Comprehensive Guide to Modern Lung Cancer Treatments and Strategies
This comprehensive article explores the latest lung cancer treatments including surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. It highlights how personalized medicine and advances in technology are improving treatment outcomes. Early detection and tailored strategies remain crucial for effective management of lung cancer, providing hope and better quality of life for patients. Learn about each treatment modality and how they are integrated to combat this prevalent disease effectively.

Comprehensive Guide to Modern Lung Cancer Treatments and Strategies
Lung cancer is one of the most common and deadly cancers worldwide, particularly in countries like the United States. Due to its high prevalence and often late diagnosis, effective treatment strategies are vital to improve survival rates and quality of life for patients. Managing lung cancer involves a multidisciplinary approach, tailored to the specific type, location, and stage of the disease. Early detection and prompt, appropriate treatment options can significantly influence outcomes.
Understanding the various treatment modalities available today provides patients and healthcare providers with critical insights into managing this formidable disease. These treatment options have evolved over the years, incorporating advancements in surgical techniques, targeted therapies, immunotherapies, and supportive care. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore each of these approaches in detail, discussing their procedures, benefits, potential side effects, and suitable scenarios for their application.
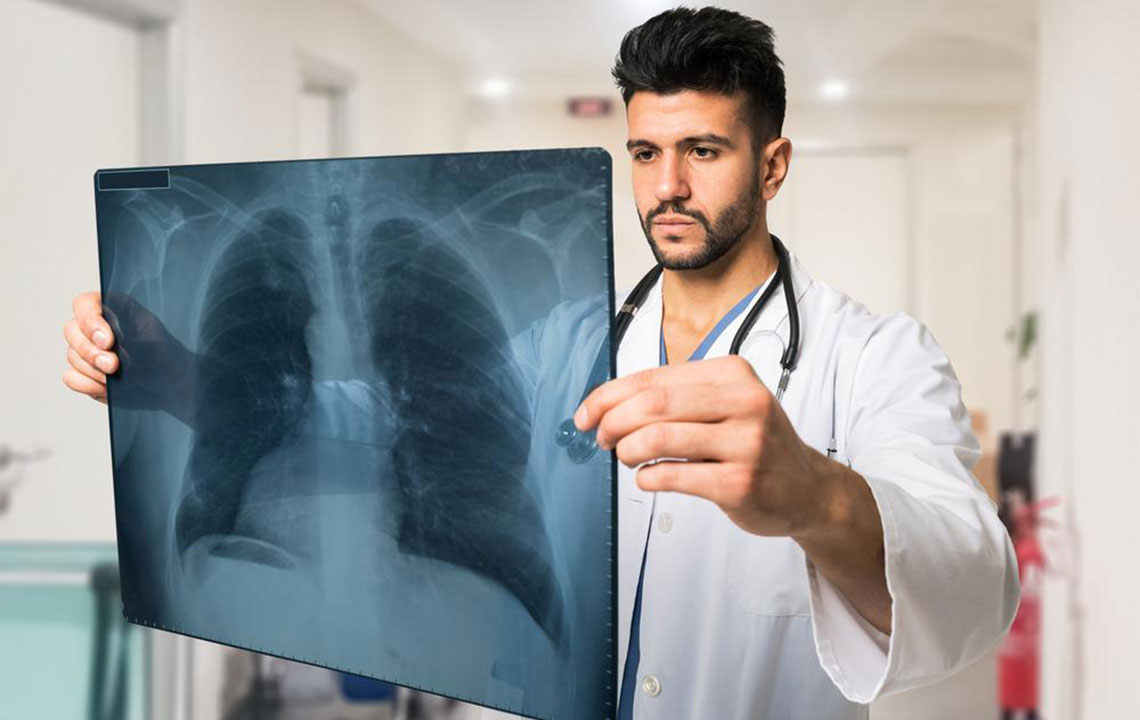
Surgical Intervention: Surgery remains a cornerstone treatment, particularly for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Surgeons aim to completely remove the tumor along with a margin of healthy tissue to ensure no residual cancerous cells remain. This process often includes removing nearby lymph nodes to assess whether the cancer has spread, which is crucial for staging and subsequent treatment planning.
Lymph node examination during surgery helps determine the extent of disease spread and guides further therapy decisions. Post-operative recovery often involves the remaining lung tissue expanding to compensate for the removed segment, enabling patients to breathe normally in most cases.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment using powerful anti-cancer drugs designed to target and destroy rapidly dividing cancer cells. It can be administered via intravenous infusion or orally in pill form. Chemotherapy is often used after surgery to eliminate microscopic residual disease, reducing the risk of recurrence. The treatment regimen varies depending on the cancer stage, type, and patient health status.
Radiation Therapy: When surgical options aren’t suitable—due to patient health, tumor location, or stage—radiation therapy offers an effective alternative. This treatment employs high-energy radiation beams to directly target cancer cells, causing DNA damage that leads to cell death. Radiation can be used as a primary treatment, in combination with chemotherapy, or palliatively to alleviate symptoms such as pain or bleeding. Advances in radiation technology, like stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT), allow for precise targeting, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
Targeted Therapy: A significant breakthrough in lung cancer treatment involves targeted therapies, which focus on specific genetic mutations or abnormalities within cancer cells. Doctors perform molecular testing to identify mutations such as EGFR, ALK, ROS1, and others. Drugs like Erlotinib, Crizotinib, Ceritinib, Nivolumab, and Bevacizumab are designed to inhibit these genetic pathways, thereby controlling tumor growth more precisely with fewer side effects than traditional chemotherapy. This approach is especially beneficial for patients with advanced or metastatic lung cancer exhibiting these genetic features.
Immunotherapy: Emerging as a revolutionary treatment, immunotherapy enhances the body’s innate immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. Immune checkpoint inhibitors such as Nivolumab and Pembrolizumab block proteins (like PD-1/PD-L1) that allow cancer cells to evade immune detection. This therapy has shown promising results, especially in metastatic lung cancer, improving overall survival and quality of life. Immunotherapy is often combined with other modalities for synergistic effects, tailoring treatment to the patient's immune profile.
In conclusion, the landscape of lung cancer treatment is continuously evolving, integrating precision medicine with traditional approaches to offer personalized care. Early diagnosis, molecular testing, and a multidisciplinary approach are key to optimizing survival and minimizing side effects. Patients are encouraged to discuss all available options with their healthcare team to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on their individual condition.