Comprehensive Dietary Strategies for Managing Ulcerative Colitis Effectively
Manage ulcerative colitis through tailored dietary strategies that reduce inflammation and improve gut health. Learn about probiotic foods, low-fiber options, anti-inflammatory proteins, and lifestyle tips to ease symptoms and support remission. Consult healthcare professionals for personalized plans to enhance your quality of life.

Comprehensive Dietary Strategies for Managing Ulcerative Colitis Effectively
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory condition that primarily affects the innermost lining of the large intestine (colon) and rectum. As a form of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), this condition can cause a range of uncomfortable and debilitating symptoms, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, rectal bleeding, and fatigue. While ongoing medical research aims to discover a definitive cure, managing symptoms through tailored dietary practices remains a cornerstone of effective treatment. Each individual’s nutritional requirements and tolerances may vary, making personalized dietary plans essential for symptom control and improving overall quality of life. It’s highly recommended to work closely with healthcare professionals, including dietitians, to customize your diet plan based on your unique needs and medical history.
Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in reducing intestinal inflammation, preventing nutritional deficiencies, and supporting the healing process. Certain foods have anti-inflammatory properties and can help alleviate symptoms and decrease the frequency of flare-ups. Conversely, some foods may trigger symptoms and should be avoided or limited. An informed approach to diet, combined with appropriate medical treatment, can lead to better disease management, fewer flare-ups, and a more comfortable life.
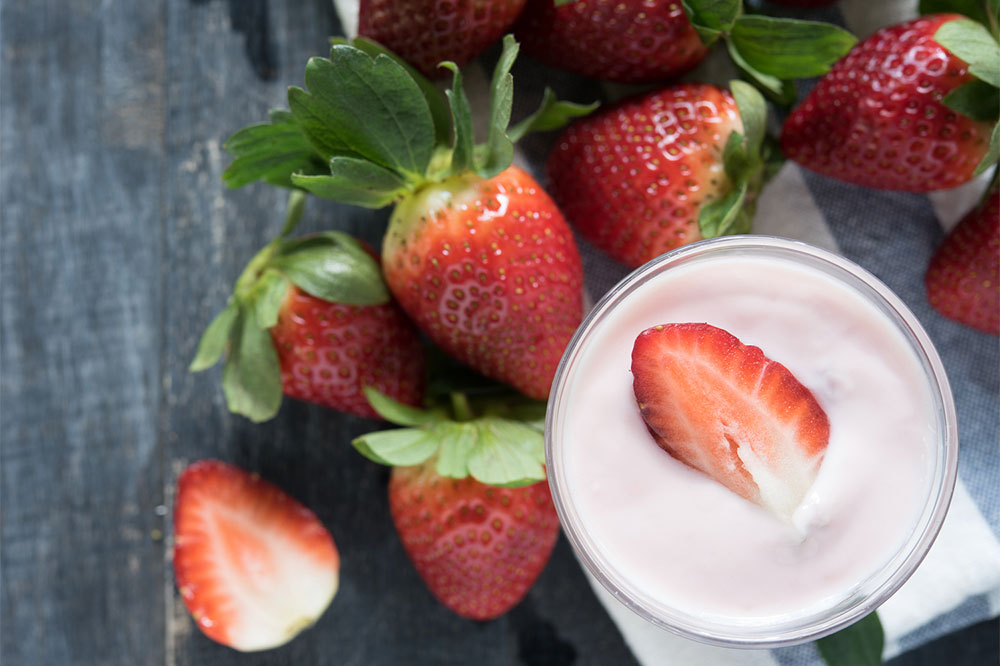
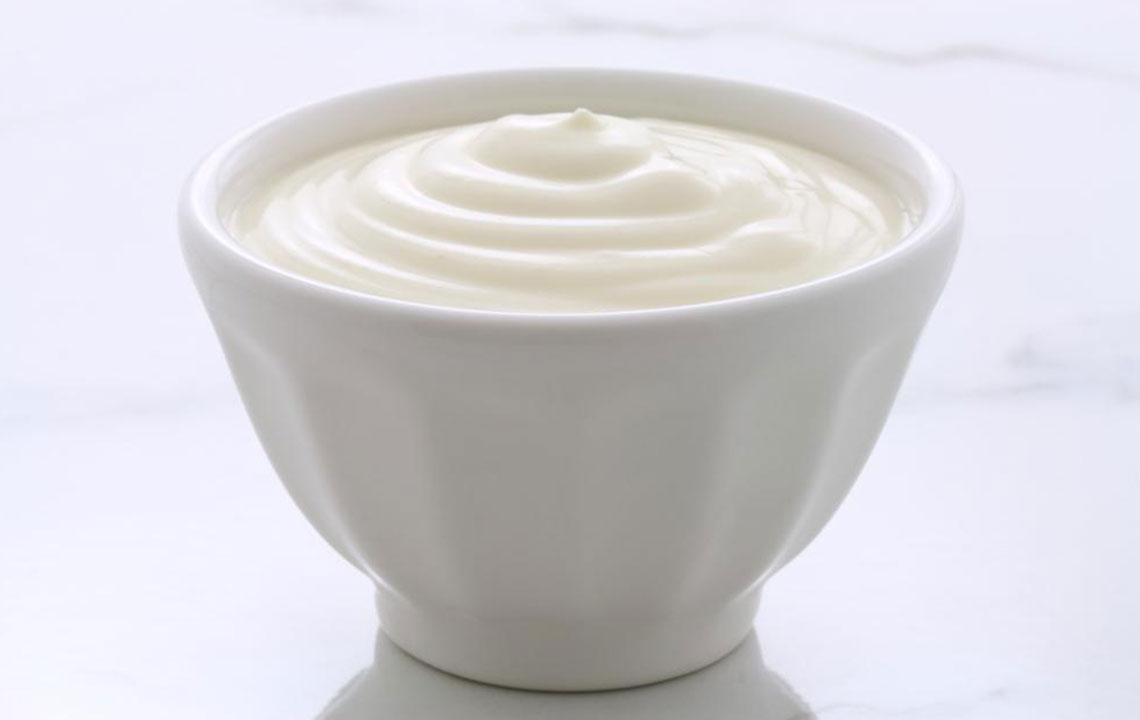
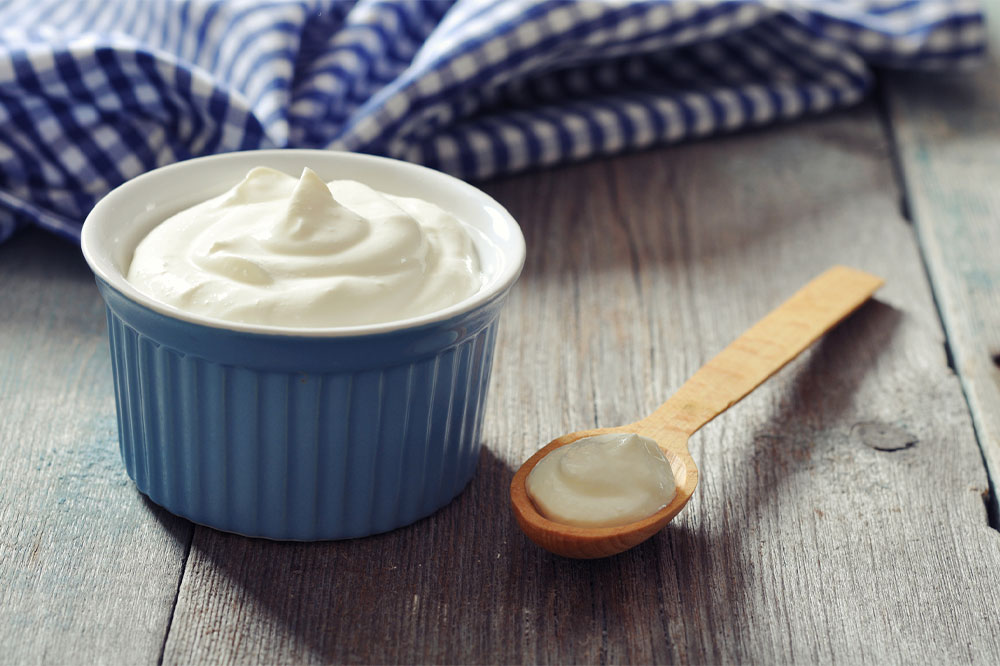
Probiotic-Rich Foods: The Role of Yogurt and Fermented Products
Yogurt is a potent source of probiotics—live beneficial bacteria that support a healthy gut microbiome. An imbalance of gut bacteria is often associated with worsening inflammation in ulcerative colitis. Incorporating probiotic-rich foods such as plain yogurt can help restore the natural bacterial balance, potentially reducing inflammation and improving gut function. It is recommended to choose varieties that are live and unpasteurized to maximize probiotic content. Eating yogurt regularly, such as during breakfast or as part of a snack, can be an easy and enjoyable way to enhance your probiotic intake. Besides yogurt, fermented foods like kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and miso can also support gut health when tolerated.
Opt for Gentle, Low-Fiber Foods to Minimize Gut Irritation
During flare-ups or when experiencing symptoms, it's advisable to consume low-fiber, easily digestible foods that do not irritate the inflamed intestinal lining. Nutrient-rich, low-fiber options like bananas are gentle on the gastrointestinal tract and can help manage diarrhea and abdominal discomfort. Cooked vegetables, such as carrots, zucchini, and squash, are softer and easier to digest compared to raw vegetables. White rice, plain pasta, and refined grains provide carbohydrates that are easier to tolerate and can supply energy without aggravating symptoms. It's crucial to consult your healthcare provider or registered dietitian before making major dietary modifications to ensure they meet your individual nutritional needs and do not interfere with your treatment plan.
Incorporate Anti-Inflammatory Protein Sources
Salmon is renowned for its high content of omega-3 fatty acids, which have well-documented anti-inflammatory effects. Including fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines, and herring in your diet can help mitigate intestinal inflammation linked with ulcerative colitis. These omega-3s may also support immune function and overall gut health. Moreover, lean meats such as chicken breast and turkey provide essential protein and nutrients necessary for tissue repair and maintaining muscle mass. Adequate protein intake helps prevent malnutrition and anemia, common issues for people with UC. When selecting meats, opt for skinless and minimally processed options to keep fat and additive intake in check.
Colorful Vegetables and Fruits Promote Gut Health
Including antioxidant-rich foods like green beans, berries (strawberries, blueberries, blackberries), peeled carrots, and cooked dark leafy greens such as kale and spinach can be significantly beneficial. These foods contain vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals that help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the gut. Their inclusion in your diet can enhance immune function and support cellular repair. Berries are especially rich in flavonoids and vitamin C, which have anti-inflammatory properties. However, individual tolerances vary, so it's important to introduce new foods gradually and monitor your symptoms carefully. Maintaining a food diary can assist in identifying personal trigger foods, enabling better management of flare-ups.
Additional Dietary Tips for Managing Ulcerative Colitis
Effective management of ulcerative colitis extends beyond selecting specific foods. It includes maintaining a balanced diet, avoiding known trigger foods such as spicy, greasy, or high-fiber items during flare-ups, and staying well-hydrated. Stress reduction techniques, regular exercise, and adequate sleep are also vital components of a comprehensive management strategy. Keeping a food journal can help track dietary intake and symptom patterns, providing valuable insights for you and your healthcare team. Regular consultation with your healthcare provider ensures your diet aligns with your disease activity, nutritional needs, and overall health goals.
Ultimately, dietary management is a critical aspect of living with ulcerative colitis. While individual responses to foods may differ, adopting an anti-inflammatory, nutrient-rich, and gentle diet can reduce symptoms, promote remission, and improve quality of life. Always discuss any dietary changes with your healthcare provider to create a personalized plan tailored to your specific health status.