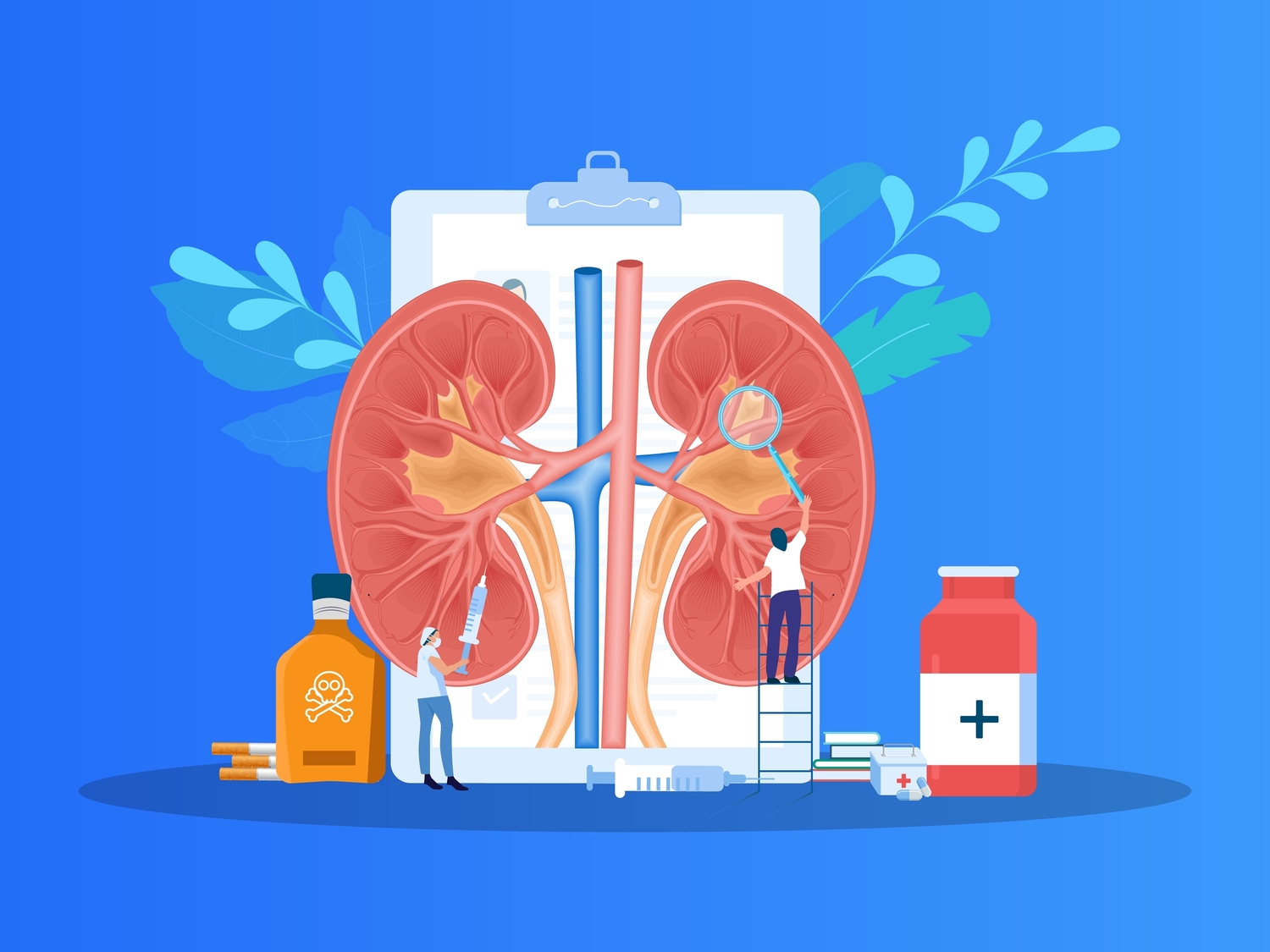
Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Kidney Health and Preventing Disease Progression
Effective kidney health management involves early detection, lifestyle modifications, medication, dialysis, and transplant options. Taking proactive steps and collaborating with healthcare providers can significantly improve outcomes and prevent disease progression, ensuring better quality of life for those with kidney issues.

Maintaining healthy kidney function is essential for overall well-being, yet many individuals encounter challenges related to kidney health due to various lifestyle and genetic factors. The kidneys play a vital role in filtering waste, balancing electrolytes, regulating blood pressure, and supporting overall metabolic health. When issues arise within these vital organs, they can significantly impact quality of life and require targeted interventions. Fortunately, awareness, early detection, and a combination of treatment approaches can effectively manage kidney health issues and prevent progression to more severe conditions.
Understanding Kidney Problems
Kidney disorders are prevalent worldwide, affecting millions of people across different age groups. Common conditions include chronic kidney disease (CKD), acute kidney injury, kidney stones, infections, and congenital disorders. The primary causes behind these problems are often related to lifestyle choices, chronic illnesses, and genetics. For example, diabetes and hypertension are the leading contributors, accounting for a significant percentage of diagnosed cases.
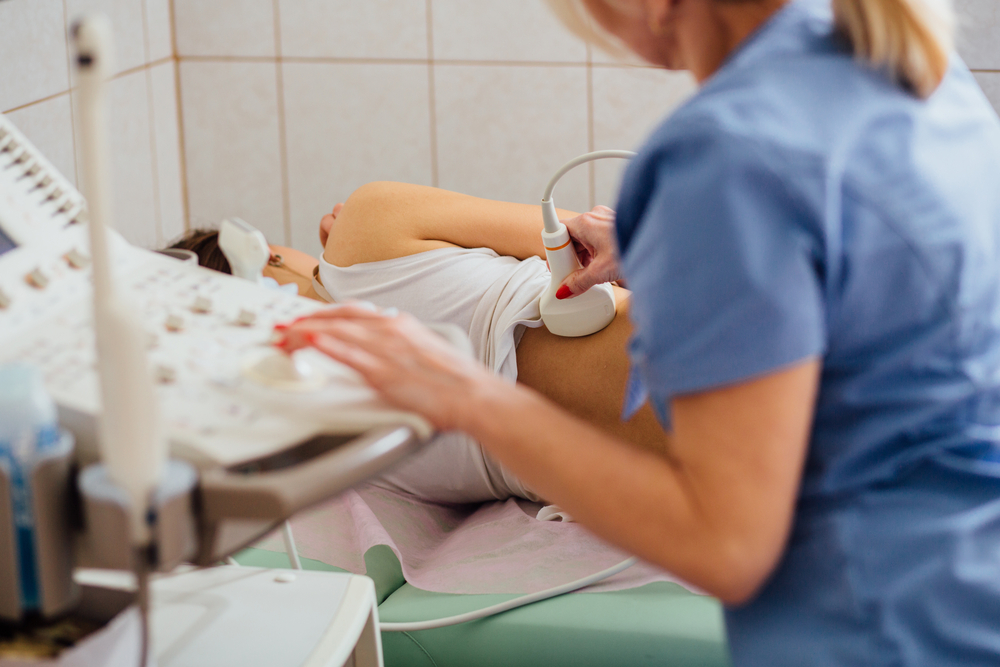
Other contributing factors include genetic predispositions, autoimmune diseases, certain medications, and unhealthy lifestyles such as poor diet, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and lack of physical activity. Detecting kidney issues early through routine screenings can lead to more effective management and mitigate long-term damage. Symptoms like fatigue, swelling, frequent urination, and high blood pressure should prompt immediate consultation with healthcare professionals.
Four Key Approaches to Managing Kidney Health
An integrated approach combining lifestyle modifications, medication management, dialysis, and surgical options offers the best chance for maintaining kidney health and avoiding severe complications. Below, we explore these strategies in detail.
1. Lifestyle Adjustments for Kidney Health Preservation
One of the most effective ways to prevent or slow the progression of kidney problems is through proactive lifestyle changes. Early detection of kidney-related symptoms allows individuals to implement modifications that can significantly impact their disease trajectory. Key lifestyle strategies include:
Dietary Improvements: Reducing salt and sugar intake helps lower blood pressure and blood sugar levels, easing the workload on the kidneys. Incorporating fresh fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins while limiting processed foods minimizes toxin accumulation.
Smoking Cessation: Smoking accelerates kidney damage by impairing blood flow and increasing oxidative stress. Quitting smoking has immediate and long-term benefits for renal health.
Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can raise blood pressure and cause dehydration, both detrimental to kidney function. Moderation is key.
Physical Activity: Regular exercise helps control weight, manage blood pressure, and improve cardiovascular health, all of which are linked to better kidney outcomes.
Monitoring Blood Pressure and Blood Sugar: Regular checkups facilitate early intervention if levels are elevated, helping to prevent or slow kidney damage.
2. Pharmacological Interventions
When lifestyle changes alone are insufficient, medications play a crucial role in managing underlying conditions that affect the kidneys. These include:
Antihypertensives: Medications such as ACE inhibitors or ARBs not only lower blood pressure but also provide specific kidney protection by reducing proteinuria and intraglomerular pressure.
Blood Sugar Control Agents: For diabetic patients, proper management with insulin or oral hypoglycemics reduces the strain on the kidneys and slows disease progression.
Medications to Reduce Protein Loss: Specific drugs help decrease protein leakage in urine, which is a marker of kidney damage.
It is essential for patients to adhere strictly to prescribed medication regimens and attend regular medical follow-ups to monitor progress and adjust treatment as needed.
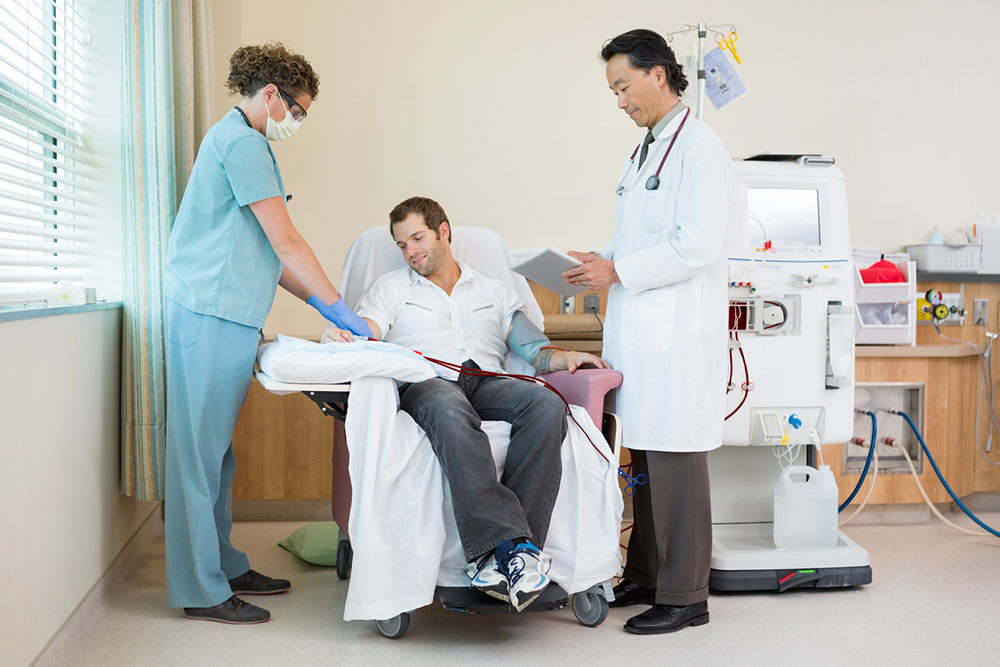
3. Dialysis: A Life-Saving Treatment for Kidney Failure
When kidneys lose their ability to filter waste effectively, dialysis becomes a critical treatment option. Dialysis aims to perform the kidneys’ functions artificially, removing toxins and excess fluids from the bloodstream. There are two primary types of dialysis:
Hemodialysis: This procedure involves circulating blood outside the body through a machine called a dialyzer, which filters out waste products before returning clean blood to the patient. Typically performed three times a week in specialized centers, hemodialysis can be life-saving for patients with advanced kidney failure.
Peritoneal Dialysis: This form of dialysis utilizes the abdominal cavity as a natural filter. A sterile fluid is introduced into the peritoneal cavity, absorbing waste products and excess fluids, then drained out through a catheter. This method offers increased flexibility and independence, often performed at home.
While dialysis effectively manages kidney failure symptoms, it requires ongoing commitment and lifestyle adjustments. Patients must comply with dietary restrictions and monitor fluid intake carefully to optimize treatment outcomes.
4. Kidney Transplantation: The Definitive Cure for End-Stage Kidney Disease
For patients with severe kidney damage where dialysis is no longer effective or sustainable, a kidney transplant offers renewed hope. Transplant surgery involves replacing the failed kidneys with a healthy donor organ. This procedure can significantly improve quality of life and survival rates if the patient is a suitable candidate.
Post-transplant, recipients require lifelong immunosuppressive medication to prevent organ rejection. The transplant process involves extensive evaluation to determine compatibility and assess overall health status. Availability of donor organs is a challenge worldwide, but advancements in transplant techniques and organ preservation are gradually expanding access.
Choosing transplantation over ongoing dialysis can provide patients with increased energy, better physical function, and fewer dietary restrictions, thereby improving overall health and wellbeing.
Holistic Approach and Patient Engagement
Effectively managing kidney health requires more than just medical intervention—it involves active participation from patients. Educating patients about the importance of early detection, adherence to medication, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring is vital for successful outcomes. Healthcare providers should work collaboratively to develop personalized treatment plans that accommodate individual circumstances.
Regular screenings, including blood tests and urine analysis, are important for early identification of kidney problems. Patients should also be encouraged to maintain a balanced diet, stay physically active, and avoid behaviors that could exacerbate kidney damage.
Conclusion
Kidney health management is a multifaceted process that combines early detection, lifestyle adjustments, pharmacological therapy, dialysis, and transplantation. While each approach has its role, the most effective strategy involves proactive, comprehensive care tailored to the individual’s needs. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, sticking to prescribed treatments, and seeking timely medical advice can significantly reduce the risk of severe kidney conditions, ensuring a better quality of life and optimal health outcomes.