Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Adult-Onset Spinal Muscular Atrophy and Enhancing Longevity
This comprehensive article explores effective strategies to manage adult-onset spinal muscular atrophy (Type 4) and improve longevity. It covers vital aspects like nutrition, rehabilitative therapy, tailored physical activity, and respiratory care. Providing insights into personalized treatment plans and lifestyle modifications, the guide empowers adults with SMA to maintain independence, enhance their health, and enjoy a higher quality of life over the years. With expert advice and proactive management, individuals can effectively control symptoms and extend their lifespan while living fulfilling lives.

Innovative Approaches to Managing Adult-Onset Spinal Muscular Atrophy and Extending Lifespan
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a hereditary neuromuscular disorder characterized by progressive muscle wasting and weakness resulting from the degeneration of motor neurons within the spinal cord. While SMA is commonly diagnosed during infancy or early childhood, a specific form known as Type 4 can manifest in adulthood, presenting unique challenges and requiring tailored management strategies. This adult-onset variant shares many symptoms with earlier-onset SMA, such as muscle weakness, decreased mobility, twitching, and respiratory difficulties, but often progresses more slowly. Understanding effective methods to manage Type 4 SMA and promote longevity is essential for improving patients’ quality of life. This comprehensive guide explores key strategies, including nutritional support, rehabilitative therapies, and lifestyle adjustments, to empower adults living with SMA. With the right approach, individuals can maintain independence and enjoy a more active, healthier lifespan.
Optimizing Nutrition for Muscle Health and Overall Wellness – Adequate and balanced nutrition forms the foundation for managing SMA in adults. A diet rich in essential nutrients supports muscle strength, boosts immunity, and enhances energy levels. Regular consultations with registered dietitians help develop personalized meal plans that meet individual caloric and nutritional needs, considering factors such as decreased physical activity and potential swallowing difficulties. Emphasizing high-protein foods, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates can support muscle repair and growth. Additionally, incorporating vital vitamins and minerals—such as vitamin D, calcium, magnesium, and antioxidants—can further promote muscular health and protect against oxidative stress linked to nerve degeneration. For supportive hydration, adults should aim for adequate fluid intake, especially if respiratory function is compromised, to prevent dehydration and respiratory infections.
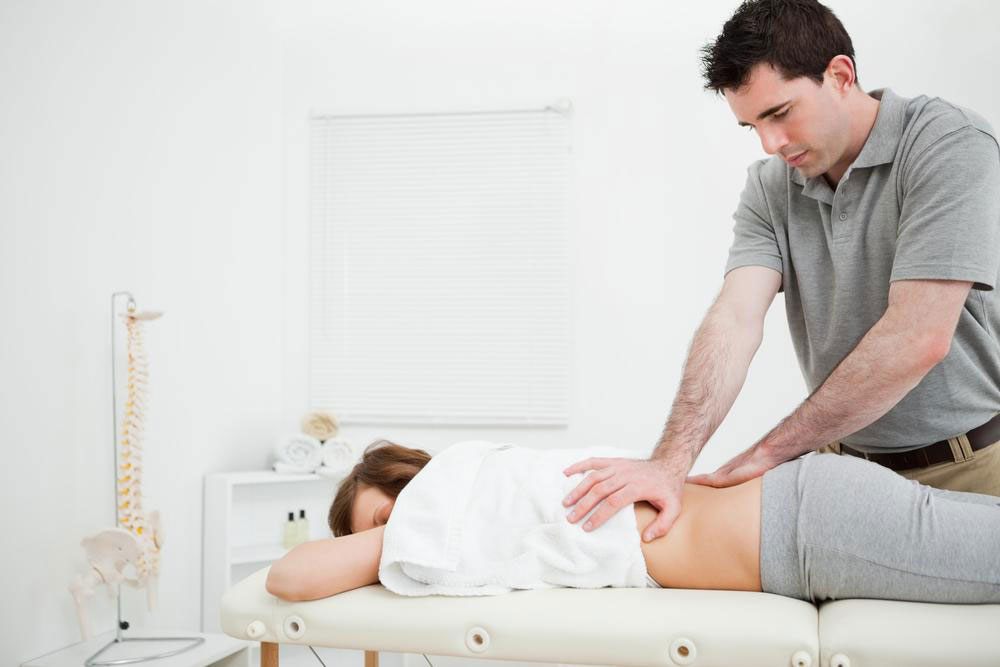
Rehabilitative Therapy: Restoring Mobility and Function – Consistent rehabilitative efforts are critical in managing adult-onset SMA. Occupational therapists focus on enhancing daily living skills, adapting environments, and recommending assistive devices to foster independence. Physical therapy aims to maintain or improve muscle strength, flexibility, and joint mobility through targeted exercises. Therapists may prescribe gentle stretching, light resistance activities, and mobility training suited to individual capabilities. Regular sessions help prevent contractures, reduce muscle atrophy, and minimize complications such as scoliosis or joint deformities. Moreover, respiratory therapy plays a vital role for those experiencing breathing difficulties by teaching breathing exercises and cough assist techniques, thereby reducing the risk of pulmonary infections and enhancing overall respiratory function. Engagement in a multidisciplinary rehabilitation plan often results in better symptom management and improved quality of life.
Promoting Physical Activity While Preventing Overexertion – Engaging in suitable physical activities is crucial for preserving muscle and joint health in adults with SMA. Low-impact exercises, such as walking, swimming, or tailored strength training, can help maintain motor skills and cardiovascular health. It is essential to customize exercise routines under professional guidance, ensuring activities are safe and sustainable. Overexertion can lead to fatigue, muscle strain, or exacerbation of symptoms, so pacing is important. Incorporating regular stretching routines and breathing exercises can improve flexibility and respiratory efficiency. Additionally, practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques can reduce stress and support overall well-being. Developing an individualized exercise plan with healthcare providers ensures optimal benefits while minimizing risks. Consistency and moderation are key to maintaining mobility and enhancing overall health for long-term benefits.
Each person living with adult-onset SMA has a unique experience, and disease progression varies widely. Maintaining a proactive approach—including regular medical evaluations, medication adherence, and lifestyle modifications—can significantly influence lifespan and quality of life. Staying informed about the latest advances, such as emerging treatments and supportive technologies, and working closely with a multidisciplinary care team are pivotal steps toward managing the condition effectively. Empowered with knowledge and appropriate interventions, adults with SMA can lead fulfilling lives, defying limitations and extending their years sustainably.