portion control is also vital when incorporating fruits into a diabetic-friendly diet, as moderation makes a significant difference in managing blood sugar levels effectively.
Overall, maintaining a diet that minimizes the intake of these foods is essential for individuals managing diabetes. Replacing harmful options with nutrient-dense, high-fiber, and unsaturated fat-rich foods can improve insulin sensitivity, support cardiovascular health, and promote overall well-being. Proper dietary choices, combined with regular physical activity and medical guidance, can greatly enhance quality of life for diabetics. Always consult with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians to develop a personalized nutrition plan tailored to your specific needs and health goals.