Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of an Enlarged Spleen
This comprehensive article explains the signs and symptoms of an enlarged spleen, medically known as splenomegaly. It covers common indicators like abdominal pain, fatigue, and digestive discomfort, as well as warning signs requiring urgent care. The guide emphasizes the importance of early detection, diagnostic methods, possible causes, and preventive measures. Understanding these symptoms helps individuals seek prompt medical attention, facilitating effective treatment and avoiding complications. Suitable for anyone interested in health awareness, this detailed overview provides valuable insights into spleen health and related issues.

Understanding the Key Signs and Symptoms of an Enlarged Spleen (Splenomegaly)
The spleen is a vital organ situated in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen, just beneath the rib cage, and is roughly the size of a fist. Despite its small stature, it performs crucial functions essential for maintaining overall health, particularly in immune response and blood filtration. However, due to various underlying health issues, the spleen can become abnormally enlarged—a condition medically termed splenomegaly. Recognizing the early signs and symptoms of an enlarged spleen is important, as it allows for prompt medical intervention before complications arise.
While some individuals with splenomegaly may experience mild or no symptoms initially, others may encounter significant discomfort or health issues. The degree of spleen enlargement varies from person to person, influenced by factors such as age, sex, and overall health. Detecting the condition early often relies on awareness of common symptoms and regular medical check-ups.
Splenomegaly occurs when the spleen becomes swollen due to infections, liver diseases, blood disorders, or other medical conditions. The enlarged organ may struggle to perform its normal functions, leading to a range of clinical signs. Because the size of the spleen naturally varies among individuals, doctors often rely on physical examinations and imaging studies to identify abnormal enlargement beyond typical limits.
Understanding the symptoms that point toward spleen enlargement can empower patients to seek timely medical care. Below are some of the most common and significant signs to monitor:
Digestive Distress and Fullness
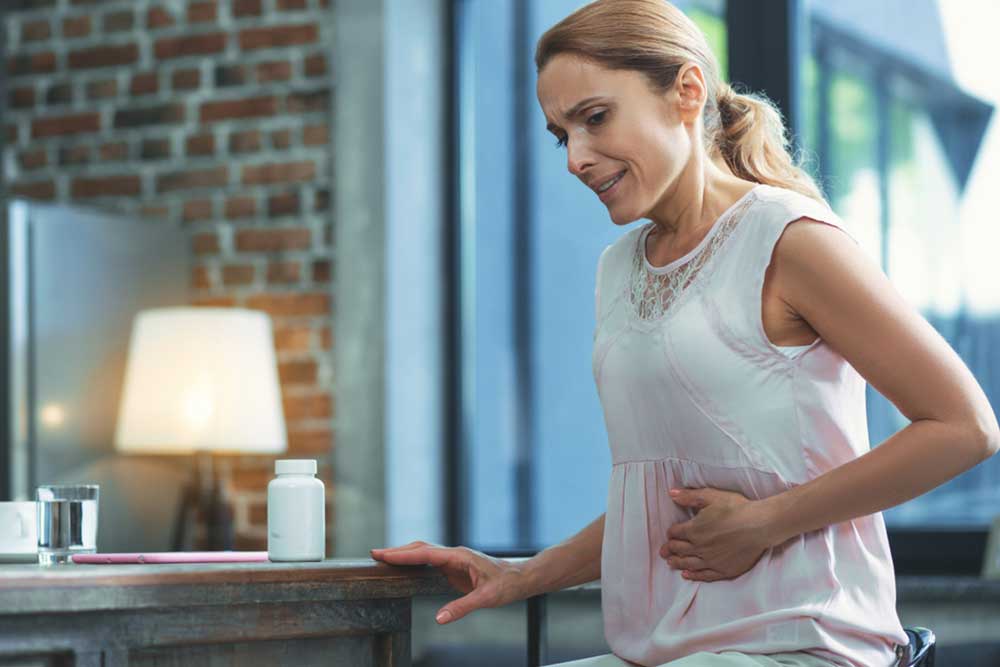
Many individuals notice a sensation of fullness or bloating in the upper left abdomen, especially after eating. This discomfort may be caused by the spleen pressing against the stomach. In some cases, gross enlargement increases the risk of organ rupture, which can lead to internal bleeding and toxin buildup.
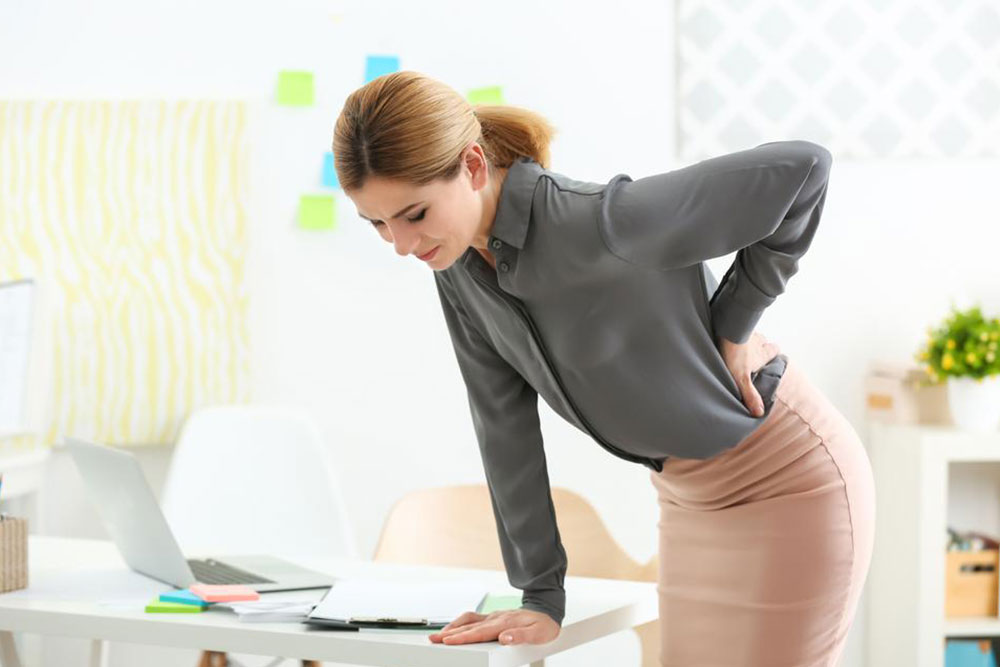
Pain or Tenderness in the Upper Left Abdomen
Discomfort or soreness around the spleen area is common. This pain often radiates to the left shoulder or shoulder blade—a phenomenon known as Kehr's sign. It tends to worsen with deep breaths, movement, or palpation during physical exams.
Persistent Fatigue and Weakness
An enlarged spleen can affect blood cell production and filtration, leading to anemia or other blood-related issues. Consequently, individuals often experience unexplained tiredness, low energy levels, and reduced stamina, which may interfere with daily activities and quality of life.
Additional Symptoms to Watch For
Other clinical signs include jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), easy bruising, frequent infections, unintended weight loss, and bleeding or clotting problems. Some patients may also experience symptoms related to underlying causes, such as fever or enlarged lymph nodes.
It is important to note that some of these symptoms are non-specific and can be related to other health conditions. Therefore, if you experience any of these signs persistently or severely, consulting a healthcare professional for appropriate evaluation and diagnosis is crucial.
Diagnosing an enlarged spleen involves physical examinations, blood tests, and imaging modalities like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI. Once confirmed, understanding the cause of splenomegaly is essential for directing effective treatment and management plans.
Causes of Spleen Enlargement
Various health issues can cause the spleen to enlarge, including infections like mononucleosis, liver diseases such as cirrhosis, blood disorders like leukemia or lymphoma, and certain inflammatory conditions. Differentiating these causes is key to providing targeted therapy.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience severe abdominal pain, signs of internal bleeding such as dizziness, fainting, or rapid heartbeat, or notice a lump in the upper left abdomen, seek emergency medical care immediately. Early detection and treatment significantly improve outcomes and can prevent serious complications.
Preventive Measures and Management
Although not all causes of splenomegaly are preventable, maintaining overall health through good hygiene, vaccination, and regular medical check-ups can reduce risk factors. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may include medications, managing symptoms, or surgical interventions in severe cases.
Understanding the signs and symptoms of an enlarged spleen empowers individuals to seek timely professional advice, ensuring better health management and reducing potential risks associated with this condition.