Comprehensive Guide to Alternatives for Quitting Smoking: Strategies and Tips
This comprehensive guide explores effective alternatives and strategies to help individuals quit smoking successfully. From vaping to oral substitutes, nicotine replacement therapy, and prescribed medications, discover proven methods to overcome nicotine addiction. Combining behavioral support and safe substitutes can significantly increase success rates, promoting a healthier, smoke-free lifestyle. Learn how to manage cravings, handle withdrawal symptoms, and stay motivated throughout your journey to quit smoking.
Comprehensive Guide to Alternatives for Quitting Smoking: Strategies and Tips
Overcoming nicotine addiction is a formidable challenge faced by many individuals worldwide. The addictive nature of nicotine reliably stimulates intense cravings, making cessation a complex process that often requires a combination of behavioral changes and supporting alternatives. Recognizing the importance of tailored strategies can significantly improve success rates. While quitting cold turkey may seem appealing, research indicates that a gradual, phased approach combined with safe substitutes can better manage withdrawal symptoms and reduce relapse risks. This comprehensive guide explores effective alternatives and methods to help smokers transition away from cigarettes, promoting a healthier lifestyle.
Understanding and utilizing various cessation aids can ease the journey toward a smoke-free life. Below are some popular and proven options that can help individuals successfully quit smoking and maintain long-term abstinence.
1. Vaping and E-Cigarettes: Safer Substitutes for Tobacco Smoking
Among the most widely adopted alternatives, vaping or electronic cigarettes have gained tremendous popularity. These devices simulate the act of smoking by delivering nicotine in vapor form, which significantly reduces exposure to the harmful toxins and carcinogens found in traditional tobacco smoke. For many smokers, especially long-term smokers and those struggling with hand-to-mouth habits, e-cigarettes provide a familiar ritual without the extensive health risks associated with combustible cigarettes.
Vape devices come in various styles, from sleek pen-like models to advanced mods, allowing users to customize their experience. Starter kits designed for beginners typically include everything needed for easy use. These kits often contain pre-filled cartridges or refillable tanks, providing options that cater to different preferences and nicotine levels. Transitioning from smoking to vaping can help ease nicotine withdrawal symptoms and curb the urge to smoke by satisfying oral fixation and habitual behaviors.
Despite their benefits, it’s important to use vaping products responsibly. While vaping is generally considered less harmful than smoking, it still involves nicotine consumption and potential health risks. Consulting with healthcare professionals and choosing reputable brands can maximize safety and effectiveness in smoking cessation efforts.
2. Oral Substitutes: Healthy Ways to Satisfy Oral Fixation
While less conventional, substituting smoking with healthy oral activities can significantly aid in breaking the oral fixation associated with nicotine dependence. Chewing raw vegetables such as carrots, celery sticks, or cucumber slices offers a crunchy, satisfying alternative that keeps the mouth engaged. These natural snacks are not only low in calories but also packed with nutrients, making them a health-conscious choice.
For individuals less inclined toward vegetables, sugarless gum or candies can serve as effective substitutes. Chewing gum or sucking on mints provides a sensory experience similar to smoking, helping to diminish cravings and reduce the psychological urge to have a cigarette. These oral activities can be incorporated into daily routines, providing comfort and distraction during moments of temptation.
Adopting such substitutes can be especially beneficial for those transitioning from high nicotine intake, as they promote healthier habits and reduce the risk of oral health issues associated with smoking.
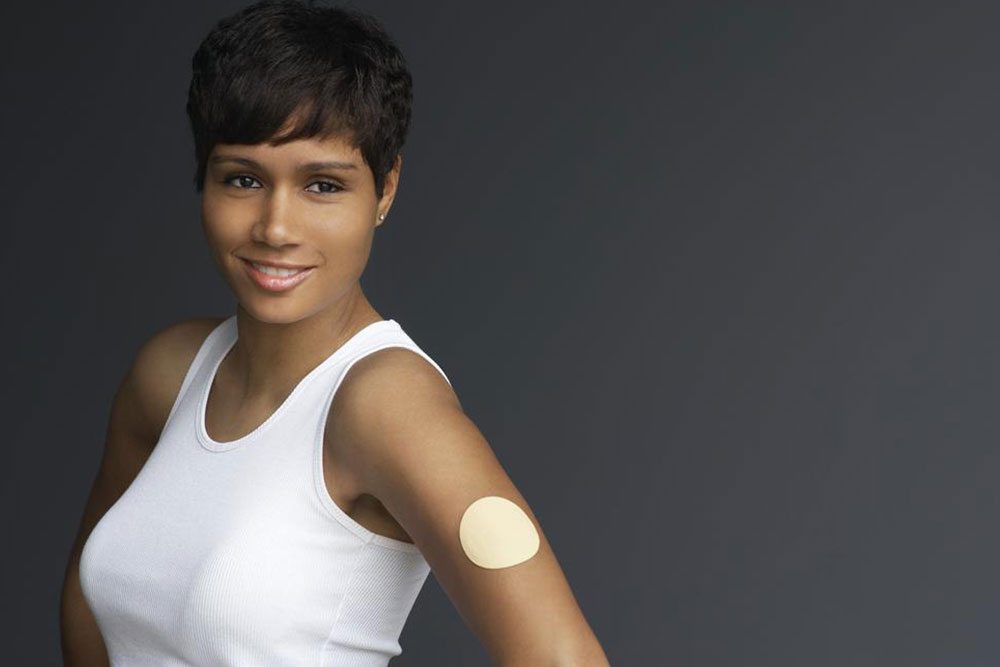
3. Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT): Controlled Nicotine Management
Nicotine replacement therapy remains a cornerstone in smoking cessation programs. Products such as nicotine gums, patches, lozenges, inhalers, and nasal sprays deliver controlled doses of nicotine, allowing smokers to gradually decrease their dependence while avoiding exposure to the hazardous components of cigarette smoke.
Among these options, nicotine gums are easy to use and provide immediate relief from cravings. They are designed to be chewed slowly, releasing nicotine steadily into the bloodstream. Unlike traditional smoking, NRT products deliver nicotine without inhaling tar and carcinogens, making them a safer alternative.
It’s essential to follow proper usage instructions and seek guidance from healthcare providers to develop a tailored cessation plan. While nicotine gums are effective, they do have potential side effects, and their use should be monitored, especially for individuals with specific health conditions.
4. Pharmacological Support: Prescription Medications
For many individuals, pharmacological support through FDA-approved medications can considerably increase the chances of successfully quitting. The two most commonly prescribed drugs are Bupropion (Zyban) and Varenicline (Chantix). These medications work by altering brain chemistry to reduce cravings and alleviate withdrawal symptoms, making the transition easier.
It’s crucial to consult with healthcare providers before starting any medication, as they can assess individual health profiles and prescribe appropriate dosages. Typically, these treatments last from 12 to 24 weeks and are most effective when combined with behavioral support and counseling.
While effective, these medications may have side effects and are not suitable for everyone. Medical supervision ensures safe use and maximizes the likelihood of long-term cessation success.
5. Behavioral and Psychological Support
In addition to physical substitutes, behavioral therapy, support groups, and counseling are integral components of a comprehensive smoking cessation program. Addressing emotional and psychological triggers associated with smoking can dramatically improve outcomes.
Many programs offer cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), motivational interviewing, or group support sessions designed to reinforce commitment and address underlying habits. These approaches help individuals develop coping strategies, manage stress, and build a support network that encourages sustained abstinence.
Combining various methods—such as pharmacotherapy, behavioral therapy, and alternative substitutes—can significantly boost success rates and offer a holistic pathway toward a smoke-free future.
Conclusion: Embracing a Smoke-Free Lifestyle
Quitting smoking is a multifaceted process that requires patience, persistence, and the right tools. Implementing effective alternatives like vaping, oral substitutes, NRT, and medications can greatly enhance the chances of success. Prioritizing health through informed choices and seeking professional guidance sets a foundation for a healthier future free from the dependence on cigarettes. Remember, every small step towards quitting is a victory that paves the way for a longer, healthier life.