Comprehensive Guide to Managing Meniscus Tear Pain and Recovery Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores effective management strategies for meniscus tear discomfort, including immediate care, medical evaluation, and rehabilitation techniques. It provides detailed insights into symptoms, treatment options, and recovery timelines, emphasizing the importance of timely intervention and professional guidance to ensure optimal knee health and restore mobility. Ideal for athletes, active individuals, or anyone experiencing knee pain due to meniscus injury, this article offers practical advice to facilitate recovery and prevent further damage.
Comprehensive Guide to Managing Meniscus Tear Pain and Recovery Strategies
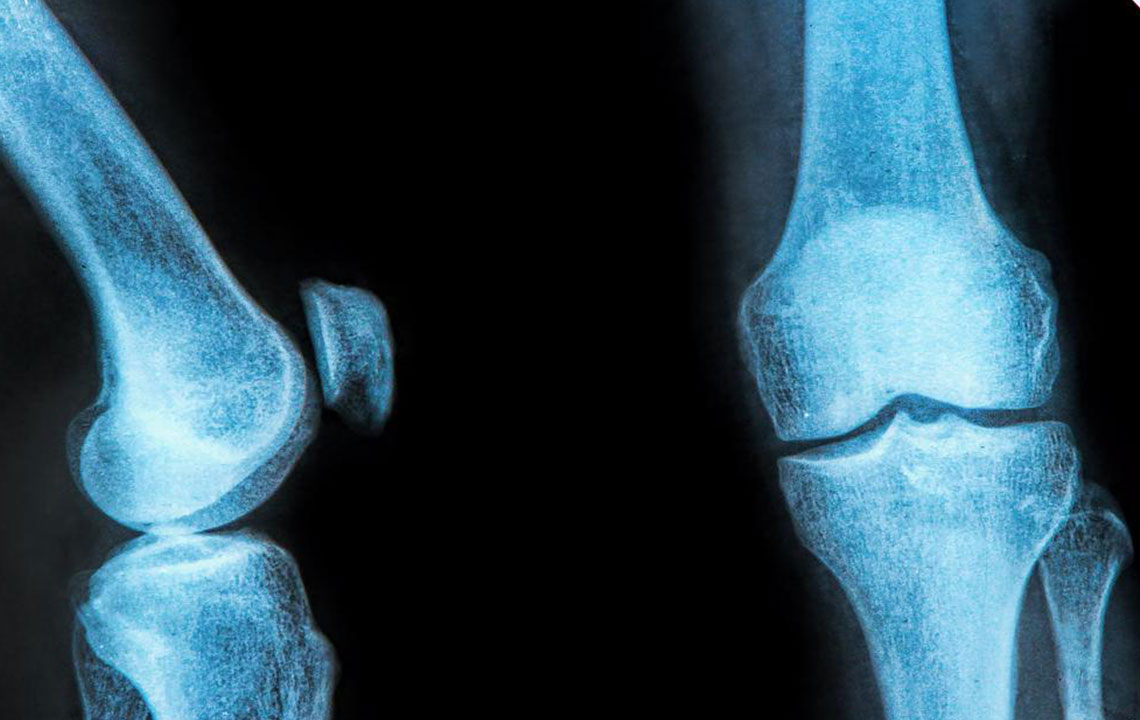
The meniscus is a critical piece of cartilage within the knee joint, acting as a shock absorber that helps maintain the knee's stability and smooth functionality. Located between the thighbone (femur) and the shinbone (tibia), each knee contains two menisci: the lateral meniscus on the outer side and the medial meniscus on the inner side. These structures play a vital role in evenly distributing weight, reducing friction, and preventing joint degeneration. However, they are susceptible to injury, especially due to aging processes, high-impact sports activities, or sudden traumatic events.
Meniscus tears are among the most common knee injuries, often resulting from twisting or pivoting motions while bearing weight. These injuries can occur during activities such as running, jumping, or sudden direction changes in sports like basketball, soccer, or skiing. The forceful twist, combined with weight bearing, often causes a tear that leads to significant discomfort and functional impairment.
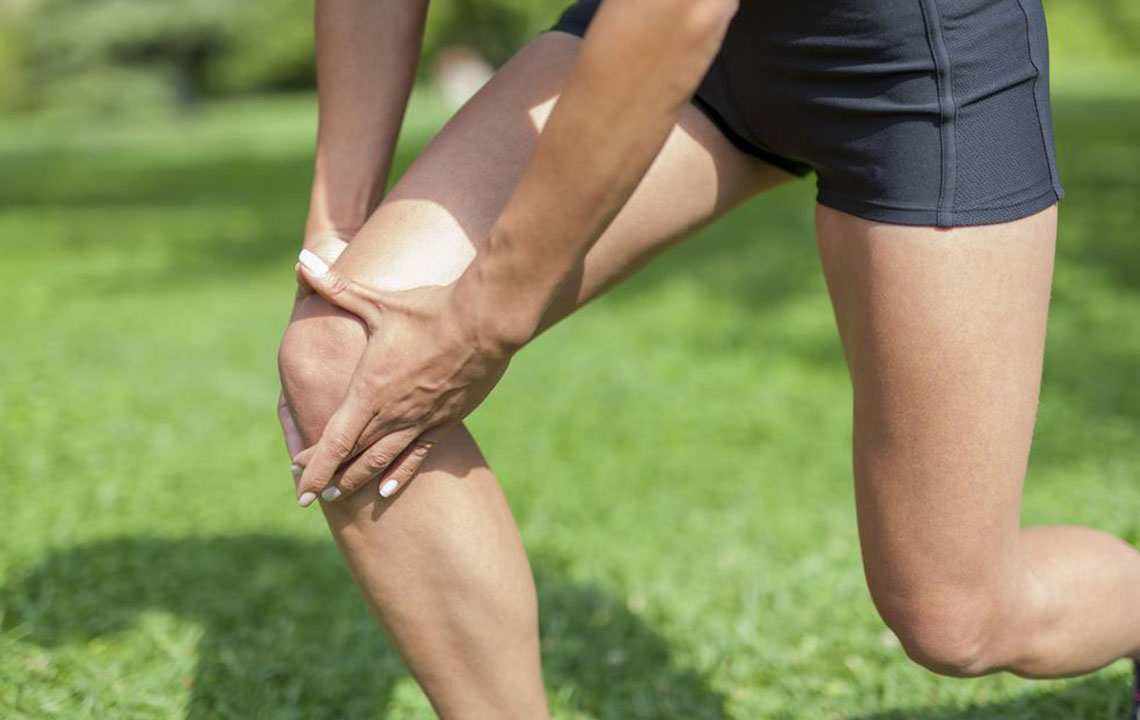
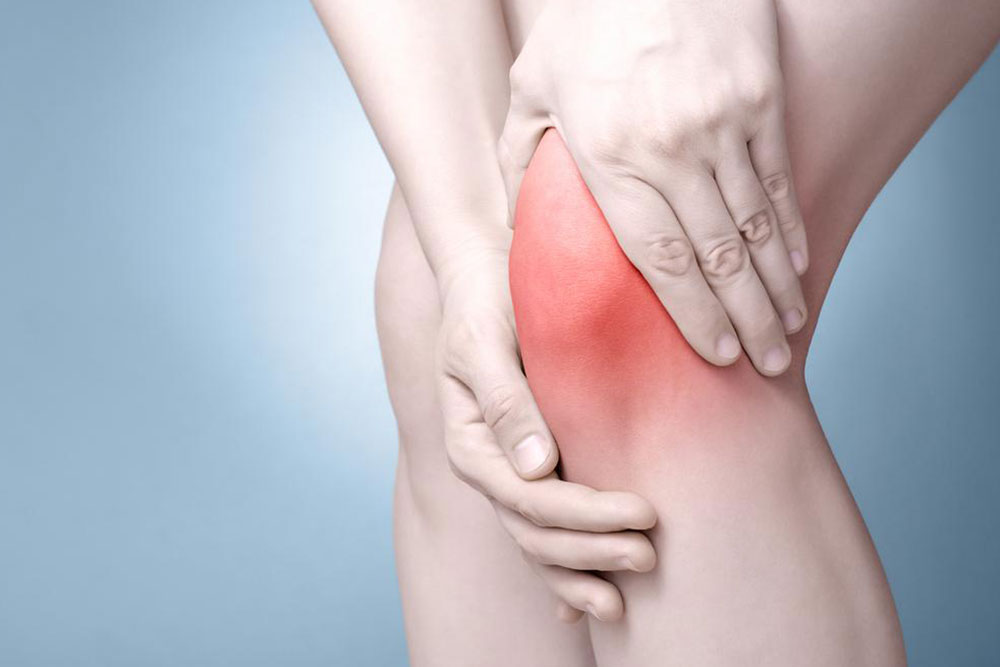
When a meniscus tear occurs, it disrupts the normal function of the knee, leading to immediate pain, swelling, and difficulty in movement. Many individuals report hearing a popping sound at the moment of injury, followed by persistent discomfort. The severity and location of the tear influence the symptoms and treatment options.
Common signs and symptoms associated with a meniscus tear include:
Persistent and severe pain localized on the inner part of the knee
A dull, continuous ache across the joint
Swelling that can develop within 24 to 48 hours after injury
Knee locking or catching, making movements difficult
Difficulty fully bending or straightening the knee
Stiffness, tightness, and congestion in the joint area
Muscle weakness surrounding the knee, leading to instability
The specific treatment plan depends on factors such as the injury's severity, the patient's age, overall health condition, and activity level.Effective management of meniscus tear pain and aiding recovery involve several strategic steps. Here are some essential tips to help alleviate discomfort, promote healing, and restore knee function:
Immediate Rest and Activity Modification: After the injury, it is crucial to rest the knee to prevent further damage. Minimize movement, avoid weight-bearing activities, and consider using crutches or a cane to reduce pressure. Resting helps decrease inflammation and provides the initial conditions necessary for healing.
Cold Therapy for Swelling Reduction: Applying cold compresses or ice packs during the first 48 to 72 hours is highly effective in reducing swelling and pain. Use cold therapy for 20-minute intervals every 3-4 hours to constrict blood vessels, slow down bleeding, and minimize inflammation.
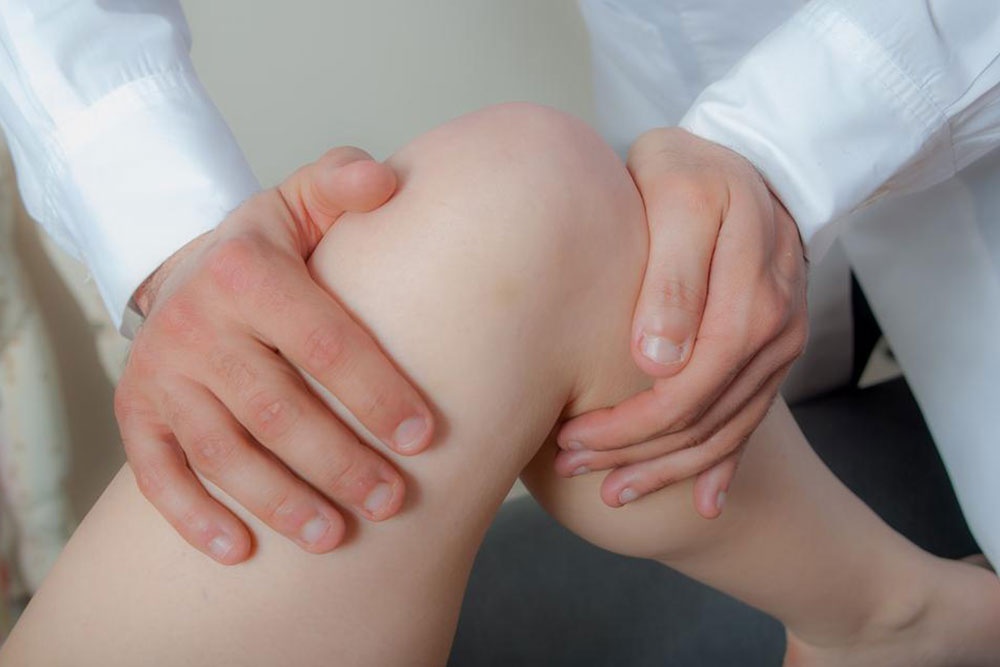
Seek Medical Evaluation for Persistent Symptoms: If pain and swelling do not improve after a week or if symptoms worsen, consult a healthcare professional. Advanced evaluation, including imaging tests like MRI, can determine the extent of the tear. Based on the diagnosis, treatment options may include conservative management or surgical intervention such as arthroscopy.
Non-Surgical vs. Surgical Treatment Options: Mild to moderate tears repaired without surgery typically require 6 to 8 weeks of rehabilitation to regain mobility. This includes rest, controlled physical therapy, and possibly a knee brace or sleeve. More severe tears, especially those causing joint locking or large fragments, might necessitate surgical procedures like meniscectomy or suturing the tear via minimally invasive arthroscopy. Post-surgical recovery can extend from 3 to 4 months, depending on the procedure and patient compliance.
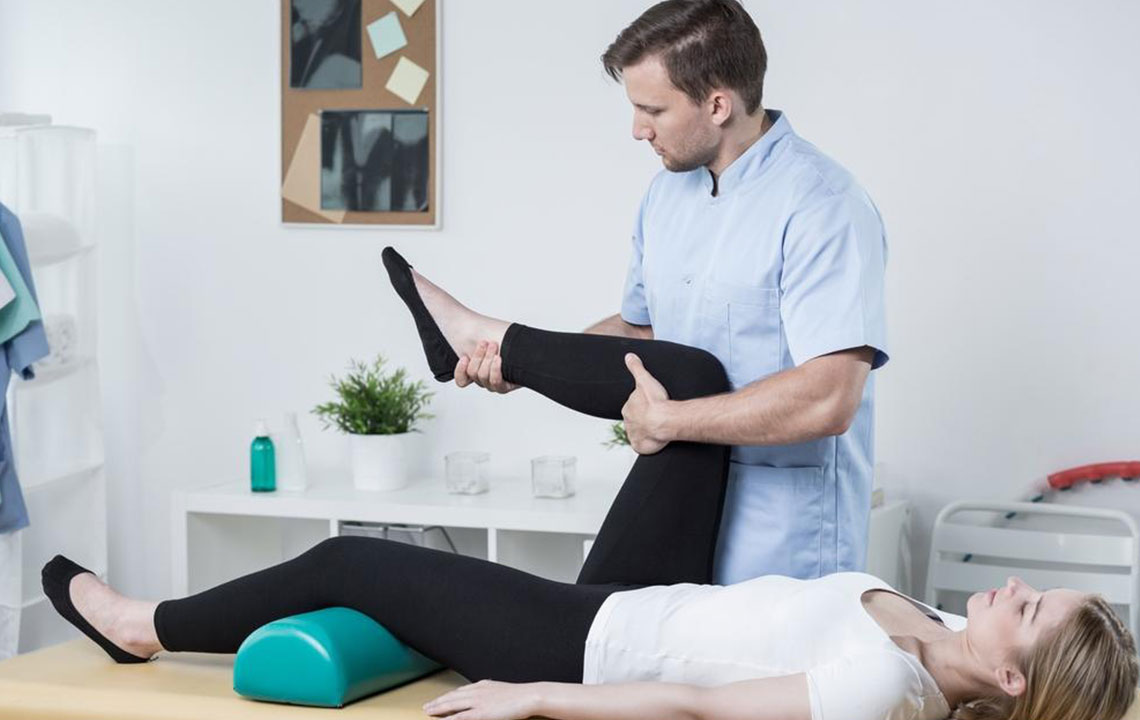
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy: Engaging with a trained physiotherapist is essential for restoring proper function and mobility. Customized exercise programs focus on strengthening surrounding muscles, improving joint stability, and gradually increasing activity levels. Physical therapy also helps prevent future injuries by enhancing muscle support around the knee.
Understanding that effective management of a meniscus tear involves a combination of rest, medical treatment, and proactive rehabilitation strategies can significantly improve outcomes. Taking timely action minimizes complications and supports a quicker return to regular activities, whether they involve sports, exercise, or daily routines.