Comprehensive Nutritional Strategies to Manage Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Effectively
This article explores comprehensive nutritional and lifestyle strategies for managing pulmonary arterial hypertension effectively. It emphasizes dietary choices such as garlic intake, avoiding stimulants, boosting iron levels, and controlling fluid intake, all while complementing medical treatments. Combining these approaches can improve blood flow, reduce symptoms, and enhance quality of life for PAH patients. The guidance outlined provides a holistic pathway to support better health outcomes and symptom control in individuals living with PAH.

Comprehensive Nutritional Strategies to Manage Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Effectively
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a serious, progressive condition characterized by increased blood pressure in the arteries that supply the lungs. This abnormal elevation in pulmonary artery pressure can lead to significant health complications, including right heart failure if not properly managed. PAH primarily affects small pulmonary vessels, resulting in reduced blood flow and oxygen exchange, which can cause symptoms similar to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma. Although it is a rare disease, affecting approximately one to two individuals per million, recent studies have shown that lifestyle and dietary modifications, combined with medical treatments, can significantly enhance the quality of life for those living with this condition. This article provides an in-depth overview of essential nutritional strategies and lifestyle adjustments that can support better management of pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Enhance Your Diet with Garlic for Improved Vascular Health
One of the most effective natural supplements for promoting vascular health is garlic. Rich in a compound called allicin, garlic has been scientifically proven to support vasodilation—that is, the widening of blood vessels—thereby lowering blood pressure within the pulmonary arteries. Vasodilation facilitates easier blood flow, reducing the workload on the heart and alleviating some symptoms of PAH. To maximize the benefits, it is recommended to incorporate raw garlic into your diet, ideally consumed within an hour of chopping or crushing to preserve its active allicin content. Cooking garlic still offers health benefits, but the allicin potency may diminish with heat exposure. Including garlic in various dishes—such as salads, stir-fries, or as a topping—can be both flavorful and beneficial.
Avoid Stimulant Substances that Worsen PAH Symptoms
Dietary choices play a crucial role in managing PAH symptoms. Be vigilant about beverages and substances that may cause blood vessel constriction, thereby aggravating pulmonary hypertension. Caffeinated drinks such as coffee and energy drinks can temporarily increase blood pressure and heart rate, potentially worsening symptoms. Alcohol, especially in excess, can lead to vasoconstriction and interfere with medications. Similarly, carbonated beverages may contain additives and preservatives that could negatively impact vascular health. Healthier alternatives include fresh fruit juices, herbal teas, and non-alcoholic mocktails, which can support hydration and overall well-being. These changes may also improve sleep quality, energy levels, and symptom management.
Increase Iron Intake to Support Pulmonary Circulation
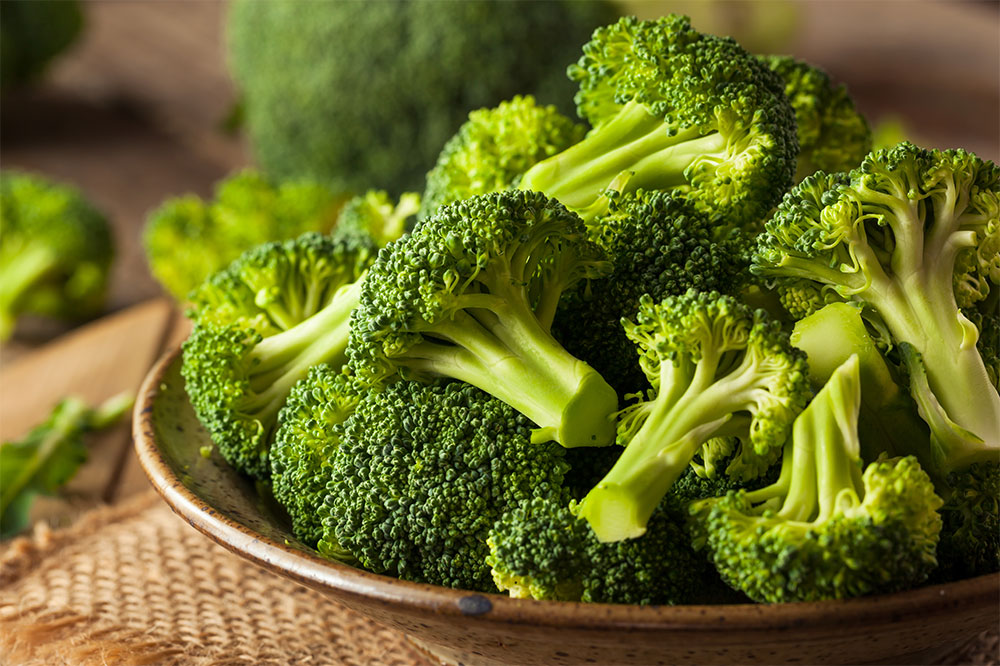
Iron deficiency has been linked to increased severity and progression of PAH because iron plays a critical role in regulating vascular constriction and supporting overall oxygen transport in the blood. Consuming iron-rich foods such as lean meats—including chicken and turkey—plant-based sources like lentils, chickpeas, spinach, and kale can contribute to maintaining healthy iron levels. To improve iron absorption, pair these foods with vitamin C-rich ingredients such as citrus fruits, tomatoes, bell peppers, and broccoli. This combination ensures optimal iron uptake, which is vital for maintaining proper blood vessel function in the lungs. Regularly monitoring iron levels under medical supervision can help prevent deficiency and its associated complications.
Manage Fluid Intake to Prevent Water Retention
In PAH, the heart's diminished pumping capacity can lead to fluid retention, which increases the workload on the heart and exacerbates symptoms like swelling and shortness of breath. Managing fluid intake is an essential part of an overall treatment plan. It is generally advised to limit daily fluid consumption to around two liters, but individual needs may vary. Patients should consult their healthcare providers to tailor fluid restrictions based on their specific condition, ongoing medication, and activity levels. Simple measures such as avoiding excessive salt intake, elevating the legs, and monitoring weight daily can help detect fluid retention early and prevent complications.
Integrate Lifestyle Changes with Medical Therapy for Better Outcomes
While nutritional practices are vital, they should complement prescribed medical treatments to effectively manage PAH. Medications like Adempas® (riociguat) are commonly used to improve blood flow, reduce symptoms, and slow disease progression. Combining these therapies with lifestyle modifications such as a balanced diet, appropriate fluid management, regular gentle exercise, and avoidance of stress can yield better results. It is essential to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop an individualized treatment and nutritional plan that aligns with your specific health needs. Adherence to medical guidance ensures safety and maximizes therapeutic benefits.
In conclusion, managing pulmonary arterial hypertension requires a holistic approach that includes targeted dietary strategies, lifestyle modifications, and medical treatment. Incorporating superfoods like garlic, avoiding vasoconstrictive substances, maintaining adequate iron levels, managing fluid intake, and collaborating with your healthcare team can substantially improve symptoms and overall quality of life. Empower yourself with knowledge and proactive management to live better with PAH.