Comprehensive Guide to Effective Treatments for Plaque Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, and Management Strategies
Explore comprehensive insights into plaque psoriasis, including causes, symptoms, potential complications, diagnostic methods, and advanced treatment options. This detailed guide emphasizes the importance of personalized management strategies and lifestyle modifications to control the condition and prevent serious health issues. Learn how early diagnosis and tailored therapies can improve quality of life for patients with this autoimmune skin disorder.

Comprehensive Guide to Effective Treatments for Plaque Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, and Management Strategies
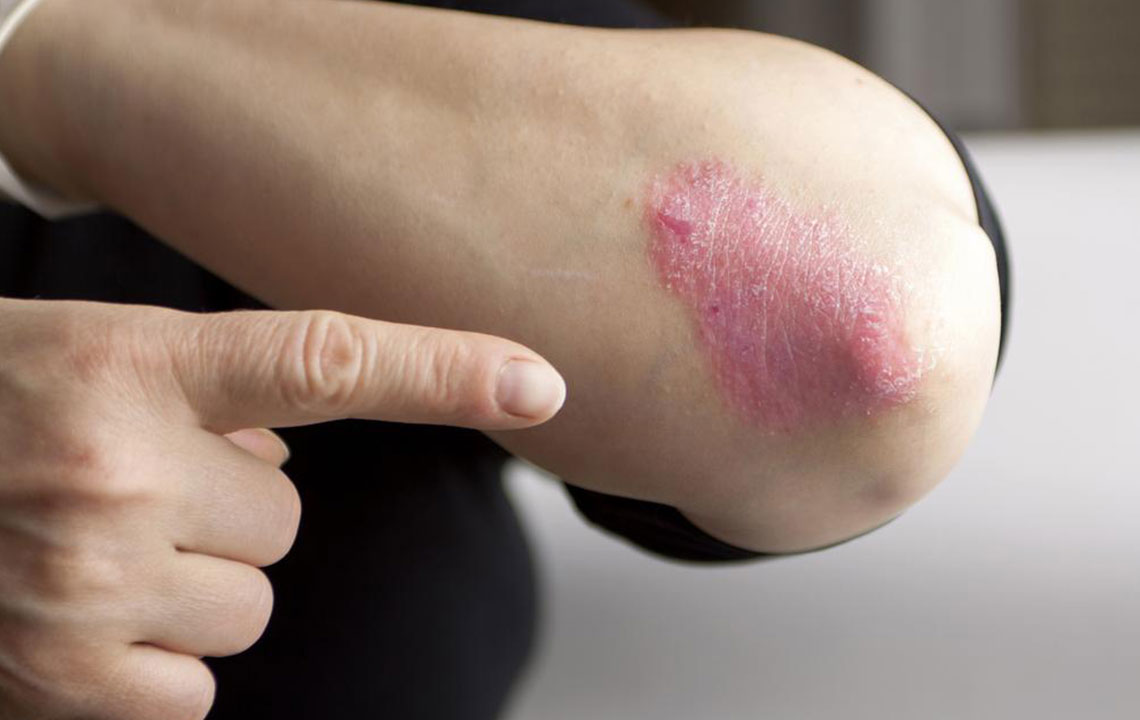
Plaque psoriasis is a common and chronic autoimmune skin disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by the appearance of thick, scaly patches on various parts of the body, especially the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back, this condition can significantly impact one's quality of life. Understanding the underlying causes, recognizing early signs, and selecting appropriate treatment options are essential steps in managing the disease effectively. Although genetic predisposition plays a crucial role, environmental factors such as stress, infections, obesity, smoking, and certain medications can trigger or exacerbate the condition. A comprehensive understanding of these factors, combined with personalized treatment strategies, can help control symptoms and prevent potential complications.
Understanding the Risk Factors Associated with Plaque Psoriasis
Genetics significantly influence the likelihood of developing plaque psoriasis. Studies have identified specific gene mutations linked to the disease, yet not everyone with these mutations develops psoriasis, indicating that environmental factors are crucial in disease expression. This complex interplay between genetics and environment determines the onset, severity, and progression of the disease.
While a hereditary predisposition contributes to psoriasis, environmental triggers are often necessary to activate the condition.
Having a family history of psoriasis increases the risk, but it does not guarantee development.
Environmental factors such as skin injuries, infections, stress, and lifestyle choices can precipitate or worsen symptoms.
Harmful habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are known to be associated with increased risk and severity.
Obesity is linked to higher occurrences of psoriasis, likely due to increased systemic inflammation.
Health Complications Linked with Plaque Psoriasis
If left untreated or poorly managed, plaque psoriasis can lead to several serious health problems. Recognizing these risks underscores the importance of early and effective intervention.
Severe joint inflammation known as psoriatic arthritis can develop, leading to joint pain, swelling, and potential deformity if not addressed promptly.
Ocular issues such as conjunctivitis, blepharitis, and uveitis are more common among psoriasis patients, impacting vision and eye comfort.
Research shows a higher prevalence of neurological conditions such as Parkinson’s disease among individuals with psoriasis.
Other associated health concerns include metabolic syndromes like type 2 diabetes, obesity, hypertension, kidney problems, and increased cardiovascular risks, emphasizing the systemic nature of the disease.
Diagnosing Plaque Psoriasis
Healthcare professionals typically diagnose plaque psoriasis based on skin appearance and lesion distribution during physical examination.
Commonly affected areas include elbows, knees, scalp, lower back, and sometimes the genitals.
Nail changes such as pitting, thickening, or ridging provide additional diagnostic clues, especially when skin lesions are less obvious.
In uncertain cases, a skin biopsy may be performed, where a small tissue sample is examined under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis.
Effective Treatment Strategies for Plaque Psoriasis
Management approaches are tailored to disease severity, from mild to severe cases.
Mild psoriasis often responds well to lifestyle modifications and trigger avoidance, including skin moisturizing, stress management, and diet adjustments.
Topical therapies are the frontline treatment, involving corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, coal tar, and topical calcineurin inhibitors. These treatments aim to reduce inflammation, slow skin cell proliferation, and alleviate discomfort.
Phototherapy, which uses controlled ultraviolet (UV) light exposure, can significantly improve symptoms, especially for extensive or stubborn plaques. Precautions must be taken to avoid overexposure and skin damage.
For moderate to severe psoriasis, systemic therapies are prescribed. These include oral medications, such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, or retinoids, and biologic agents like monoclonal antibodies targeting immune pathways.
Biologics have revolutionized treatment by offering targeted immune modulation, resulting in substantial symptom relief and disease control in eligible patients.
While psoriasis is non-contagious, and there is currently no cure, effective management focuses on reducing symptoms, preventing flare-ups, and improving overall well-being. Lifestyle adjustments, medication adherence, and regular dermatologist consultations are key components of a successful treatment plan. Emerging therapies and ongoing research continue to enhance options available for those affected, aiming to improve their quality of life significantly.